
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And Analysis
3rd Edition
ISBN: 9781337788281
Author: James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald Pagach
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
thumb_up100%
General accounting
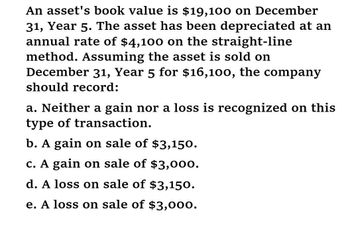
Transcribed Image Text:An asset's book value is $19,100 on December
31, Year 5. The asset has been depreciated at an
annual rate of $4,100 on the straight-line
method. Assuming the asset is sold on
December 31, Year 5 for $16,100, the company
should record:
a. Neither a gain nor a loss is recognized on this
type of transaction.
b. A gain on sale of $3,150.
c. A gain on sale of $3,000.
d. A loss on sale of $3,150.
e. A loss on sale of $3,000.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- An asset's book value is $18,600 on December 31, Year 5. Assuming the asset is sold on December 31, Year 5 for $14,400, the company should record: Multiple Choice A gain on sale of $13,200. Neither a gain nor a loss is recognized on this transaction. A loss on sale of $4,200. A loss on sale of $13,200. A gain on sale of $4,200.arrow_forwardCan you please give true answer?arrow_forwardLei Company acquired a financial asset at its market value of P4,800,000. Broker fees of P300,000 were incurred in relation to the purchase. At what amount should the financial asset initially be recognized if it is classified as: 1. At Fair value through profit or loss _________________ 2. As available for sale _____________________arrow_forward
- 5. During the current year an entity sold a piece of equipment used in production. The equipment had been accounted for using the revaluation method and details of the accounts and sale are presented below: Sales price P100,000 Equipment carrying amount (net) 90,000 Revaluation surplus 20,000 Which of the following is correct regarding recording the sale? Group of answer choices The gain that should be recorded in other comprehensive income is P10,000 The gain that should be recorded in profit and loss is P10,000; the P20,000 revaluation surplus may be transferred to retained earnings. The gain that should be recorded in other comprehensive income is P30,000 The gain that should be recorded in profit and loss is P30,000arrow_forwardMadison Company acquired a depreciable asset at the beginning of Year 1 at a cost of $12 million and 6 years useful life. At December 31, Year 1, Madison gathered the following information related to this asset: Fair value of the asset (net selling price) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . $7.5 million Sum of future cash flows from use of the asset . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . $10 million Present value of future cash flows from use of the asset . . . . . . . . . . . $8 million Impairment loss of the asset at end of year 1 (if any) Select one:a. IFRS $0 and US GAAP: $ 2 millionb. IFRS $2.5 million and US GAAP $2 millionc. IFRS $2 million and US GAAP $0 million d. IFRS $4 million and US GAAP $0 millionarrow_forwardam. 122.arrow_forward
- On December 31, Year 1, Valur Co. had the following available-for-sale investment disclosure within the Current Assets section of the balance sheet: Available-for-sale investments (at cost) $145,000Plus valuation allowance for available-for-sale investments 40,000Available-for-sale investments (at fair value) $185,000There were no purchases or sales of available-for-sale investments during Year 2. On December 31, Year 2, the fair value of the available-for-sale investment portfolio was $200,000. The net income of Valur Co. was $210,000 for Year 2.Compute the comprehensive income for Valur Co. for the year ended December 31, Year 2.arrow_forward16. ABC Co.'s biological asset has a fair value less costs to sell of P 100,000 and P120,000, respectively. The year-end adjusting entry will most likely include a. a credit to unrealized gain of P 20,000 to be recognized in profit or loss b. a credit to unrealized gain of P 20, 000 to be recognized in other comprehensive income c. a debit to unrealized gain of P 20,000 to be recognized in profit or loss d. none of thesearrow_forward5. How should accounting fees for acquisition be treated? A. Expensed in the period of acquisition B. Capitalized as part of acquisition cost C. Deferred and amortized D. Deferred until the company is disposed of or wound-up 6.The excess of the price paid over the fair value of the net identifiable assets acquired should be recognized as A. Goodwill to be amortized periodically for 20 yearS. B. Expenses immediately C. Goodwill not subject to amortization but subject to impairment D. Goodwill to be amortized for 40 years 7.Under PFRS 3 (Business Combinations) A. Both direct and indirect costs are to be capitalized B. Both direct and indirect costs are to be expensed C. Direct costs are to be capitalized and indirect costs are to be expensed D. Indirect costs are to be capitalized and direct costs are to be expensedarrow_forward
- A company which prepares financial statements to 31 December classifies a non-current asset as held for sale on 1 SEPTEMBER 20X2. The asset's carrying amount at that date is $20,000 and its fair value is $15,600, with estimated costs to sell of $600. The asset is sold in June 20X3 for $16,000(net of costs). Calculate any impairment losses or gains that should be recognised in the company's statement of profit or loss for the year ended 31 December 20X2 if the asset's fair value less costs to sell at 31 December 20X2 is: a)14,000 b)17,000 c)22,000 In each case, also calculate the profit or loss that should be recognised on the disposal of the asset in 20X3 and comment on the results shown.arrow_forwardChoose the response that correctly states the amount of a seller's gain or loss on repossessed real property with a fair market value of $54,000 on the date of repossession. The unpaid balance of the installment obligation at the time of repossession is $56,000, the gross profit percentage is 25%, and the costs of repossession were $800. A) Loss of $13,200 B) Loss of $11,200 C) Gain of $11,200 D) Gain of $13,200 Kenisha spent a total of $115,000 to purchase a business, including $15,000 in legal fees for the preparation of the sales contract, and $100,000 paid to the seller. She received a building with a fair market value (FMV) of $70,000, land with an FMV of $10,000, and furniture and fixtures with an FMV of $20,000. What is Kenisha's basis in the building, land, and furniture? A) $70,000 building; $10,000 land; $20,000 furniture and fixtures. B) $75,000 building; $15,000 land; $25,000 furniture and fixtures. C) $80,500 building; $11,500 land; $23,000 furniture and fixtures. D)…arrow_forwardOn 31 December 2023, the statement of financial position of Dominic Ltd showed the following non-current assets after charging depreciation. Leasehold land $ 800 000 Accumulated depreciation (400 000) $ 400 000 Equipment $ 340 000 Accumulated depreciation (180 000) $ 160 000 The company has adopted fair value for the valuation of non-current assets, as per the revaluation method. On 31 December 2023, an independent valuer assessed the fair value of the leasehold land to be $420 000 and the equipment to be $100 000. The Asset Revaluation Surplus Account balance on 31 December 2023 is $15,000 before the revaluation takes place. Required 1. Prepare any necessary entries to revalue the leasehold land and the equipment as at 31 December 2023. Hint: Show separate entries for revaluation gain or loss, you may only offset current year’s loss with asset revaluation surplus balance amount before the revaluation took place. 2. Assume that the leasehold land and equipment had remaining useful…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning

Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And Analysis
Accounting
ISBN:9781337788281
Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald Pagach
Publisher:Cengage Learning
