
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Topic Video
Question
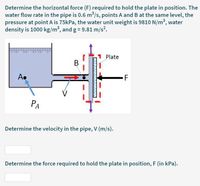
Transcribed Image Text:Determine the horizontal force (F) required to hold the plate in position. The
water flow rate in the pipe is 0.6 m/s, points A and B at the same level, the
pressure at point A is 75kPa, the water unit weight is 9810 N/m3, water
density is 1000 kg/m³, and g= 9.81 m/s2.
1 Plate
В
A.
-F
РА
Determine the velocity in the pipe, V (m/s).
Determine the force required to hold the plate in position, F (in kPa).
P.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 1 m/s 4 m/s 30 m 15 m B Fan 30 m 15 m 60 m 3 m/s For the duct system shown, determine the size of ducts AB, BC and CD using equal friction method . Assume friction rate of 0.09 mm of water per m length of duct. Use following correlation for friction rate Др, = 2.454 x10 mm of water / m where Q is in m/ s andD is in m. -3 1.623 Q 4.832 /Darrow_forwardThe diameter of the pipe at point B is larger than at point A. - At which point is the water speed greater? Point B Point A It is the same at both points. Cannot be determined from the information given.arrow_forward(3) The cart shown below is restrained from moving by a cable connected to a fixed wall. The tank has a circular cross section of diameter D and the flow exit has a circular cross section of diameter Do. Do not assume that H(t) is constant. The fluid has density p and the exit is open to the atmosphere. Wall H D- Do Cable Vo (1) Determine H(t) and the exit velocity Vo(t). (2) Determine the tension in the cable as a function of time Your answers should be in terms of given parameters (D, Do, p, g) о,arrow_forward
- 7. A siphon draws oil (sg=0.86) as shown in the figure. Determine the volume flow rate of oil from the tank, m3/s. * 3.0 m Oil (sg = 0.86) 10.0 m 50-mm - inside diameter 25-mm diameterarrow_forwardacia inicio ys If the plate shown is inclined at an angle as shown, what are the forces F, and F, necessary to maintain its position? The flow is frictionless, + v = 100 fps in=2 slugs/s 7722 l ve ارد ) -Frarrow_forwardPlease explain on how to get the theta, Qin and Qout. It should be theta = 54.2461 deg Q in = 0.0382 m3/s Q out = 0.0191 m3/s my professor said. but I don't have solution. used 9.807m/s² not 9.81.. thank youarrow_forward
- Oil flows through the 100-mm-diameter pipe with a velocity of 8 m/s (Figure 1). The flow occurs in the horizontal plane. Take p = 900 kg/m³. ▼ Part A If the pressure in the pipe at A and B is assumed to be 90 kPa, determine the component of force the flow exerts on the elbow. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. ▾ View Available Hint(s) ▾ Hint 1. How to determine the component of force the flow exerts on the elbow Build a free body diagram of the control volume containing oil within the pipe and elbow between cross-sections at A and B. Then using the linear momentum equation determine the component of the force the flow exerts on the elbow. F₂ = Part B HÅ Submit Previous Answers Request Answer Value Fy = X Incorrect; Try Again; 4 attempts remaining Submit Units If the pressure in the pipe at A and B is assumed to be 90 kPa, determine they component of force the flow exerts on the elbow. Express your answer to three significant figures and…arrow_forwardWater flows out of the reducing elbow at 1.0 ft3/s(Figure 1). The pipe and elbow and the water within have a total weight of 250 lb. The water is discharged to the atmosphere at B. 0.25 ft 60° 3 ft 0.5 ft a) Determine the horizontal component of force that are necessary to hold the elbow in place at A. b) Determine the vertical component of force that are necessary to hold the elbow in place at A.arrow_forwardThe turbine at C draws a power P kW. If the intake B has a diameter of de mm. The pressure dg(mm) dĄ(mm) at the intake B is Ps kPa and the velocity of the water (density = 1kg/L) at that point is v (m/s). The frictional losses between A and B are At neglected, and the exit A has a diameter of da B1 mm. Consider the data in the table to M = last two digits of your student ID P (kW) = 0.5M + 68.5 da(mm) = M + 150 dp (mm) %3D М + 400 PB (kPa) = M + 380 v (m/s) = 0.1M + 4 a- Calculate the velocity at the exit A b- Calculate the discharge at the exit A c- Calculate the turbine head d- Calculate the pressure at A m=13arrow_forward
- The pump shown in the figure below produces a steady flow of 12 gal/s through the nozzle. Determine the nozzle exit diameter, D2, if the exit velocity is to be V₂ = 109 ft/s. D₂ = Pump i Section (1) Section (2) V₂ inarrow_forward3 - Oil flows through the horizontal pipe under a pressure of 400 kPa and a velocity of 2.5 m/s at A. Determine the pressure in the pipe at B if the pressure at C is 150 kPa.Disregard any difference in elevation. Consider the specific mass of the oil equal to 880 kg/m3.arrow_forwardA high-pressure washing system's pump supplies 1 gallon of water persecond at 100 psi pressure. The nozzle should be designed so that the static pressureof the water as it exits the nozzle is the same as the atmospheric pressure. If theinside diameter of the hose leading from the pump to the nozzle is 2 in., whatshould the diameter of the nozzle exit be? What will be the velocity of the waterat the exit of the nozzle?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY