
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
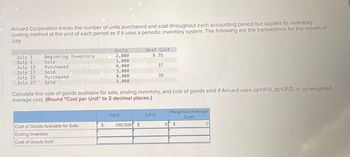
Transcribed Image Text:Aircard Corporation tracks the number of units purchased and sold throughout each accounting period but applies its inventory
costing method at the end of each period as if it uses a periodic inventory system. The following are the transactions for the month of
July.
Units
Unit Cost
July 1
July 5
July 13
July 17
July 25
July 27
Beginning Inventory
2,000
$ 35
Sold
1,000
Purchased
6,000
37
Sold
3,000
Purchased
8,000
39
Sold
5,000
Calculate the cost of goods available for sale, ending inventory, and cost of goods sold if Aircard uses (a) FIFO, (b) LIFO, or (c) weighted
average cost. (Round "Cost per Unit" to 2 decimal places.)
Weighted Average
FIFO
LIFO
Cost
Cost of Goods Available for Sale
$
280,000 $
0
$
0
Ending Inventory
Cost of Goods Sold
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Step 1: Introduction
VIEW Step 2: Calculation of Cost of Goods Avilable for Sale
VIEW Step 3: Calculation of cost of goods sold and Ending Inventory - FIFO Method
VIEW Step 4: Calculation of cost of goods sold and Ending Inventory - LIFO Method
VIEW Step 5: Calculation of cost of goods sold and Ending Inventory - Weighted Average method
VIEW Solution
VIEW Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 6 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Harbor Company uses a periodic inventory system. The company’s records show the beginning inventory of product no. T-12 on January 1 and the purchases of this item during the current year to be as follows: Date Purchases Units Unit cost Total cost January 1 Beginning inventory 800 11.25 9,000 February 23 Purchase 1,000 13.20 13,200 April 20 Purchase 3,200 10.50 33,600 May 4 Purchase 3,800 12.21 46,398 November 30 Purchase 1,100 10.64 11,704 Totals 9,900 units $113,902 A physical count indicates 1,500 units in inventory at year-end. Determine the cost of the ending inventory based on each of the following methods. Inventory valuation Average cost method FIFO LIFOarrow_forwardAkira Company had the following transactions for the month. Numberof Units TotalCost Beginning inventory 130 $1,300 Purchased Mar. 31 190 2,280 Purchased Oct. 15 160 2,400 Total goods available for sale 480 5,980 Ending inventory 70 ? Calculate the gross margin for the period for each of the following cost allocation methods, using periodic inventory updating. Assume that all units were sold for $29 each. Round your intermediate calculations to 2 decimal places and final answers to the nearest dollar amount. Gross Margin A. First-in, First-out (FIFO) $fill in the blank 1 B. Last-in, First-out (LIFO) $fill in the blank 2 C. Weighted Average (AVG) $fill in the blank 3arrow_forwardFLCL Company had the following transactions for the month: Calculate the ending inventory dollar value for the period for each of the following cost allocation methods, using periodic inventory updating. Provide your calculations. first-in, first-out (FIFO) last-in, first-out (LIFO) weighted averagearrow_forward
- Scrappers Supplies tracks the number of units purchased and sold throughout each accounting perlod but applies Its inventory costing method at the end of each period, as if it uses a periodic inventory system. Assume its accounting records provided the following information at the end of the annual accounting period, December 31. Transactions Units Unit Cost Beginning inventory, January 1 Transactions during the year: a. Purchase on account, March 2 b. Cash sale, April 1 ($48 each) c. Purchase on account, June 30 d. Cash sale, August 1 ($48 each) 170 $ 32 330 34 (410) 220 38 (80) Required: 1-a. Calculate the Cost of Goods Sold and Ending Inventory for Scrappers Supplies assuming it applies the LIFO cost method perpetually at the time of each sale. TIP: The sale of 410 units on April 1 is assumed, under LIFO, to consist of the 330 units purchased March 2 and 80 units from beginning inventory. 1-b. Does the use of a perpetual inventory system result in a higher or lower Cost of Goods…arrow_forwardPark Company’s perpetual inventory records indicate the following transactions in the month of June: 1. Compute the cost of goods sold for June and the inventory at the end of June using each of the following cost flow assumptions: a. FIFO b. LIFO c. Average cost (Round unit costs to 3 decimal places and other amounts to the nearest dollar.) 2. Next Level Why are the cost of goods sold and ending inventory amounts different for each of the three methods?what do these amounts tell us about the purchase price of inventory during the year? 3. Next Level Which method produces…arrow_forwardOahu Kiki tracks the number of units purchased and sold throughout each accounting period but applies its inventory costing method at the end of each month, as if it uses a periodic inventory system. Assume Oahu Kiki’s records show the following for the month of January. Sales totaled 340 units. Date Units Unit Cost Total Cost Beginning Inventory January 1 200 $ 80 $ 16,000 Purchase January 15 500 90 45,000 Purchase January 24 300 110 33,000 Required: Calculate the number and cost of goods available for sale. Calculate the number of units in ending inventory. Calculate the cost of ending inventory and cost of goods sold using the (a) FIFO, (b) LIFO, and (c) weighted average cost methods.arrow_forward
