
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780134580999
Author: Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Transcribed Image Text:18
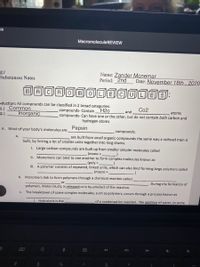
MacromoleculeREVIEW
gy
Substances Notes
Name: Zander Mcnemar
Period: 2nd
Date: November 18th , 2020*
oduction: All compounds can be classified in 2 broad categories:
1.) Common
compounds- Contain
Н2о
Со2
Inorganic
and
compounds- Can have one or the other, but do not contain both carbon and
2.)
atoms
hydrogen atoms
A. Most of your body's molecules are
Pepsin
compounds.
a.
are built from small organic compounds the same way a railroad train is
built, by linking a lot of smaller units together into long chains.
i. Large carbon compounds are built up from smaller simpler molecules called
(mono =.
ii. Monomers can bind to one another to form complex molecules known as
(poly =
iii. A polymer consists of repeated, linked units, which can also bind forming large polymers called
(macro =
b. Monomers link to form polymers through a chemical reaction called
or
During the formation of
polymers, Water (H2O), is released or is by-product of the reaction.
C.
The breakdown of some complex molecules, such as polymers, occurs through a process known as
i. Hydrolysis is the
of a condensation reaction. The addition of water, to some
24
%
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- The molecule below is a monomer of O triglycerides O proteinsarrow_forwardPolymers are... a. synthesized via hydrolysis reactionsb. broken down via dehydration reactionsc. made up of monomer chainsd. all of the abovee. none of the abovearrow_forward1. Draw a circle around and give the name of each functional group in the following twomolecules. (Note: each line represents a covalent bond. If no atom is shown, assume there’s a carbon there.)arrow_forward
- 1. Is there more than one way to fold a protein, given the conflicting demands of the different "R" groups and the protein existing in a watery environment? 2. Explain what an R group is. 3. Compare the backbone of a polypeptide with that of a nucleic acid. 4. Proteins perform critical functions in all of our cells. Without proteins, life wouldn’t exist. Think of some specific proteins and describe what function they perform. 5. Explain the difference between secondary and tertiary protein structures.arrow_forwardThe model below shows a chemical reaction that takes place in cells. B Which statement correctly describes the details of the reaction shown above? A A polymer is built from monomers as water is removed. U HO-1 2 3 с HO- 1 2 3 H HO D H₂O A lipid polymer is built from monomers as water is removed. A polymer is hydrolyzed into its component monomers as water is added. Adhesion is occurring between water molecules. -Harrow_forward6. Proteins contain other amino acids that can compete with cysteine and react with bromoacetamide. Compare the structure of cysteine and serine below. Why can serine react similarly to cysteine? Think about periodic table trends that influence electronic factors. SH I H N H cysteine Brief explanation of why serine can react similarly to cysteine: serine OHarrow_forward
- Simple sugars Enzyme 1. Carbohydrate Steroids 2. Lipid Guanine 3. Protein 4. Nucleic Acid Triglyceride Alpha helices > > > > > >arrow_forwardIn a portion of polypeptide shown below, which bond is described by o rotation? NH,-- -CO- A. a В. b OC.c D. d E. Both 'a' and 'e'arrow_forwardAt physiological pH, the 06-methylguanine:T wobble base pair predominates. Two hydrogen bonds form between the two bases. Draw the structure of this base pair. Use bond Any to draw hydrogen bonds. H;C H N- N- R -N. N-H- R Harrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education

Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780134580999
Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:PEARSON

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781259398629
Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa Stouter
Publisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,

Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780815344322
Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter Walter
Publisher:W. W. Norton & Company

Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781260159363
Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, Cynthia
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.

Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9781260231700
Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael Windelspecht
Publisher:McGraw Hill Education