
Concept explainers
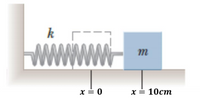
A block of mass m = 1 kg is attached a spring of force constant k = 500 N/m as shown in the figure below.
The block is pulled to a position x = 10 cm to the right of equilibrium and released from rest. The horizontal
surface is frictionless.
(a) What’s the period of block’s oscillation?
(b) Find the speed of the block as it passes through the equilibrium point x = 0.
(c) Please represent block’s motion with the displacement vs. time function x(t) and draw the motion
graph x(t) for at least one periodic cycle. Note, please mark the amplitude and period in the motion
graph. Assume the clock starts from when the block is just released.
(d) Please find out the block’s velocity and acceleration at t = 0.14s.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

- Chapter 15, Problem 051 GO In the figure, a stick of length L = 1.9 m oscillates as a physical pendulum. (a) What value of distance x between the stick's center of mass and its pivot point o gives the least period? (b) What is that least period? L/2 (a) Number Units (b) Number Units udy Click if you would like to Show Work for this question: Open Show Workarrow_forwardThe potential energy of an object attached to a spring is 2.50 J at a location where the kinetic energy is 1.40 J. If the amplitude ? of the simple harmonic motion is 22.0 cm, calculate the spring constant ? and the magnitude of the largest force ?spring, max that the object experiences.arrow_forwardThe potential energy of an object attached to a spring is 2.60 J at a location where the kinetic energy is 1.30 J. If the amplitude ?of the simple harmonic motion is 19.0 cm, calculate the spring constant ? and the magnitude of the largest force ?spring, max that the object experiences.arrow_forward
- A horizontal spring attached to a wall has a force constant of 720 N/m. A block of mass 1.90 kg is attached to the spring and oscillates freely on a horizontal, frictionless surface as in the figure below. The initial goal of this problem is to find the velocity at the equilibrium point after the block is released. (a) What objects constitute the system, and through what forces do they interact? (b) What are the two points of interest? (c) Find the energy stored in the spring when the mass is stretched 6.40 cm from equilibrium and again when the mass passes through equilibrium after being released from rest. x = 6.40 _____ J x = 0 ______J (e) Substitute to obtain a numerical value. (f) What is the speed at the halfway point?arrow_forwardFind the mechanical energy of a block-spring system having a spring constant of 1.3 N/cm and an oscillation amplitude of 2.5 cm. Don't forget to convert units.arrow_forwardA light elastic string, of natural length 0.8 m and modulus of elasticity 35-4 N, has one end A attached to a fixed point and the other end B attached to a particle P of mass 3 kg. Initially P is held at rest at A. It is then released and allowed to fall. Calculate the speed of P when the length of the string is 1-2 m.arrow_forward
- A simple pendulum with a bob with a mass of m and a string with a length of L oscillates with a large amplitude in a vertical plane. The maximum speed it attains during an oscillation is v,. The string makes an angle 0, with the vertical at some instant during the course of motion. Use the principle of conservation of energy to find an expression for the magnitude of the tension force on the bob in terms of known quantities and constant.arrow_forwardThe figure below shows a graph of v, versus t for the motion of a motorcyclist as he starts from rest and moves along the road in a straight line. v. (m/s) 10 8. 6 2 t (s) 12 4. 8 10 (a) Find the average acceleration for the time interval t = 0 to t = 12.0 s. 0.3 V m/s2 (b) Estimate the time at which the acceleration has its greatest positive value. 3 What is the value of the acceleration at that instant? 0.2 Your response is off by a multiple of ten. m/s2 (c) When is the acceleration zero? Acceleration is zero whent = 0 The correct answer is not zero. s and when t > 0 The correct answer is not zero. s.arrow_forwardA cart of mass 0.72 kg is attached to one end of of a spring and placed on a low-friction track, inclined at an angle of 56.0 degrees with respect to the horizontal. The cart is found to be in equilibrium when the spring is stretched to a total length of 44.8 cm. Given that the rest length for the spring is 12.8 cm, what is the spring constant for the spring?arrow_forward
- The potential energy of an object attached to a spring is 2.70 J at a location where the kinetic energy is 1.60 J. If the amplitude ? of the simple harmonic motion is 17.0 cm, calculate the spring constant ? and the magnitude of the largest force ? spring,max that the object experiences.arrow_forwardWhen a 20 N can is hung from the bottom of a vertical spring, it causes the spring to stretch 20 cm. (a) What is the spring constant? (b) This spring is now placed horizontally on a frictionless table. One end of it is held fixed, and the other end is attached to a 5.0 N can. The can is then moved (stretching the spring) and released from rest. What is the period of the resulting oscillation?arrow_forward
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON





