
Concept explainers
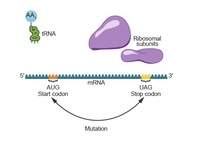
A plant geneticist was examining the inversion mutation XI 501 in barley where a segment of DNA is removed, flipped, and reinserted in reverse order. The original protein functioned to assist in the separation of daughter cells during meiosis. A model of the initiation of normal protein translation is shown in the diagram. The action of the mutation is shown in orange.
Using the model, which of the following predicts how the XI 501 mutation affects the protein produced?
A - It creates a protein with the order of amino acids reversed, causing the protein to fold backward, reducing pollen functionality.
B - It creates a nonsense protein that does not function in the cell, causing the cell to use energy to remove the proteins, reducing pollen fertility.
C - It creates a protein that terminates at the mutation, causing the pollen to carry more than one copy of the genetic material in each granule.
D - It creates a protein with half the amino acids correct and half reversed, reducing protein effectiveness and pollen viability.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

- What is the correct answer, and why?arrow_forward1. (a) By binding one L-tryptophan molecule/monomer, the trp repressor binds to DNA to sup- press synthesis of L-tryptophan in E. coli. Below is the amino acid sequence of the helix - reverse turn - helix region of the trp repressor that binds to DNA compared to the sequence of the corresponding DNA binding motif of the Prl protein. A diagram of the trp repressor dimer is also shown. Trp Prl Trp Prl 80 -Gly-Glu-Met-Ser-Gln-Arg-Glu-Leu-Lys-Asn-Glu-Leu-Gly-Ala-Gly-Ile- -Ser-Glu-Glu-Ala-Lys-Glu-Glu-Leu-Ala-Lys-Lys-Cys-Gly-Ile-Thr-Val- trp helix 5 70 trp helix 4 Prl helix 80 Prl helix Ala-Thr-Ile-Thr-Arg-Gly-Ser-Asn-Ser-Leu-Lys-Ala-Ala- Ser-Gln-Val-Ser-Asn-Trp-Phe-Gly-Asn-Lys-Arg-Ile-Arg- reverse turn 90 Comparing the two protein sequences above, identify all amino acid pairs that differ in electrostatic charge due to proton dissociable groups (assume pH 7). Indicate the charge of both residues for each such pair. (b) Circle the pair of residues for which the electrostatic charge due to…arrow_forwardIf the following nucleotide sequence, CTC/TGT/AAG/ACC/TTT experienced a mutation resulting in the deletion of the second cytosine in the first DNA triplet so the sequence is now CT_/TGT/AAG/ACC/TTT, what would be the amino acid sequence created from this mutated DNA strand? Table of mRNA codons UUA, UUG = leucine AGG, AGA = arginine %3D CAU, CAC = histidine GUU, GÜC, GUA = valine GAA. GAG=glutamic acid GCU, GUA, GUG = alanine GAU, GAC = asparagine GGU, GGC, GGA = glycine UCA, UCU =serine CGU, CGC, CGA = argininearrow_forward
- a. How can a single eukaryotic gene give rise to several different types of mRNA molecules?b. Excluding the possible rare polycistronic message,how can a single mRNA molecule in a eukaryoticcell produce proteins with different activities?arrow_forwardConsider the mechanism of the enzyme RNase: What would happen to the Km (i.e., would it increase, decrease, or stay the same) if the his12 was mutated to a lysine? Explain. What would happen to the Kcat (i.e., would it increase, decrease, or stay the same) if the his12 was mutated to a valine? Explain.arrow_forwardYou are studying a gene containing three exons (exon 1 = 66 nucleotides , exon 2 = 99 nucleotides , and exon 3 = 333 nucleotides ) that produces a primary RNA transcript 748 nucleotides long . Gel electrophoresis analysis shows different size mature transcripts are produced in three different cell types . The sizes of the mature transcripts are the following : 1. Neuronal nalcells = 498 nucleotides 2. Muscle cells = 600 nucleotides 3. Liver cells = 399nu nucleotides Primary RNA ranscript = 748 nucleotides a. Name the strategy that allows the same gene to produce different mature transcripts in different tissues . b. Describe the ways (or combinations of exons /introns ) used to produce each one ofthe three mature transcripts . Label the each mature transcripts and include its length . c. Indicate the length of the polypeptide encoded by each mature transcriptarrow_forward
- A small section of Saccharomyces cerevisiae gene has the amino acid sequence valine, histidine, cysteine, and lysine. A mutation in the above section of the amino acid sequence resulted in the substitution of amino acid histidine with amino acid glutamine. The mutation in the antisense strand DNA of Saccharomyces cerevisiae gene described above involves a. the substitution of thymine base from GTG b. the deletion of second cytosine base from CAC c. the deletion of second guanine base from GTG d. the substitution of second cytosine base from CACarrow_forwardGiven the following diagram of how protein AWESOME1 binds to it's target DNA, describe the potential effects of each of the 5 mutations shown below. The wild-type sequence of a helix #1 is also shown in the blue box, and all the mutations are in helix #1 (see numbers for identifying particular residues). a helix #1 R(1)-V-I-L-Y-F-W-I-M-Y-F-S-H-Y-W-R(16) #1 Predict the consequence of the following mutations: 1) Arg(1) to Glu 2) Arg(1) to Ala 3) Phe(6) to lle 4) Trp(7) to Phe 5) Met(9) to Pro inarrow_forward
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education