- The Luann Company uses the periodic inventory system. The following July data are for an item in Luann's inventory: July 1 Beginning inventory 30 units @ 10 Purchased $9 per unit 50 units @ $11 per unit 15 Sold 60 units 26 Purchased 25 units @ $13 per unit Calculate the cost of goods sold for July and ending inventory at July 31 using (a) first-in, first-out, (b) last-in, first-out, and (c) the weighted-average cost methods. Note: Round your cost per unit to three decimal places, if needed. Then round your final answers to the nearest dollar. A. First-in, First-out: Ending Inventory Cost of Goods Sold: B. Last-in, first-out: Ending Inventory Cost of Goods Sold: C. Weighted-average cost: Ending Inventory Cost of Goods Soldarrow_forwardOahu Kiki tracks the number of units purchased and sold throughout each accounting period but applies its inventory costing method at the end of each month, as if it uses a periodic inventory system. Assume Oahu Kiki's records show the following for the month of January. Sales totaled 310 units. Beginning Inventory Purchase Purchase Date January 1 January 15 January 24 Units 140 470 240 Unit Cost $ 85 95 115 Total Cost $ 11,900 44,650 27,600 Required: 1. Calculate the number and cost of goods available for sale. 2. Calculate the number of units in ending inventory. 3. Calculate the cost of ending inventory and cost of goods sold using the (a) FIFO, (b) LIFO, and (c) weighted average cost methods.arrow_forwardMojo Industries tracks the number of units purchased and sold throughout each accounting period but applies its inventory costing method at the end of each period, as if it uses a periodic inventory system. Assume its accounting records provided the following information at the end of the accounting period, January 31. The inventory's selling price is $14 per unit. Transactions Inventory, January 1 Unit Cost Units Total Cost $ 5.00 190 $ 950 Sale, January 10 (140) Purchase, January 12 5.50 Sale, January 17 Purchase, January 26 6.50 240 (100) 70 1,320 455 Required: 1. Compute the amount of goods available for sale, ending inventory, and cost of goods sold at January 31 under each of the following inventory costing methods: a. Weighted average cost. b. First-in, first-out. c. Last-in, first-out. d. Specific identification, assuming that the January 10 sale was from the beginning inventory and the January 17 sale was from the January 12 purchase. 2-a. Of the four methods, which will…arrow_forward
- In chronological order, the inventory, purchases, and sales of a single product for a recent month are as follows (see attached). 1.Using the periodic inventory system, compute the cost of ending inventory, cost of goods sold, and gross margin. Use the average-cost, FIFO, and LIFO inventory costing methods. (Round unit costs to cents and totals to dollar.) 2.Explain the differences in gross margin produced by the three methods.arrow_forwardGladstone Limited tracks the number of units purchased and sold throughout each accounting period but applies its inventory costing method at the end of each period, as if it uses a periodic inventory system. Assume its accounting records provided the following information at the end of the annual accounting period, December 31. Transactions Beginning inventory, January 1 Transactions during the year: a. Purchase, January 30 b. Sale, March 14 ($12 each) c. Purchase, May 1 d. Sale, August 31 ($12 each) Required: Units 1,900 Unit Cost $ 4.00 2,500 6.00 (1,700) 1,200 (1,900) 8.00 1. Compute the amount of goods available for sale, ending inventory, and cost of goods sold at December 31, under each of the following inventory costing methods. For Specific identification, assuming that the March 14, sale was selected two-fifths from the beginning inventory and three-fifths from the purchase of January 30. Assume that the sale of August 31, was selected from the remainder of the beginning…arrow_forwardOahu Kiki tracks the number of units purchased and sold throughout each accounting period but applies its inventory costing method at the end of each month, as if it uses a periodic inventory system. Assume Oahu Kiki's records show the following for the month of January. Sales totaled 260 units. Beginning Inventory Purchase Purchase Date January 1 January 15 January 24 Units 100 360 240 Unit Cost $ 75 95 115 Total Cost $ 7,500 34,200 27,600 Required: 1. Calculate the number and cost of goods available for sale. 2. Calculate the number of units in ending inventory. 3. Calculate the cost of ending inventory and cost of goods sold using the (a) FIFO, (b) LIFO, and (c) weighted average cost methods.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education