
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
A large share of the world supply of diamonds comes from Russia and South Africa. Suppose that the marginal cost of mining diamonds is constant at $3,000 per diamond, and the demand for diamonds is described by the following schedule: see attached
If there were many suppliers of diamonds, the price would be $________per diamond and the quantity sold would be __________diamonds.
If there were only one supplier of diamonds, the price would be _________per diamond and the quantity sold would be_________diamonds.
Suppose Russia and South Africa form a cartel.
In this case, the price would be _________________per diamond and the total quantity sold would be __________
diamonds. If the countries split the market evenly, South Africa would produce_____________diamonds and earn a profit of.
diamonds. If the countries split the market evenly, South Africa would produce_____________diamonds and earn a profit of.
If South Africa increased its production by 1,000 diamonds while Russia stuck to the cartel agreement, South Africa's profit would _increase or decrease________ to.
Why are cartel agreements often not successful? Choose one below:
a. One party has an incentive to cheat to make more profit.
b. Different firms experience different costs.
c. All parties would make more money if everyone increased production.
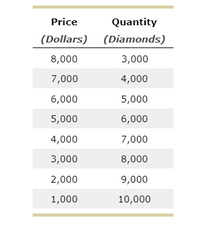
Transcribed Image Text:Price
Quantity
(Dollars) (Diamonds)
8,000
3,000
7,000
4,000
6,000
5,000
5,000
6,000
4,000
7,000
3,000
8,000
2,000
9,000
1,000
10,000
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Assume the following equations describe the conditions for an unregulated monoply: Qd = q = 160,000 - 2,500P TC = 400,000 +22q + 0.0001q2 where Qd is the quantity demanded for both the market and the firm, P is the commodity's price in dollars, TC is total cost in dollars, and q is the quantity of output produced by the firm. Based upon the above equations, answer the following questions: a. What is the firm's equation for total revenue expressed as a function of quantity? b. What is the firm's equation for marginal revenue expressed as a function of quantity? What is the firm's equation for marginal cost expressed as a function of quantity? c. What is the firm's profit-maximizing quantity of output? d. What price will the firm charge for the commodity? Assume the total cost function and the market demand remain unchanged. The equations are: Qd = q = 160,000 - 2,500P TC = 400,000 +22q + 0.0001q2 The monopolist now engages in first-degree price discrimination. e. What quantity of…arrow_forwardThe following graph plots the marginal cost (MC) curve, average total cost (ATC) curve, and average variable cost (AVC) curve for a firm operating in the competitive market for jumpsuits.arrow_forwardI need help with part barrow_forward
- Price ($) 40 36 32 28 24 226 20 16 12 8 4 0 4 8 12 16 20 24 28 32 36 40 Quantity per period a. If the firm wishes to maximize its total revenue, at what price should It sell its pots? 12 What is its total revenue? $ 216 b. Suppose that the firm were to increase its price by $4 from the price in (a). What will be the change in its total revenue? Give your answer as an absolute number. 56 What is the co-efficient for the price elasticity of demand between those two prices? Round your price answer to two decimal places. -2 Ⓡ c. Suppose that the firm were to decrease its price by $4 from the price in (a). What will be the change in its total revenue? Give your answer as an absolute number. 40 What is the co-efficient for price elasticity of demand between those two prices? Round your price answer to two decimal places. -0.54arrow_forwardUsing the data in the graph below, answer the following questions. 17 MC 16 15 ATC 14 13 12 D 11 MR 10 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 Output Price ($)arrow_forwardAssume that you are an economic consultant. The firm that hired you has provided the information below. The firm is a price searcher and wants to maximize its profit (or minimize its loss). InformationPrice: $4Elasticity of demand at price of $4 is Ed=-1Quantity of output: 2000Total variable cost: 4000Average fixed cost: 1Marginal cost is constant and equal to the average variable cost: MC=ACV=2. Which of the following answers correctly describes this case? a) The firm is maximizing profits at the current price of $4.b) The firm should increase price and reduce quantity produced.c) None of the other answersd) Firm should reduce price and increase quantity produced.arrow_forward
- D9) Suppose that the demand for rough laborers is LD = 100 – 10W, where W = the wage in dollars per hour and L = the number of workers. If immigration increases the number of rough laborers hired from 50 to 60, by how much will the short-run profits of employers in this market change?arrow_forwardCOURSE: MICROECONOMICS - Cournot Model:In the market for a given good there are only 2 firms satisfying the demand, and their respective total cost functions respond to the form: CTi = 10Qi + 5 and the demand is estimated to be: P = 31 - QIf the decision variable for both firms is that the quantity they will produce and realize will be decided simultaneously it is asked to:(a) calculate the profit and reaction function of each firmb) graph market equilibriumc) calculate the profits that both companies will obtain in equilibriumarrow_forwardIn reference to the chart, complete the calculations for Total Revenue by determining how many customers will purchase at each of the segment prices.arrow_forward
- Suppose that the world price of oil is roughly $90.00 per barrel and that the world demand and total world supply of oil equal 34 billion barrels per year (bb/yr), with a competitive supply of 20 bb/yr and 14 bb/yr from OPEC. Statistical studies have shown that the long-run price elasticity of demand for oil is -0.40, and the long-run competitive price elasticity of supply is 0.40. Using this information, derive linear demand and competitive supply curves for oil. Let the demand curve be of the general form Q=a-bP and the competitive supply curve be of the general form Q=c+dP, where a, b, c, and d are constants. The equation for the long-run demand curve is A.Q=47.50-0.15P. B.Q=13.50-47.50P. C.Q=47.50-P. D.Q=47.50+0.15P. E.Q=13.50-0.15P.arrow_forwardOn the graph input tool, change the number found in the Quantity Demanded field to determine the prices that correspond to the production of 0, 6, 12, 15, 18, 24, and 30 units of output. Calculate the total revenue for each of these production levels. Then, on the following graph, use the green points (triangle symbol) to plot the results. Calculate the total revenue if the firm produces 6 versus 5 units. Then, calculate the marginal revenue of the sixth unit produced. The marginal revenue of the sixth unit produced is________. Calculate the total revenue if the firm produces 12 versus 11 units. Then, calculate the marginal revenue of the 12th unit produced. The marginal revenue of the 12th unit produced is_________.arrow_forwardSuppose the government regulates the price of a good to be no lower than some minimum level. Moreover, suppose firms misinterpret the regulated price as a signal to produce more output. Using the graph to the right, compute this fictional industry's net gain or loss resulting from this policy. Price ($) As a whole, firms in this industry will experience a net of $ because of this policy. (Enter your response rour nearest whole number.) loss 4.50 3.50 gain Q ☑ S Ps = $5.50 D :100 140 180 Quantityarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education