
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780134580999
Author: Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
2) A species is a group of individual organisms that interbreed and produce fertile, viable offspring. According to this definition, one species is distinguished from another when, in nature, it is not possible for matings between individuals from each species to produce fertile offspring. Evolution is an important mechanism in the formation of new species. The evolution of a new species requires several components including all, BUT
A) Evolution of a new species requires a long time.
B) Evolution of a new species requires the need for a genetic change.
C) Evolution of a new species requires a separation that prevents interbreeding.
D) Evolution of a new species requires mutations that produce new genetic traits.
Not Graded
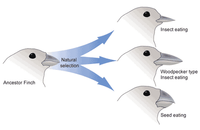
Transcribed Image Text:The image depicts the concept of natural selection as it pertains to the evolution of finches. It illustrates the diversification of finch species from a common ancestor. The diagram includes three finch variations:
1. **Ancestor Finch**: This is the original finch species from which new species evolved.
2. **Insect Eating Finch**: This finch has evolved a beak suitable for feeding on insects.
3. **Woodpecker Type Insect Eating Finch**: This finch has a specialized beak for a more woodpecker-like approach to eating insects.
4. **Seed Eating Finch**: This finch has a beak adapted for feeding on seeds.
Arrows labeled "Natural selection" indicate the evolutionary process leading to these adaptations. Each arrow points from the ancestor finch to one of the evolved forms, signifying how specific dietary needs led to the development of different beak types.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A population of lizards in Northern California is brown and is not poisonous to birds. A population of lizards in Southern California is orange and is poisonous to birds. In central California, where the two species overlap, a new species of non-poisonous, orange lizards arose. Which of the following statements best explains the existence of non-poisonous orange lizards? A) Non-poisonous brown lizards changed color once they noticed birds did not eat orange lizards. B) Non-poisonous orange lizards have a selective advantage since birds avoid orange lizards. C) Non-poisonous lizards turn orange by eating orange flowers and then pass the trait on D) Non-poisonous orange lizards have a selective disadvantage since they cannot blend in. E) Non-poisonous brown lizards are more attractive to mates.arrow_forward8) Each of the observations provides evidence that supports the idea of common ancestry and evolution. Which one is from the field of molecular biology? A) Mammals have two openings in the skull behind each eye socket, whereas reptiles and bird only have one opening. B) DNA analysis shows that the DNA of Neanderthals is more similar to the DNA of non‑African humans than that of Africans. C) Two closely related but distinct species of squirrels inhabit the north and south rims of the Grand Canyon. D) The embryos of both birds and mammals divide in a radial cleavage pattern instead of a spiral cleavage pattern present in insects.arrow_forwardFor natural selection to occur, there must be competition for resources, competition for survival, or 15) different reproductive success. Why is this so? A) Without competition, there is no pressure to mutate.B) The struggle of competition makes individuals stronger.C) Natural selection acts on the different abilities of individuals to survive and pass on their genes to the next generation.D) Populations evolve to preserve the species and don't change unless they must. Then explain why the answer is correct and why the others one are inccorect.arrow_forward
- The migration of breeding individuals between populations causes a corresponding movement of alleles, which is referred to as: a) mutation b) genetic drift c) gene flow d) random mating e) directional selection Question 58 (Mandatory) Which term indicates the evolution of many closely related species from one or a few ancestral species in a relatively short period of time? This is particularly noticeable on islands. Microevolution b) Communal radiation Adaptive radiation d) Preadaption e) Hyper speciation Darrow_forwardEven though Hardy and Weinburg showed that the process of random reproduction will not alter gene frequency in a population over time, in wild populations we observe that gene frequencies do change overtime so what has happened? A) sexual selection B) Evolution due to sexual selection C) none of these D) any of these E) Evolution due to genetic driftarrow_forwardWhat is Sympatric speciation? A) When a population is separated from the main group by a barrier and becomes a new species B) When a population mutates into a new species C) When a population develops into a new species without any physical barriers to isolate themarrow_forward
- 1.) The process in which the genetic composition of a population changes with time is known as evolution. Which of the following mechanisms is not an agent of evolutionary change? A) natural selection B) mutation C) genetic drift D) random mating 2.) Which statement below is not consistent with a population in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium? A) Genetic drift is occuring B) Random mating is occuring. C) Population size is large. D) Migration is not occuring.arrow_forwardWhen the isthmus of Panama (land bridge that connects north and south America) arose about 3 million years ago, it caused species of fish to diverge into sister species located in either the caribean or pacific ocean. Why did they form separate species? A) Because this is an example of sympatric speciation B) Because the tides are different on each side of the land bridge C) Because different predators in each ocean caused the populations to diverge D) Because the populations were reproductively isolatedarrow_forwardCharles Darwin’s claim, that the species level of classification is just as arbitrary as that of any other taxonomic level, is supported by all of the following observational failures except: the inability of a sexually-reproducing eukaryotic species to interbreed with a different species the inability of a cloning species lacking biparental reproduction to interbreed with a different species the inability of an asexual eukaryotic species to interbreed with a different species the inability of an extinct species (like a dinosaur) to interbreed with a different species the inability of a prokaryotic species to interbreed with a different speciesarrow_forward
- Fixity of Species refers to… Group of answer choices A-the theory that species exist at a fixed location along a physiological continuum B-the fact that species are defined by fixed adaptations to their direct environment C-the theory presented by Thomas Malthus that population densities of any given species are most affected by mortality and fertility rates D-the pre-darwinian notion that species, once created, can never change E-the late 19th century concept that because mendelian traits are fixed they are evidence that variation within and between species are designed by God specifically for those speciesarrow_forwardA population of interbreeding birds has been split by a geological event after which the isolated part of the population started to evolve into an incipient species with different mating rituals. Due to a recent environmental change the two populations are now able to potentially mate again in what is called a hybrid zone. Mating does take place every now and then but the hybrid offspring appear less able to survive. As a consequence, mating rituals start to diverge even further. We call this process of continued divergence? O Fusion O Behavioral isolation Reinforcement O Postzygotic isolation O Stabilityarrow_forwardSwordtails, platyfish and Poecilia species are incapable of interbreeding with each other but swordtail species 1 can produce viable hybrids with swordtail species 2. In addition, both Poecilla fish, platyfish, and swordtails can all be distinguished genetically, but swortail species 1 and 2 cannot be genetically distinguished. Using this information indicate how many distinct 1) Biological, 2) morphological, and 3) phylogenetic species would be found in this group of fish. If you cannot determine this for any of the 3 species categories, state what you would need to know in order to do so. Edit View Insert Format Tools Table 12pt v Paragraph v BIUAv er Tv: 1. There are four 2.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education

Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780134580999
Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:PEARSON

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781259398629
Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa Stouter
Publisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,

Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780815344322
Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter Walter
Publisher:W. W. Norton & Company

Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781260159363
Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, Cynthia
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.

Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9781260231700
Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael Windelspecht
Publisher:McGraw Hill Education