
Concept explainers
-
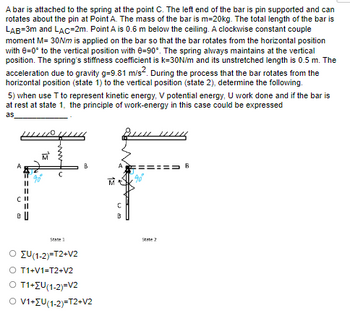
A bar is attached to the spring at the point C. The left end of the bar is pin supported and can rotates about the pin at Point A. The mass of the bar is m=20kg. The total length of the bar is LAB=3m and LAC=2m. Point A is 0.6 m below the ceiling. A clockwise constant couple moment M= 30Nm is applied on the bar so that the bar rotates from the horizontal position with θ=0° to the vertical position with θ=90°. The spring always maintains at the vertical position. The spring’s stiffness coefficient is k=30N/m and its unstretched length is 0.5 m. The acceleration due to gravity g=9.81 m/s2. During the process that the bar rotates from the horizontal position (state 1) to the vertical position (state 2), determine the following.
5) when use T to represent kinetic energy, V potential energy, U work done and if the bar is at rest at state 1, the principle of work-energy in this case could be expressed as____________ .
∑U(1-2)=T2+V2
T1+V1=T2+V2
T1+∑U(1-2)=V2
V1+∑U(1-2)=T2+V2
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

- A bar is attached to the spring at the point C. The left end of the bar is pin supported and can rotates about the pin at Point A. The mass of the bar is m=20kg. The total length of the bar is LAB=3m and LAC=2m. Point A is 0.6 m below the ceiling. A clockwise constant couple moment M= 30Nm is applied on the bar so that the bar rotates from the horizontal position with θ=0° to the vertical position with θ=90°. The spring always maintains at the vertical position. The spring’s stiffness coefficient is k=30N/m and its unstretched length is 0.5 m. The acceleration due to gravity g=9.81 m/s2. During the process that the bar rotates from the horizontal position to the vertical position, determine the following. (3) the potential energy of the spring when AB is vertical__________(J)arrow_forwardA bar is attached to the spring at the point C. The left end of the bar is pin supported and can rotates about the pin at Point A. The mass of the bar is m=20kg. The total length of the bar is LAB=3m and LAC=2m. Point A is 0.6 m below the ceiling. A clockwise constant couple moment M= 30Nm is applied on the bar so that the bar rotates from the horizontal position with θ=0° to the vertical position with θ=90°. The spring always maintains at the vertical position. The spring’s stiffness coefficient is k=30N/m and its unstretched length is 0.5 m. The acceleration due to gravity g=9.81 m/s2. During the process that the bar rotates from the horizontal position to the vertical position, determine the following. (4) the work done by the reaction force of the pin.____________ (J)arrow_forwardA bar is attached to the spring at the point C. The left end of the bar is pin supported and can rotates about the pin at Point A. The mass of the bar is m=20kg. The total length of the bar is LAB=3m and LAC=2m. Point A is 0.6 m below the ceiling. A clockwise constant couple moment M= 30Nm is applied on the bar so that the bar rotates from the horizontal position with θ=0° to the vertical position with θ=90°. The spring always maintains at the vertical position. The spring’s stiffness coefficient is k=30N/m and its unstretched length is 0.5 m. The acceleration due to gravity g=9.81 m/s2. During the process that the bar rotates from the horizontal position to the vertical position, determine the following. (1) if datum is set as when θ=90°, the gravational potential energy of the bar when AB is horizontal will be ____________(J) (two decimal places)arrow_forward
- A bar is attached to the spring at the point C. The left end of the bar is pin supported and can rotates about the pin at Point A. The mass of the bar is m=20kg. The total length of the bar is LAB=3m and LAC=2m. Point A is 0.6 m below the ceiling. A clockwise constant couple moment M= 30Nm is applied on the bar so that the bar rotates from the horizontal position with θ=0° to the vertical position with θ=90°. The spring always maintains at the vertical position. The spring’s stiffness coefficient is k=30N/m and its unstretched length is 0.5 m. The acceleration due to gravity g=9.81 m/s2. During the process that the bar rotates from the horizontal position (state 1) to the vertical position (state 2), determine the following. 