
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question

Transcribed Image Text:Assume that both populations are normally distributed.
(a) Test whether μ₁ µ₂ at the α = 0.01 level of significance for the given sample data.
(b) Construct a 99% confidence interval about μ₁ - H₂.
(a) Test whether μ₁ μ₂ at the α = 0.01 level of significance for the given sample data.
Determine the null and alternative hypothesis for this test.
OA. Holl #U2
H₁ H1 H2
OB. Ho H₁ H₂
H₁:1₁ > H₂
O C. Ho H₁ = μ¹2
H₁ H₁ > H₂
O D. Ho H₁ H2
H₁ H1 H₂
n
X
S
Population 1 Population 2
18
18
19.2
23.4
5.3
4.3
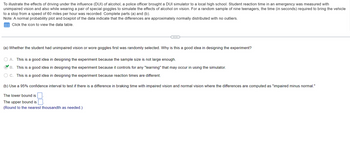
Transcribed Image Text:To illustrate the effects of driving under the influence (DUI) of alcohol, a police officer brought a DUI simulator to a local high school. Student reaction time in an emergency was measured with
unimpaired vision and also while wearing a pair of special goggles to simulate the effects of alcohol on vision. For a random sample of nine teenagers, the time (in seconds) required to bring the vehicle
to a stop from a speed of 60 miles per hour was recorded. Complete parts (a) and (b).
Note: A normal probability plot and boxplot of the data indicate that the differences are approximately normally distributed with no outliers.
Click the icon to view the data table.
(a) Whether the student had unimpaired vision or wore goggles first was randomly selected. Why is this a good idea in designing the experiment?
O A. This is a good idea in designing the experiment because the sample size is not large enough.
B. This is a good idea in designing the experiment because it controls for any "learning" that may occur in using the simulator.
C. This is a good idea in designing the experiment because reaction times are different.
(b) Use a 95% confidence interval to test if there is a difference in braking time with impaired vision and normal vision where the differences are computed as "impaired minus normal."
The lower bound is
The upper bound is
(Round to the nearest thousandth as needed.)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Use the given statistics to complete parts (a) and (b). Assume that the populations are normally distributed. (a) Test whether μ₁ > μ₂ at the α = 0.01 level of significance for the given sample data. (b) Construct a 99% confidence interval about μ₁ - H₂. Find the test statistic for this hypothesis test. (Round to two decimal places as needed.) Determine the P-value for this hypothesis test. (Round to three decimal places as needed.) State the conclusion for this hypothesis test. n (b) The 99% confidence interval about μ₁ −µ₂ is the range from a lower bound of (Round to three decimal places as needed.) X S Population 1 20 48.2 4.1 Population 2 23 45.4 12.7 A. Do not reject Ho. There is sufficient evidence at the x = 0.01 level of significance to conclude that μ₁ > μ₂. B. Reject Ho. There is sufficient evidence at the α = 0.01 level of significance to conclude that μ₁ > μ₂. C. Do not reject Hỏ. There is not sufficient evidence at the x = 0.01 level of significance to conclude that µ₁ >…arrow_forward1. Find the critical value for a 95% confidence interval for B1 2. Compute the margin of error for 95% confidence interval 3. Contruct a 95% confidence interval for b1arrow_forwardUse the given statistics to complete parts (a) and (b). Assume that the populations are normally distributed. (a) Test whether μµ₁ > µ₂ at the α = 0.10 level of significance for the given sample data. (b) Construct a 90% confidence interval about μ₁-12- (a) Identify the null and alternative hypotheses for this test. OA. Ho H₁ H₂ H₁: H₁ H₂ OD. Ho: H1 H₂ H₁: H₁ H₂ OB. Ho: H₁ H₂ H₁: H₁ = H₂ O E. Ho: H1 H₂ H₁: H₁ H₂ OC. Ho H₁ H₂ H₁: H₁ = H₂ OF. Ho: H₁ H₂ H₁: H₁ = H₂ n X S Population 1 Population 2 15 20 48.8 46.3 7.3 11.5arrow_forward
- Let x = age in years of a rural Quebec woman at the time of her first marriage. In the year 1941, the population variance of x was approximately σ2 = 5.1. Suppose a recent study of age at first marriage for a random sample of 31 women in rural Quebec gave a sample variance s2 = 3.0. Use a 5% level of significance to test the claim that the current variance is less than 5.1. Find a 90% confidence interval for the population variance. (a) What is the level of significance? (c) Find or estimate the P-value of the sample test statistic. a) P-value > 0.100b) 0.050 < P-value < 0.100 c) 0.025 < P-value < 0.050d) 0.010 < P-value < 0.025e) 0.005 < P-value < 0.010f) P-value < 0.005 Based on your answers in parts (a) to (c), will you reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis? a) since the P-value > α, we fail to reject the null hypothesis.b) Since the P-value > α, we reject the null hypothesis. c) Since the P-value ≤ α, we reject the null hypothesis.d) Since…arrow_forwardIn a test of hypothesis, the null hypothesis is that the population mean is less than or equal to 32 and the alternative hypothesis is that the population mean is greater than 32. The population has a normal distribution with variance of 12.5. The test is to be made at the 10% significance level. A sample of size 41 is selected from this population. The approximate value of ßatu = 32. 35 is a. 0.5403 O d. 0.7414 O e. 0.9000 O b. 0.2586 O c. 0.9723arrow_forwardUse the given statistics to complete parts (a) and (b). Assume that the populations are normally distributed. Test whether μ1>μ2 at the α=0.10 level of significance for the given sample data. a. Find the test statistic b. Determine the p value c. The 99% confidence interval about μ1−μ2 is the range from a lower bound of ? to an upper bound of ?arrow_forward
- Test the claim about the difference between two population means μ₁ and μ₂ at the level of significance α. Assume the samples are random and independent, and the populations are normally distributed. Claim: μ₁ = μ₂; α = 0.01 Population parameters: σ₁ = 3.4, 0₂ = 1.4 Sample statistics: x₁ = 17, n₁ = 28, x₂ = 15, n₂ = 29 Determine the alternative hypothesis. Ha: H₁ H₂ Determine the standardized test statistic. Z= (Round to two decimal places as needed.) Determine the P-value. P-value= (Round to three decimal places as needed.) What is the proper decision? A. Reject Ho. There is not enough evidence at the 1% level of significance to reject the claim. B. Fail to reject Ho. There is enough evidence at the 1% level of significance to reject the claim. C. Reject Ho. There is enough evidence at the 1% level of significance to reject the claim. D. Fail to reject Ho. There is not enough evidence at the 1% level of significance to reject the claim.arrow_forwardLet x = age in years of a rural Quebec woman at the time of her first marriage. In the year 1941, the population variance of x was approximately σ2 = 5.1. Suppose a recent study of age at first marriage for a random sample of 41 women in rural Quebec gave a sample variance s2 = 3.0. Use a 5% level of significance to test the claim that the current variance is less than 5.1. Find a 90% confidence interval for the population variance. Find the requested confidence interval for the population variance. (Round your answers to two decimal places.) lower and upper limitarrow_forwardTest the claim about the difference between two population means μ₁ and μ2 at the level of significance x. Assume the samples are random and independent, and the populations are normally distributed. Claim: μ₁ = μ₂; α = 0.01 Population statistics: 01 = 3.3, 02 = 1.4 Sample statistics: x₁ = 14, n₁ = 30, x₂ = 12, n₂ = 27 Determine the alternative hypothesis. Ha: H₁ H2arrow_forward
- 20% of all college students volunteer their time. Is the percentage of college students who are volunteers different for students receiving financial aid? Of the 306 randomly selected students who receive financial aid, 70 of them volunteered their time. What can be concluded at the αα = 0.10 level of significance? For this study, we should use Select an answer z-test for a population proportion t-test for a population mean The null and alternative hypotheses would be: H0:H0: ? μ p Select an answer = ≠ > < (please enter a decimal) H1:H1: ? μ p Select an answer > ≠ = < (Please enter a decimal) The test statistic ? z t = (please show your answer to 3 decimal places.) The p-value = (Please show your answer to 4 decimal places.) The p-value is ? > ≤ αα Based on this, we should Select an answer accept reject fail to reject the null hypothesis. Thus, the final conclusion is that ... The data suggest the populaton proportion is significantly…arrow_forwardUse the given statistics to complete parts (a) and (b). Assume that the populations are normally distributed. (a) Test whether μ1>μ2 at the α=0.01 level of significance for the given sample data. (b) Construct a 99% confidence interval about μ1−μ2. Population 1 Population 2 n 23 20 x 47.2 44.6 s 6.8 10.7 (a) Identify the null and alternative hypotheses for this test. A. H0: μ1≠μ2 H1: μ1=μ2 B. H0: μ1=μ2 H1: μ1≠μ2 C. H0: μ1=μ2 H1: μ1<μ2 D. H0: μ1>μ2 H1: μ1=μ2 E. H0: μ1=μ2 H1: μ1>μ2 Your answer is correct. F. H0: μ1<μ2 H1: μ1=μ2 Find the test statistic for this hypothesis test.arrow_forwardLet x = age in years of a rural Quebec woman at the time of her first marriage. In the year 1941, the population variance of x was approximately σ2 = 5.1. Suppose a recent study of age at first marriage for a random sample of 51 women in rural Quebec gave a sample variance s2 = 3.2. Use a 5% level of significance to test the claim that the current variance is less than 5.1. Find a 90% confidence interval for the population variance. (a) What is the level of significance? State the null and alternate hypotheses. Ho: σ2 = 5.1; H1: σ2 > 5.1Ho: σ2 < 5.1; H1: σ2 = 5.1 Ho: σ2 = 5.1; H1: σ2 < 5.1Ho: σ2 = 5.1; H1: σ2 ≠ 5.1 (b) Find the value of the chi-square statistic for the sample. (Round your answer to two decimal places.) What are the degrees of freedom? What assumptions are you making about the original distribution? We assume a uniform population distribution.We assume a normal population distribution. We assume a binomial population distribution.We assume a exponential…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman