
Biochemistry
9th Edition
ISBN: 9781319114671
Author: Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.
Publisher: W. H. Freeman
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
A schematic diagram of the helical structure of cytochrome b562 is reproduced below. This
protein belongs to the family of -proteins that have a four-helix bundle. Number the helices 1 – 4
according to their N C direction. Indicate relative orientations of the macrodipoles of helices 1 – 4
adjacent to the diagram of cytochrome b562. Remember that according to the definition of a dipole
that the arrow points towards the positive end.
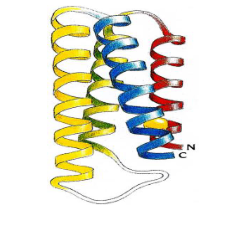
Transcribed Image Text:WA
UN
N
с
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- In the protein adenylate kinase, the C-terminal region has the sequence Val-Asp-Asp-Val-Phe- Ser-Gin-Val-Cys-Thr-His-Leu-Asp-Thr-Leu-Lys The hydrophobic residues in this sequence are presented in boldface type. Use helix wheel to demonstrate this peptide is an amphipathic helix.arrow_forwardGiven the structures of the ribonucleotides as (shown in Image A) and deoxyribonucleotides (as shown in Image B), Draw the structure of the polyribonucleotide UAGCCUG and the structure of thepolydeoxyribonucleotide CGTAGAT.arrow_forwardTo visualize the spatial arrangement of amino acid residues in an a-helix, it is helpful to imagine you are looking down the long axis of the helix, just as you would look down a soda straw. Viewed in this orientation, the residues form a circle, with each residue offset from its neighbor by 100 degrees. This representation is called a helical wheel. Use the circle below to indicate the position of each residue around the helix of the enzyme lysozyme. NH ...Arg - Cys - Glu- Leu - Ala Ala - Ala Met-Lys COO- The first two amino acids, Arg-1 and Cys-2, are shown as an example. Arg-1 O Glu-3 Which amino acid in the polypeptide is the first to pass the origin (i.e., which amino acid passes Arg- 1 first, completing one full circle)? Select the best answer. O Leu-4 O Ala-5 O Ala-6 O Ala-7 Met-8 O Lys-9 100° O none of the above Cys-2arrow_forward
- 3) You are working on a protein with the following sequence in an area of interest. -Asp-Leu-Leu-Gln-Glu-Glu-Asp-Glu-Ser-Arg a. The current structure, solved at pH 7.4, of this segment has an alpha helix that is disrupted a er the Gln. Why might the alpha helix stop at this residue? b. This protein is involved in Lysosomes in vivo. The secondary structure of this region is expected to change into a complete alpha helix. Why might this change into a complete helix? ( Hint: Lysosomes are acidic!)arrow_forwardα-Keratin is an intermediate filament with a basic structural unit of two a helices in a coiled coil. Each helix has a seven-residue repeating unit (heptad repeat). A representation of the a helices of a coiled coil dimer is shown. Each letter represents a different amino acid residue. f g d e Review the table of amino acids. a d g f Identify the three true statements about the structure of keratin. ☐ The a helix of the coiled coil is wound less tightly than predicted for an α helix. ☐ Each polypeptide in the dimer has 3.6 residues per turn, and a nonpolar group occurs every 3.5 residues, resulting in a slight winding, or twist, around the other polypeptide, forming a coiled coil. Arg-Ala-His-Glu-His-Thr-Asp is a likely repeat in the a helix of keratin. ☐ Val-Thr-Asp-Ala-Glu-Arg-His is a likely repeat in the a helix of keratin. ☐ The residues at positions b and c are less likely to be polar or charged because they are in contact with the solvent. ☐ Keratin molecules are very strong due…arrow_forwardWhat does this statement mean: "Upon folding of a protein many main chain amides replace their hydrogen bonds to water for those with other amide bonds" Is this true for alpha helix in proline racemase? and is there a pattern?arrow_forward
- PfCRT is found to have 10 peaks on a hydropathy plot given its primary sequence. Researchers also noted that each peak is comprised of about 30 amino acids. The digestive vacuole membrane is 45Å in Plasmodium species. Explain why researchers conclude there are 10 transmembrane helices from these two pieces of data.arrow_forwardWrite a structural formula for a tetrapeptide composed of phenyl-alanine, glycine, aspartic acid, and histidine in which the phenylalanine is N-terminal and the histidine is C-terminal. How many different tetrapeptides could be written that fit the criteria in this question?arrow_forwardMembrane-spanning proteins are notoriously difficult to characterize by x-ray crystallography. Hollonut of VISA Toplon a. Explain how the information in the diagrams below can be used in the detection of membrane- spanning proteins consisting of alpha helices, given that the lipid portion of a typical bilayer is approximately 30 Å thick. Amino terminus 5.4 A (3.6 residues) b. Identify and briefly describe how the features of a transmembrane protein composed of ß-sheets differ from that above.arrow_forward
- What would the order of migration be (bottom to top in the gel) in a SDS-PAGE for the following proteins? Concanavalin A (ConA) (a homotetramer of 106 kDa), lysozyme (a monomer of 14.3 kDa) & horse liver alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH) (a homodimer of 80 kDa). a. ADH, ConA, lysozyme b. ConA, ADH, lysozyme c. Lysozyme, ADH, ConA Od. Lysozyme, ConA, ADHarrow_forwardAssume a fragment of two-stranded antiparallel β-structure is 3.3 nm long. What is the approximate number of amino acids in this fragment?arrow_forwardis it true that aplha and beta are made up of same amino acids but Beta chain is longer than alpha chain?what is other difference and similarity?is the amino aicd sequence exactly the same as well?are their structure the same ?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781319114671Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.Publisher:W. H. Freeman
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781319114671Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.Publisher:W. H. Freeman Lehninger Principles of BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781464126116Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. CoxPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Lehninger Principles of BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781464126116Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. CoxPublisher:W. H. Freeman Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...BiochemistryISBN:9781118918401Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. PrattPublisher:WILEY
Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...BiochemistryISBN:9781118918401Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. PrattPublisher:WILEY BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...BiochemistryISBN:9780134015187Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. PetersonPublisher:PEARSON
Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...BiochemistryISBN:9780134015187Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. PetersonPublisher:PEARSON

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781319114671
Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781464126116
Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. Cox
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781118918401
Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. Pratt
Publisher:WILEY

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781305961135
Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougal
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781305577206
Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...
Biochemistry
ISBN:9780134015187
Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. Peterson
Publisher:PEARSON