5) when use T to represent kinetic energy, V potential energy, U work done and if the bar is at rest at state 1, the principle of work-energy in this case could be expressed as____________ . V1+∑U(1-2)=T2+V2 T1+V1=T2+V2…arrow_forwardA bar is attached to the spring at the point C. The left end of the bar is pin supported and can rotates about the pin at Point A. The mass of the bar is m=20kg. The total length of the bar is LAB=3m and LAC=2m. Point A is 0.6 m below the ceiling. A clockwise constant couple moment M= 30Nm is applied on the bar so that the bar rotates from the horizontal position with θ=0° to the vertical position with θ=90°. The spring always maintains at the vertical position. The spring’s stiffness coefficient is k=30N/m and its unstretched length is 0.5 m. The acceleration due to gravity g=9.81 m/s2. During the process that the bar rotates from the horizontal position to the vertical position, determine the following. (2) ) the work done by the couple moment. __________(J) (two decimal places)arrow_forwardA bar is attached to the spring at the point C. The left end of the bar is pin supported and can rotates about the pin at Point A. The mass of the bar is m=20kg. The total length of the bar is LAB=3m and LAC=2m. Point A is 0.6 m below the ceiling. A clockwise constant couple moment M= 30Nm is applied on the bar so that the bar rotates from the horizontal position with θ=0° to the vertical position with θ=90°. The spring always maintains at the vertical position. The spring’s stiffness coefficient is k=30N/m and its unstretched length is 0.5 m. The acceleration due to gravity g=9.81 m/s2. During the process that the bar rotates from the horizontal position to the vertical position, determine the following. (2) ) the work done by the couple moment. __________(J) (two decimal places)arrow_forward
- A bar is attached to the spring at the point C. The left end of the bar is pin supported and can rotates about the pin at Point A. The mass of the bar is m=20kg. The total length of the bar is LAB=3m and LAC=2m. Point A is 0.6 m below the ceiling. A clockwise constant couple moment M= 30Nm is applied on the bar so that the bar rotates from the horizontal position with θ=0° to the vertical position with θ=90°. The spring always maintains at the vertical position. The spring’s stiffness coefficient is k=30N/m and its unstretched length is 0.5 m. The acceleration due to gravity g=9.81 m/s2. During the process that the bar rotates from the horizontal position to the vertical position, determine the following. (1) if datum is set as when θ=90°, the gravational potential energy of the bar when AB is horizontal will be ____________(J) (two decimal places)arrow_forwardA bar is attached to the spring at the point C. The left end of the bar is pin supported and can rotates about the pin at Point A. The mass of the bar is m=20kg. The total length of the bar is LAB=3m and LAC=2m. Point A is 0.6 m below the ceiling. A clockwise constant couple moment M= 30Nm is applied on the bar so that the bar rotates from the horizontal position with θ=0° to the vertical position with θ=90°. The spring always maintains at the vertical position. The spring’s stiffness coefficient is k=30N/m and its unstretched length is 0.5 m. The acceleration due to gravity g=9.81 m/s2. During the process that the bar rotates from the horizontal position to the vertical position, determine the following. (4) the work done by the reaction force of the pin.____________ (J)arrow_forwardhelp me, please, is mecanica vectorialarrow_forward
- Problem Statement Based on Problem 4-151 from the textbook. The pipe assembly is subjected to the action of a wrench at B and a couple at A. Simplify this system to a resultant wrench and specify the locaiton of the wrench along the axis of pipe CD, measured from point C. F = 42.8 N 0.6 m X Z C 0.8 m (60k) N 0.25 m {-401) N B 0.25 m - Fi 0.3 m 0.7 m V-60k) N A 0.3 m Fi 0.5 m D yarrow_forwardA uniform rod of length L mass M which is attached at one end to a frictionless pivot and is free to rotate about the pivot in the vertical plane as shown in figure. Find the location on the rod at which you can place 1 kuruş that will stay in contact as the rod is released. -L- d=? AURE Pivot Mgarrow_forwardThe linkage shown is used in a vehicle suspension system. Find the forces indicated below when a static force of F = 1000 lb is applied to the tire at point C at an angle of 0 = 17° as shown. Assume the connection of the wheel to member AB is rigid. 1 h₁ K: LOFF 0 W₁ h₂ h3 h4 h5 B W₁₂ AXHIMAL W4 hs: h₂ cc i❀O BY NC SA 2013 Michael Swanbom W3 - W₁ Values for dimensions on the figure are given in the following table. Note the figure may not be to scale. Variable Value Variable Value h₁ 6.6 in W1 7.5 in 16.6 in W2 4.6 in 14.6 in W3 8.3 in 10.2 in W4 6.2 in 5.2 in W5 9.7 inarrow_forward
 Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
