
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780134580999
Author: Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
thumb_up100%
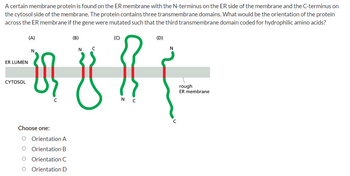
Transcribed Image Text:A certain membrane protein is found on the ER membrane with the N-terminus on the ER side of the membrane and the C-terminus on
the cytosol side of the membrane. The protein contains three transmembrane domains. What would be the orientation of the protein
across the ER membrane if the gene were mutated such that the third transmembrane domain coded for hydrophilic amino acids?
(B)
(D)
N
с
N
N
=481 (-
rough
ER membrane
C
ER LUMEN
CYTOSOL
(A)
Choose one:
Orientation A
Orientation B
Orientation C
O Orientation D
(C)
N C
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Consider the peptide Asp-Lys-Phe-Glu-Asn-Tyr-Gln-Val-Cys. In a single beaker, you treat this peptide with 2 proteases. One protease cleaves at the N-terminus of aromatic R groups and the other cleaves at the C-terminus of polar, non-ionizable R groups. Following the enzymatic digestion, you want to separate your peptide fragments so that you can identify them. You choose to separate the fragments using an anion exchange column. Beginning at pH=6 you apply your peptide fragments to the column and you gradually decrease the pH of the column stopping the separation when the pH of the column equals 4. Omitting chemical structures, write the amino acid sequence of the peptide fragments that are produced from this digest. Write the order that these fragments will elute from the column (if at all). (Relevant pKa values are: 2.1, 3.8, 4.3, 8.3, 9.6, 10.1, and 10.5)arrow_forwardIn Figure 9-12, is the terminal amino acid emerging fromthe ribosome encoded by the 5′or 3′end of the mRNA?arrow_forwardTransport of histidine into a bacterial cell was measured at several different histidine concentrations, see table below. Based on these data, is histidine uptake facilitated by a carrier or channel protein? a b Histidine (uM) 2.5 7 16 31 72 с Select an answer and submit. For keyboard navigation, use the up/down arrow keys to select an answer. A carrier protein because it becomes saturated. A carrier protein because it does not become saturated. A channel protein because it becomes saturated. Transport (uM/min) d A channel protein because it does not become saturated. 42.5 119 240 490 1000 X Your answerarrow_forward
- EF-G is a macromolecular mimic of EF-tu. It's role in translation is to To cause the large subunit of the ribosome to disassociate with the small subunit of the ribosome Bind to the vacant A-site subsequent to peptide bond formation and resolve the hybrid state of the ribosome To recruit the signal recognition particle (SRP) to the ribosome and to facilitate synthesis of membrane proteins O To cause the large subunit to associate with the small subunit of the ribosome Shuttle an amino-acylated tRNA to the A site to initiate the peptidyl transfer reactionarrow_forwardYou are studying a eukaryotic protein PKK in the lab. You fuse the DNA encoding GFP (green fluorescent protein) to the C terminus of the PKK gene. You also create the following GFP-PKK variants -GFP Wild- type: N- Signal sequence Transmembrane domain Kinase domain Variant 1: N- GFP Transmembrane domain Kinase domain Variant 2: N- -GFP Signal sequence Transmembrane domain Variant 3: N- -GFP Signal sequence Kinase domain Variant 4: N- -GFP Kinase domain If you examine wild-type PKK trafficking in a eukaryotic cell, which of the following are true? Select all that apply This fusion protein will be trafficked to the nucleus This fusion protein is a cell membrane protein This fusion protein will be trafficked to the Endoplasmic Reticulum This fusion protein is a nuclear proteinarrow_forwardTrypsin cleaves a polypeptide backbone at the C-terminal side of Arg or Lys residues, whereas chymotrypsin cleaves after aromatic residues. A polypeptide was treated with trypsin to generate a series of fragments of the following sequences: Gly-Gly-Ile-Arg Ser-Phe-Leu-Gly Trp-Ala-Ala-Pro-Lys Ala-Glu-Glu-Gly-Leu-Arg And the same polypeptide was treated with chymotrypsin to generate the following fragments: Leu-Gly Ala-Glu-Glu-Gly-Leu-Arg-Trp Ala-Ala-Pro-Lys-Gly-Gly-Ile-Arg-Ser-Phe Assemble the protein sequence.arrow_forward
- What would be the effect of a mutation that causes a poly(A)-binding protein to be nonfunctional?arrow_forwardWhich of the following mutations in the protein-coding region of a gene is more likely to lead to complete loss of function of the encoded protein: an insertion of six nucleotides or a deletion of two nucleotides? Briefly explain your answer.arrow_forwardGiven the following diagram of how protein AWESOME1 binds to it's target DNA, describe the potential effects of each of the 5 mutations shown below. The wild-type sequence of a helix #1 is also shown in the blue box, and all the mutations are in helix #1 (see numbers for identifying particular residues). a helix #1 R(1)-V-I-L-Y-F-W-I-M-Y-F-S-H-Y-W-R(16) #1 Predict the consequence of the following mutations: 1) Arg(1) to Glu 2) Arg(1) to Ala 3) Phe(6) to lle 4) Trp(7) to Phe 5) Met(9) to Pro inarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education

Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780134580999
Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:PEARSON

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781259398629
Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa Stouter
Publisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,

Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780815344322
Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter Walter
Publisher:W. W. Norton & Company

Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781260159363
Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, Cynthia
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.

Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9781260231700
Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael Windelspecht
Publisher:McGraw Hill Education