
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
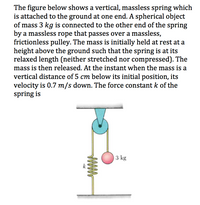
Transcribed Image Text:The figure below shows a vertical, massless spring which
is attached to the ground at one end. A spherical object
of mass 3 kg is connected to the other end of the spring
by a massless rope that passes over a massless,
frictionless pulley. The mass is initially held at rest at a
height above the ground such that the spring is at its
relaxed length (neither stretched nor compressed). The
mass is then released. At the instant when the mass is a
vertical distance of 5 cm below its initial position, its
velocity is 0.7 m/s down. The force constant k of the
spring is
3 kg
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A simple pendulum is suspended from the ceiling by means of a string and has a length of 1.56 m long. Suppose you start with the pendulum hanging vertically, at rest. You then give it a push so that it starts swinging with a speed of 1.73 m/s. What maximum angle (in degrees) will it reach, with respect to the vertical, before falling back down? 38.3 degrees 31.9 degrees 25.5 degrees 20.4 degreesarrow_forwardA 0.20-kg mass is attached to a string and then released from rest, swinging in an arc as a pendulum. At the bottom of it swing, where it is 0.80 m above the floor, the string is cut and the mass becomes a projectile. It stricks the floor 0.56 meters (horizontally) from the point it was cut. From what height was the mass originally released?arrow_forwardA block of mass mA = 20kg on an inclined plane and a bucket of mass mbucket = 14kg are attached to the ends of a massless string passing through a massless pulley as shown in the figure below. The inclined plane makes an angle of 0 = 37° with the horizontal and the coefficients of kinetic and static friction are μ = 0.2 and μ = 0.5. The system is initially at rest and a student starts to fill the bucket with balls, each of whose mass is 100 grams, one at a time until the system starts to move. Determine the number of balls the student placed in the bucket. Take g = 9.80m/s² and please note that the number balls must be an integer! Answer: MA mbucketarrow_forward
- A 0.28 kg mass is held against a compressed spring with a spring constant of 2,446 N/m. The mass is initially at rest upon a horizontal surface and the spring force is directed parallel to the plane of the surface. If the coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.716, with what speed does the mass leave contact with the spring if the spring is initially compressed by 0.068 m?arrow_forwardAn inclined plane of angle 0 20.0° has a spring of force constant k = 525 N/m fastened securely at the bottom so that the spring is parallel to the surface as shown in the figure below. A block of mass m = 2.61 kg is placed on the plane at a distance d 0.315 m from the spring. From this position, the block is projected downward toward the spring with speed v = 0.750 m/s. By what distance is the spring compressed when the block momentarily comes to rest? Enter a number. differs from the correct answer by more than 10%. Double check your calculations. m marrow_forwardA simple pendulum is made from a 0.666-m-long string and a small ball attached to its free end. After the ball is released pulled to one side through a small angle and then released from rest. After the ball is released, how much time elapses before it attains its greatest speed?arrow_forward
- Hanging Mass: A block of mass 14.1 kg is connected to a light cord of length 351.3 cm and a spring with an equilibrium length of 33.4 cm. The block hangs motionless as shown in the figure. The spring has a spring constant of 1799 N/ m. As the block hangs in equilibrium, the spring is horizontal and the cord makes an angle of 24 ° with respect to vertical. T k M (a) What is the tension in the cord? (b) How far is the spring stretched from its equilibrium length?arrow_forwardA block of mass m = 2.00 kg situated on a rough incline at an angle of 8 = 37.0° is connected to a spring of negligible mass having a spring constant of 100 N/m (see the figure below). The pulley is frictionelss. The block is released from rest when the spring is unstretched. The block moves 10.0 cm down the incline before coming to rest. Find the coefficient of kinetic friction between block and incline. k = 100 N/m www 8 marrow_forwardThe system is released from rest with no slack in the cable and with the spring unstretched. Determine the distances traveled by the 4.5-kg cart before it comes to rest (a) if m approaches zero and (b) if m= 2.8 kg. Assume no mechanical interference and no friction. The distances is positive if up the incline, negative if down. k = 160 N/m 4.5 kg m Answers: (a) m = 0, S= i (b) m = 2.8 kg, S= i 28° m marrow_forward
- An ideal spring is attached to the ceiling. While the spring is held at its relaxed length, a wooden block (M = 850 g) is attached to the bottom of the spring, and a ball of clay (m = 210 g) is pressed onto the bottom of the block so that they stick together. The block+clay are gently lowered through a distance of d = 2.7 cm and are then released, at which point they hang motionlessly from the bottom of the spring. After a few minutes have passed, the clay unsticks itself from the block and falls from rest to the ground. 1. What is the resulting period T of the block’s oscillation after the separation occurs? 2. As d approaches 0, what limit does T approach?arrow_forwardA 4.00 kg mass on a frictionless incline plane of angle 1 degrees is released and begins sliding down the incline. At the bottom of the incline is a spring (k=20 N/m) If the mass slides 0.10 m along the incline plane before it contacts the spring, how far is the spring compressed by the mass? (round to the nearest hundredth) How would the length of the spring compression change if there was friction between the incline plane and the mass? - The spring would be compressed the same length? -The spring would be compressed more? -The spring would be compressed less?arrow_forwardThe left end of a 1.200 m-long board is raised 0.300 m above the level table and a 0.800 kg cart (frictionless wheels) is placed on the ramp near the top (left) end. The cart is held in place by a compression spring that pushes into the cart horizontally. [ a) compute the ramp's distance along the horizontal. ] b) compute the spring Force magnitude. [c) compute the ramp Force magnitude. ] [ d) calculate the cart's acceleration if released from the spring. ] 2.450 N 7.840 N 2.024 N my answer is very different than any of these others 30.364 N 8.097 N 1.960 Narrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON