
Concept explainers
-
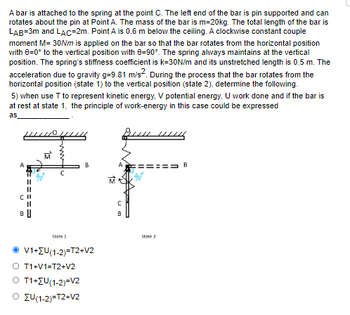
A bar is attached to the spring at the point C. The left end of the bar is pin supported and can rotates about the pin at Point A. The mass of the bar is m=20kg. The total length of the bar is LAB=3m and LAC=2m. Point A is 0.6 m below the ceiling. A clockwise constant couple moment M= 30Nm is applied on the bar so that the bar rotates from the horizontal position with θ=0° to the vertical position with θ=90°. The spring always maintains at the vertical position. The spring’s stiffness coefficient is k=30N/m and its unstretched length is 0.5 m. The acceleration due to gravity g=9.81 m/s2. During the process that the bar rotates from the horizontal position (state 1) to the vertical position (state 2), determine the following.
5) when use T to represent kinetic energy, V potential energy, U work done and if the bar is at rest at state 1, the principle of work-energy in this case could be expressed as____________ .
V1+∑U(1-2)=T2+V2
T1+V1=T2+V2
T1+∑U(1-2)=V2
∑U(1-2)=T2+V2
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

- I don't know how to even approach this problem can you help me out with it please?arrow_forwardA 40-kg disk shown is pin supported at its center. It starts from the rest and rotates to attain an angular velocity of 2 rad/s. The disk is acted upon by a constant couple moment M = 10 N.m clockwise. The spring is originally unstretched and its cord wraps around the rim of the disk. 0.2m ww Ol = a) (10 points) Find the kinetic energy of the disk. b) (30 points) Determine the angle through which the disk rotatesarrow_forwardProblem Statement Based on Problem 7-42 from the textbook. Determine the x, y, z components of force and moment at point C in the pipe assembly. Neglect the weight of the pipe. F1 (lbs): i=-22.0 i=_80.0 F2(lbs): k=-5.0 M(lbs*ft): k=-31.0 -1.5 ft 2 ft- 3 ftarrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





