
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
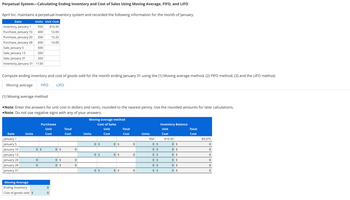
Transcribed Image Text:Perpetual System-Calculating Ending Inventory and Cost of Sales Using Moving Average, FIFO, and LIFO
April Inc. maintains a perpetual inventory system and recorded the following information for the month of January.
Units Unit Cost
$10.50
950
400
12.00
Inventory, January 1
Purchase, January 10
Purchase, January 20
Purchase, January 28
Sale, January 5
200
13.25
600
14.00
500
Sale, January 13
200
Sale, January 31
320
Inventory, January 31 1130
Date
Compute ending inventory and cost of goods sold for the month ending January 31 using the (1) Moving average method, (2) FIFO method, (3) and the LIFO method.
Moving average FIFO
(1) Moving average method
•Note: Enter the answers for unit cost in dollars and cents, rounded to the nearest penny. Use the rounded amounts for later calculations.
•Note: Do not use negative signs with any of your answers.
Date
January 1
January 5
January 10
January 13
January 20
January 28
January 31
Units
Moving Average
Ending Inventory
Cost of goods sold $
Purchases
Unit
Cost
0 $
0
0
LIFO
0
0
0 $
0 $
0 $
Total
Cost
0
0
0
Moving-average method
Cost of Sales
Unit
Cost
Units
0 $
0 $
0 $
0 $
0 $
0 $
Total
Cost
0
0
0
Units
950
0 $
0 $
0 $
0 $
0 $
0 $
Inventory Balance
Unit
Cost
$10.50
0 $
0 $
0 $
0 $
0 $
0 $
Total
Cost
$9,975
0
0
0
0
0
0
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Kingbird, Inc. uses a periodic inventory system and reports the following for the month of June. Date June 1 12 23 30 (a) Explanation Units Inventory Purchase Purchase Inventory 130 330 Cost of goods sold 200 203 Cost of the ending inventory Unit Cost $ $5 6 7 Compute the cost of the ending inventory and the cost of goods sold under FIFO, LIFO, and average-cost. (Round per unit cost to 3 decimal places, e.g. 15.647 and final answers to 0 decimal places, e.g. 5,125.) Total Cost FIFO $650 1,980 1,400 LA LIFO LA LA Average-costarrow_forwardNittany Company uses a periodic inventory system. At the end of the annual accounting period, December 31 of the current year, the accounting records provided the following information for product 1: Units Unit Cost Inventory, December 31, prior year 1,980 $7 For the current year: Purchase, March 21 5,090 9 2,970 10 Purchase, August 1 Inventory, December 31, current year 4,100 Compute ending inventory and cost of goods sold for the current year under FIFO, LIFO, and average cost inventory costing methods. Note: Round "Average cost per unit" to 2 decimal places and final answers to nearest whole dollar amount.arrow_forwardThe following units of a particular item were available for sale during the calendar year: Jan. 1 Apr. 19 Inventory Sale 4,000 units at $50 2,500 units June 30 Purchase 4,500 units at $54 Sept. 2 Sale 5,000 units Purchase 2,000 units at $56 Nov. 15 The firm uses the weighted average cost method with a perpetual inventory system. Determine the cost of goods sold for each sale and the inventory balance after each sale. Present the data in the form illustrated in Exhibit 5. Date Purchases Quantity Purchases Unit Cost Purchases Total Cost Quantity Weighted Average Cost Flow Method Cost of Goods Sold Cost of Goods Sold Unit Cost Cost of Goods Sold Total Cost Jan. 1 Apr. 19 June 30 Sept. 2 Nov. 15 ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ Dec. 31 Balancesarrow_forward
- The following are the transactions for the month of July. Units Unit Cost Unit Selling Price July 1 Beginning Inventory 55 $ 10 July 13 Purchase 275 11 July 25 Sold (100 ) $ 14 July 31 Ending Inventory 230 Calculate cost of goods available for sale and ending inventory, then sales, cost of goods sold, and gross profit, under FIFO. Assume a periodic inventory system is used. How would i creat a FIFO periodic table?arrow_forwardAlrcard Corporation tracks the number of units purchased and sold throughout each accounting perlod but applies its Inventory costing method at the end of each perlod as if it uses a perlodic Inventory system. The following are the transactions for the month of July. Units 2,800 1,000 6,000 3,eee 8,e00 Unit Cost July 1 July 5 July 13 July 17 July 25 July 27 Beginning Inventory Sold $ 25 Purchased 29 Sold Purchased 31 Sold 5,eee Calculate the cost of goods available for sale, ending Inventory, and cost of goods sold if Aircard uses (a) FIFO. (b) LIFO. or (c) welghted average cost. (Round "Cost per Unit" to 2 decimal places.) Weighted Average Cost FIFO LIFO Cost of Goods Available for Sale Ending Inventory Cost of Goods Soldarrow_forwardcompany's inventory records show the following data for the month of July. Date July 1 July 5 July 10 July 20 July 25 July 1 Date Activities Beginning inventory Purchase Sale Purchase Sale July 5 Average cost July 5 July 10 July 20 200 units @ $50 If the company uses the weighted average method and the perpetual inventory system, what would be the cost of its ending inventory? Average cost July 20 July 25 Total July 25 Goods purchased Number of Cost per units unit 50 at $ 75.00 Units Acquired at Cost Units Sold at Retail 100 units @ $72 = $7,200 50 units @ $75 = $3,750 225 at $ 77.00 225 units @ $77 = $17,325 Number of units sold Cost of Goods Sold Cost per Cost of Goods Sold unit 75 at $ 50.00 = 200 at $ 50.00 $ 75 units @ $50 $ $ 3,750.00 10,000.00 10,000.00 Number of units 100 at Inventory Balance 100 at 50 at 150 at Cost per unit Inventory Balance 7,200.00 7,200.00 3,750.00 10,950.00 $ 175 at $ $ $ 75 at 150 at 225 at $ 375 at $ 50.00 = $ +73.00 = 77.00 = 75.40 75.00 = 55 72.00 = $…arrow_forward
- The units of an item available for sale during the year were as follows: Jan 1 Inventory 15 units at 122 April 15 Purchase 140 units at 116 September 9 Purchase 26 units at 122 There are 31 units of the item in the physical inventory at December 31. The periodic inventory system is used. Determine the inventory cost using the last-in, first-out (LIFO)arrow_forwardCullumber Company uses a periodic inventory system and reports the following for the month of June. Date Explanation Units Unit Cost Total Cost June 1 Inventory 106 $4 $424 12 Purchase 424 6 2,544 23 Purchase 265 8 2,120 30 Inventory 245 (a) Compute the cost of the ending inventory and the cost of goods sold under (1) FIFO, (2) LIFO, and (3) average-cost. (For calculation purposes, round average cost per unit to 2 decimal places, e.g. 5.25. Round answers to O decimal places, e.g. 125.) Cost of the ending inventory $ Cost of goods sold $ eTextbook and Media FIFO LIFO Average-Cost $ $ $ $ Assistance Usedarrow_forwardDineshbhaiarrow_forward
- Stellar Company uses the gross profit method to estimate inventory for monthly reporting purposes. Presented below is information for the month of May. Inventory, May 1 Purchases (gross) Freight-in Sales revenue Sales returns Purchase discounts (a) $161,900 697,000 31,400 924,000 73,200 12.100 Compute the estimated inventory at May 31, assuming that the gross profit is 25% of sales. The estimated inventory at May 31 $arrow_forward21. Williams Co. uses a periodic inventory system. The following are inventory transactions for the month of March: 3/1 Beginning Inventory 5,000 units at $2 3/7 Purchase 2,500 units at $3 3/16 Purchase 2,500 units at $4 3/26 Sales at $8 per unit 7,500 units Williams uses the weighted average method to determine the value of its inventory. What amount should Williams report as cost of goods sold on the income statement for the month of January?arrow_forwardCullumber Company uses a periodic inventory system. Its records show the following for the month of April, with 25 units on hand at April 30: Units Unit Cost Total Cost April 1 Inventory 30 $8 $240 12 Purchases 45 10 450 16 Purchases 17 11 187 Total 92 $877 (a) Calculate the ending inventory and cost of goods sold at April 30 using the FIFO and weighted average cost formulas. (Round the weighted average cost per unit to 2 decimal places, e.g. 52.75 and final answers to 0 decimal places, e.g. 5,275. )arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education