
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Topic Video
Question
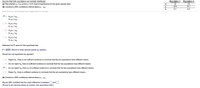
Transcribed Image Text:Assume that both populations are normally distributed.
(a) Test whether µ, + µ, at the a = 0.01 level of significance for the given sample data.
Population 2
19
Population 1
n
19
(b) Construct a 99% confidence interval about u, - H2.
12.6
10.1
2.7
3.4
A. Ho:H1 = H2
H1:H1 # H2
B. Ho:H1 + H2
H1:H1 = H2
O C. Ho:H1 = H2
H1:H1> H2
D. Ho:H1 + H2
H1:H1 > H2
Detemine the P-value for this hypothesis test.
P= 0.017 (Round to three decimal places as needed.)
Should the null hypothesis be rejected?
A. Reject Ho, there is not sufficient evidence to conclude that the two populations have different means.
B. Do not reject Ho, there is sufficient evidence to conclude that the two populations have different means.
C. Do not reject Ho, there is not sufficient evidence to conclude that the two populations have different means.
D. Reject Ho, there is sufficient evidence to conclude that the two populations have different means.
(b) Construct a 99% confidence interval about µ, - H2.
We are 99% confident that the mean difference is between
and
(Round to two decimal places as needed. Use ascending order.)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, statistics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Construct a 95% confidence interval for u -H2 with the sample Bakery A Bakery B statistics for mean calorie content of two bakeries' specialty pies and confidence interval construction formula below. Assume the populations are approximately normal with equal variances. X1 = 1880 cal X2 = 1630 cal %3D S1 = 132 cal S2 = 198 cal !! n, = 7 n2 = 15 %3D 1 1 Confidence interval (X1 -X2) -to when variances are *arrow_forwardTest whether u, <µ2 at the a =0.05 level of significance for the sample data shown in the accompanying table. Assume that the populations are normally distributed. Click the icon to view the data table. Determine the null and alternative hypothesis for this test. O A. Ho:H1 = H2 Sample Data O B. Ho:H1arrow_forwardConstruct the confidence interval for the population mean j. c =0.90, × = 8.3, 0 = 0.6, and n = 48 A 90% confidence interval for u is (_,_) (Round to two decimal places as needed.)arrow_forwardFind the 90% confidence interval for the difference in the means.arrow_forwardFor the last 12 years, Colin has contributed $110 each month into a retirement savings account. If the account earns 7% per year compounded monthly what is the balance of the account at the end of the 12th year?arrow_forwardAssume that both populations are normally distributed. a) Test whether . Population 1 Population 2 10 11.1 Pt2 at the a= 0.05 level of significance for the given sample data 10 9.8 2.3 (b) Construct a 95% confidence interval about u, - H3. 2.7 H1 H1 > H2 O C. Ho H1-H2 H1 H1> H2 D. Ho H1=H2 %3D Detemine the P-value for this hypothesis test. P = (Round to three decimal places as needed.) %24arrow_forwardConstruct a 90% confidence interval for u, - , with the sample statistics for mean calorie content of two bakeries specialty pies and confidence interval construction formula below Assume the populations are approximately normal with equal variances Bakery A Bakery B X1 = 1823 cal X, = 1629 cal S1 = 155 cal S2 = 190 cal n1 = 10 n2 = 12 Confidence interval when variances are equal n n. (n. - 1) s (n2 - 1) s where G and d.f = n, +n2 - 2 nn, - 2 Enter the endpoints of the interval (Round to the nearest integer as needed.)arrow_forwardFind the 98% confidence interval for the difference between two means based on this information about two samples. Assume independent samples from normal populations. (Use conservative degrees of freedom.) (Give your answers correct to two decimal places.) Sample Number Mean Std. Dev. 1 16 38 29 2 29 28 29 Lower Limit Upper Limitarrow_forwardI'm struggling with how to get the p value from the data in the top right corner of the picturearrow_forwardAssume that both populations are normally distributed. (a) Test whether H1 #H2 at the a = 0.05 level of significance for the given sample data. (b) Construct a 95% confidence interval about u, - H2. Population 1 Population 2 13 13 14.1 11.8 4.2 3.1 (a) Test whether u, # H, at the a = 0.05 level of significance for the given sample data. Determine the null and alternative hypothesis for this test. O A. Ho:H1 # H2 H1:H1 = H2 O B. Ho:H1 = H2 H1:41 > H2 OC. Ho:H1 H2 H1:H1> H2 D. Ho:H1 = H2 H1:41 # H2 Detemine the P-value for this hypothesis test. P = (Round to three decimal places as needed.)arrow_forwardProvide an appropriate response. Construct a 95% confidence interval for u1 -µ2. Two samples are randomly selected from normal populations. The sample statistics are given below. n1 = 8 x1= 4.1 n2 = 7 %3D x2 = 5.5 S2 = 2.51 $1 = 0.76 (-1.679, 1.987) (-3.813, 1.013) (-1,132, 1.543) (2.112, 2.113)arrow_forwardUse the given statistics to complete parts (a) and (b). Assume that the populations are normally distributed. (a) Test whether u, >uz at the a = 0.05 level of significance for the given sample data. (b) Construct a 99% confidence interval about u1 -P2. Population 2 23 Population 1 22 46.4 41.8 4.3 13.1 (a) Identify the null and alternative hypotheses for this test. O A. Ho: H1 = H2 H1: H1 # H2 O B. Ho: H1 =H2 H1: H1 H2 OF. Ho: H1 > H2 H1: H1 = H2 Find the test statistic for this hypothesis test. (Round to two decimal places as needed.)arrow_forwardarrow_back_iosSEE MORE QUESTIONSarrow_forward_iosRecommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman