
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
A reducing elbow is used to deflect water flowrate at a rate of 1920 g/s in a horizontal pipe downward by an angle theta = 43 from the flow of direction while accelerating it. The elbow discharges water into the atmosphere. The diameter of the elbow at the inlet is 6.5 cm and at the exit is 1.5cm. The elevation difference between the centers of the exit and the inlet is 22cm . The mass of the elbow and the water is 61.5 kg. Determine the anchoring force needed to hold the elbow in place
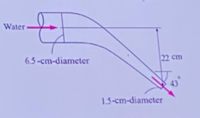
Transcribed Image Text:Water
6.5-cm-diameter
22 cm
43
1.5-cm-diameter
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A pump draws water through a 36 cm diameter suction pipe and discharges it through a 22 cm diameter pipe in which the mean flow velocity, uc is 4.3 m s-1. C Pump Water The 22 cm diameter pipe discharges horizontally into air at point C. To what height, h above the water surface at A can water be raised if 53 kW is delivered to the pump? Assume that the pump operates at 60% efficiency and that the total head losses in the pipe between A and C, hr, are equal to 2u.2 where g is the acceleration due to gravity, g=9.81ms². 2garrow_forwardA centrifugal pump has an impeller diameter and width at outlet of 45cm and 8cm, respectively. The pump delivers water against a net head of 11.3m. Its vanes are curved backwards and make an angle of 30° with the tangent at the outer periphery. Determine the discharge of the pump rotating at a design speed of 1335rpm. Make an assumption of the pump's manometric efficiency.arrow_forwardA reducing elbow in a horizontal pipe is used to deflect water flow by an angle 8= 45° from the flow direction while accelerating it. The elbow discharges water into the atmosphere. The cross-sectional area of the elbow is 150 cm² at the inlet and 25 cm2 at the exit. The elevation difference between the centers of the exit and the inlet is 40 cm. The mass of the elbow and the water in it is 56 kg. Determine the anchoring force needed to hold the elbow in place. Take the momentum-flux correction factor to be 1.03 at both the iniet and the outlet. The density of water is 1000 kg/m³, and the flow rate of water is 30 kg/s. Waters 30.0 kg/s 150 cm- 25 cm² 45° 40 cm The anchoring force needed to hold the elbow in place is The resultant direction of force is KNarrow_forward
- The water tank in the figure is being filled through section (1) at v1 = 4 m/s and through section (3) at V3 = 5 m/s. Find the rate of change dh/dt if the tank diameter is d = 1 m and exit velocity is v2 = 6 m/s.arrow_forwardUnderground water is pumped through a 10-cm- diameter pipe that consists of a 2-m-long vertical and 1-m-long horizontal section. Water discharges to atmospheric air at an average velocity of 3 m/s, and the mass of the horizontal pipe section when filled with water is 12 kg per meter length. The pipe is anchored on the ground by a concrete base. Determine the bending moment acting at the base of the pipe (point A) and the required length of the horizontal section that would make the moment at point A zero.arrow_forwardWater enters a mixed flow pump axially at a rate of 0.25 m3/s and at a velocity of 5 m/s, and is discharged to the atmosphere at an angle of 75° from the horizontal, as shown . If the discharge flow area is half the inlet area, determine the force acting on the shaft in the axial directionarrow_forward
- Fluids Question Consider a centrifugal blower that has a radius of 20 cm and a blade width of 8.2 cm at the impeller inlet and a radius of 45 cm and a blade width of 5.6 cm at the outlet, the blower delivers air at a rate of 0.70 m3/s at a rotational speed of 700 RPM. Assuming the air enters the impeller in the radial direction and exits at an angle of 50° from the radial direction, determine the minimum power consumption of the blower, take the density of the air to be 1.25 kg/m3 (ans 152W)arrow_forwardWater enters a two-armed lawn sprinkler along a vertical axis at a rate of 60 L/s and leaves the sprinkler nozzles as 2-cm diameter jets at a 30°angle, determine the rotational speed in RPM of the sprinkler.arrow_forwardDetermine the horizontal force (F) required to hold the plate in position. The water flow rate in the pipe is 0.6 m/s, points A and B at the same level, the pressure at point A is 75kPa, the water unit weight is 9810 N/m3, water density is 1000 kg/m³, and g= 9.81 m/s2. 1 Plate В A. -F РА Determine the velocity in the pipe, V (m/s). Determine the force required to hold the plate in position, F (in kPa). P.arrow_forward
- Water enters vertically and steadily at a rate of 35 L/s into the sprinkler shown, with unequal arms and unequal discharge areas. The smaller jet has a discharge area of 3 cm2 and a normal distance of 50 cm from the axis of rotation. The larger jet has a discharge area of 5 cm2 and a normal distance of 35 cm from the axis of rotation. Disregarding any frictional effects, determine (a) the rotational speed of the sprinkler in rpm and (b) the torque required to prevent the sprinkler from rotating.arrow_forwardGardeners are holding a nozzle at the end of a hose to wash way mud from landscaping. The nozzle exit has a diameter of 10cm and the water is flowing at a rate of 12 m3/min. In this situation, what is the average water exit velocity and what is the horizontal resistance force required to hold the nozzle? Any help would be greatarrow_forwardA centrifugal pump with a 30 cm diameter impeller requires a power input of 45 kW when the flow rate is 12 kL/min against an 18 m head. The impeller is changed to one with a 25 cm diameter. Determine The expected flow rate. Actual head. (i) (ii) (iii) Input power if the pump speed remains the same.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY