
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
need answers for 1,2,3 and 4
4. Build a spreadsheet: Construct an Excel spreadsheet to solve all of the preceding requirements. Show how both cost schedules and the income statement will change if the following data change: direct labor is $390,000 and utilities cost $35,000.
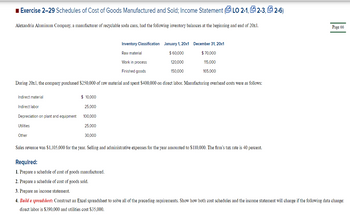
Transcribed Image Text:■ Exercise 2-29 Schedules of Cost of Goods Manufactured and Sold; Income Statement (LO 2-1, 2-3, 2-6)
Alexandria Aluminum Company, a manufacturer of recyclable soda cans, had the following inventory balances at the beginning and end of 20x1.
Inventory Classification
Raw material
Work in process
Finished goods
During 20x1, the company purchased $250,000 of raw material and spent $400,000 on direct labor. Manufacturing overhead costs were as follows:
Indirect material
Indirect labor
Depreciation on plant and equipment
Utilities
Other
$ 10,000
25,000
100,000
25,000
30,000
January 1, 20x1
$ 60,000
120,000
150.000
December 31, 20x1
$ 70,000
115.000
165.000
Sales revenue was $1,105,000 for the year. Selling and administrative expenses for the year amounted to $110,000. The firm's tax rate is 40 percent.
Page 66
Required:
1. Prepare a schedule of cost of goods manufactured.
2. Prepare a schedule of cost of goods sold.
3. Prepare an income statement.
4. Build a spreadsheet: Construct an Excel spreadsheet to solve all of the preceding requirements. Show how both cost schedules and the income statement will change if the following data change:
direct labor is $390,000 and utilities cost $35,000.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps with 5 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Below is a list of costs. Please identify each cost as either a product or period cost. Dragged and dropped options on the right-hand side will be automatically saved. For keyboard navigation... SHOW MORE ✓ Depreciation on office copier Depreciation on office building Insurance on office building Metal used in building a car Salary of CEO Salary of production manager Salary of assembly line workers Utilities of office building = = Product Period = Period = Period = Product = Product = = Period Periodarrow_forwardSolve a Related Rates Problem. A technical support contracting firm hires people to work from home using their proprietary support scripting system. The more employess they have, the more contracts they can support and therefore the more revenue they can generate. Suppose that the company's revenue and number of employees is related by R² = 297x³, where is R is the revenue in thousands of USD anda is the number of employees in hundreds. If there is no shortage of work to be done, the company currently has 3300 employees, and the company wants to increase their revenue from $3,267,000.00 this year to $5,643,000.00 next year, how many new employees should be hired in order to make that possible? The company should hire new employees before next year. Preview My Answers Submit Answers harrow_forward1. Top-down versus bottom-up estimates. pts. a. Describe the methods and uses of each of the approaches. 2. Compare the advantages and disadvantages of each of the approaches. 3. What are the three types of costs discussed in the text? Define them. 4. For a small project requiring 120 hours at $50/hr and having a direct overhead rate of 40%, calculate the direct cost (Exercise 1 in Chapter 5). To that add indirect costs (G&A) at 20% and then profit at 20% for a total project price. What are the estimated costs for: Design Programming In-house testing Which “approach to estimating” is this? What weaknesses are inherent in this approach? 5. Take another look at Exercise #5. Use Exercise Figure 5.1 on page 160. But now you are asked to do a bottom-up estimate based on the following data and compare it with the top-down estimate of $800,000. If confronted with these two estimates, what, if any, actions would you take? Deliverables Estimated Hours Rate:…arrow_forward
- Convert the accompanying database to an Excel table to find: a.The total cost of all orders. b.Thetotal quantity of airframe fasteners purchased. c. The total cost of all orders placed with Manley Valve. Question content area bottom Part 1 a. The total cost of all orders is $?????? enter your response here.arrow_forwardI will provide the question and answer but I need an explanation on how to get the answers. There are 4 answers (below) and the chart should be attached. Solve the problem. Round dollar amounts to the nearest dollar. Westminster Office Machines allocates its overhead of $1,487,304 by the sales of each product. Find the overhead for each department. List your answers if the order of the table. ($423,696, $458,304, $222,684, $382,620)arrow_forwardSuppose the smartphone manufacturer Peony Electronics provides the following information for its costs last month (in millions): (Click the icon to view the costs.) Read the requirements. Requirements 1, 2 and 3. Classify each of these costs according to its place in the value chain. Within the production category, break the costs down further into three subcategories: Direct Materials, Direct Labor, and Manufacturing Overhead. Then calculate the total cost for each value chain category. (Enter amounts in millions. If an input field is not used in the table, leave the input field empty; do not enter a zero.) Cost Delivery expense Salaries of salespeople Chipset Exterior case for phone Assembly-line workers' wages Technical support hotline Depreciation on plant and equipment Rearrange production process 1-800 (toll-free) line for customer orders Scientists' salaries Total costs Cost R and D $ 14 Peony Electronics Value Chain Cost Classification Direct Design Materials LA 60 5 $…arrow_forward
- Load the wooldridge package in your R script using the library function: library (wooldridge) Load the wage 2 dataset by writing (in your R script): data = wage 2 This dataset contains information on individuals' monthly wage (the wage variable), number of hours worked per week (the hours variable), IQ (the IQ variable), and other variables. Add a new variable to data (named hourly_wage) which is equal to monthly wage wage divided by 4 times the number of hours worked per week: hourly age = Assign the 4x hours dataframe data (after adding the new variable) to answer1. 2. What is the mean hourly wage? 3. What is the minimum number of years of education in the dataset? 4. What is the number of observations? 5. Estimate the following model: (i(i using the Im function. Assign your model to answer5. 6. What is the coefficient on educ in the model in the previous question? (Hint: Your answer should be a positive number.) Warrow_forwardezto.mheducation.com/ext/map/index.html?_con=con&external_browser=0&launchUrl=https%253A% merica AS... rk i Required information Use the following information for the Problems below. (Algo) [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] Trini Company set the following standard costs per unit for its single product Direct materials (30 pounds @ $5.00 per pound) $ 150.00 98.00 Direct labor (7 hours @ $14 per hour) Variable overhead (7 hours @ $7 per hour) Fixed overhead (7 hours @ $9 per hour) Standard cost per unit Production (in units) Standard direct labor hours (7 DLH per unit) Budgeted overhead (flexible budget) Fixed overhead Variable overhead Overhead is applied using direct labor hours. The standard overhead rate is based on a predicted activity level of 80% of the company's capacity of 51,000 units per quarter. The following additional information is available. 49.00 63.00 $360.00 70% 35,700 249,900 Direct materials (1,377,000 pounds @ $5.00 per pound)…arrow_forwardDirections: Answer the following questions by the due date. Use numerical calculations (if needed) to support your argument. Submit your answers through uploading a Microsoft Word file, Excel file or PDF. Tread-Force Fitness, Inc. assembles and sells elliptical machines. All activity costs are related to labor. Management must remove $2.00 of activity cost from the product in order for it to remain competitive. Activity-based product information for each elliptical machine is as follows: (Hrs per unit) Activity Activity Based Usage x Activity rate / hr = Activity Cost Moving 0.20 $15 $3.00 Motor Assembly 1.50 $20 $30.00 Final Assembly…arrow_forward
- Font Paragraph Styles The Borstal Company has to choose between two machines that do the same job but have different lives. The two machines have the following costs: Year Machine A Machine B 0 $ 43,500 $ 53,500 1 10,700 9,400 2 10,700 9,400 3 4 10,700+ replace 9,400 9,400+ replace These costs are expressed in real terms. a. Suppose you are Borstal's financial manager. If you had to buy one or the other machine and rent it to the production manager for that machine's economic life, what annual rental payment would you have to charge? Assume a 7% real discount rate and ignore taxes. Note: Do not round intermediate calculations. Enter your answers as a positive value rounded to 2 decimal places. b. Which machine should Borstal buy? c. If there is steady 5% per year inflation, what will be the annual rental payment for machine B for the second year? Note: Enter your answer as a positive value rounded to 2 decimal places. a. Machine A a. Machine B b. Which machine should Borstal buy? c.…arrow_forwardPlease help me with Req 4. If someone can help I will give a thumbs up. If you zoom in I believe the image should beome clearer. Thanks!arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education