
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
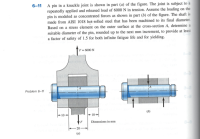
Transcribed Image Text:6-11 A pin in a knuckle joint is shown in part (a) of the figure. The joint is subject to a
repeatedly applied and released load of 6000 N in tension. Assume the loading on the
pin is modeled as concentrated forces as shown in part (b) of the figure. The shaft is
made from AISI 1018 họt-rolled steel that has been machined to its final diameter.
Based on a stress element on the outer surface at the cross-section A, determine a
suitable diameter of the pin, rounded up to the next mm increment, to provide at least
a factor of safety of 1.5 for both infinite fatigue life and for yielding.
F = 6000 N
Problem 6-11
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 2. Calculate the shear stress in a simple pin joint, assuming pin diameter of 10 mm and 3550N compressive load on the link. Draw a free body diagram (geometry & forces) Identify stress plane Calculate stress and write it (with appropriate units) in the outlined boxarrow_forwardIn the figure above, the shaft has a diameter of 50mm, and the diameter of pulleys C and D are given tobe 600 mm and 400 mm, respectively. ?1 = 1000 N, ?2 = 500 N and ?3 = 1500 N. But in addition tothe force on the pulleys, a compressive axial force of 100 kN is acting on both ends of the shaft. Theshaft is made from a brittle material with an ultimate tensile strength ??? that is half of its ultimatecompressive strength ???. The desired factor of safety is ? = 2 for the shaft.e. Determine the principal stresses corresponding to maximum bending and torsional shear stresses.Ignore transverse shear stresses due to bending.f. Use Maximum Normal Stress Theory and find the minimum required ??? and ???.g. Use Brittle Coulomb-Mohr Theory and find the minimum required ??? and ???.h. Use Modified Mohr Theory and find the minimum required ??? and ???.i. Use graphical method to check your answers in parts (a), (b) and (c).arrow_forwardQ-2 A portion of the stress–strain curve for a stainless steel alloy is shown in Figure Q-2. A 550 mm long bar is loaded in tension until it elongates 4.4 mm, and then the load is removed. (a) Determine the permanent set in the bar. (b) Determine the length of the unloaded bar. (c) If the bar is reloaded, determine the proportional limit. [Use the figure to make necessary drawings/markings to show your solution strategy!arrow_forward
- I need answer in 10 minutes please quicklyarrow_forwardFor the frame shown in Fig. 6-24a, draw the free-body diagrams of (a) the entire frame including the pulleys and cords, (b) the frame without the pulleys and cords, and (c) each of the pulleys. 3E Fx=0 +9 E fy=o 1. FIMD RXAS AT A$D Fing FoRLE componeAB 2. Ge Pits oF POLLEYS EM=0 Cx C By E Ay T. Ay AauLE OF RESOUTAT AT B, C &A 75 lb SKETCH RESULTALT (a) Fueo Manat AT BASE ア(y 7516 OF CULUneCE radius of the pulley at B linch Yadius of the Pulley at c a7s inch 75 lbs 7516 () Distance BE 7inch Distance EA 4.5 inch Distance AV : 3.sinch Ay 6) 7516 マへarrow_forwardBolts distributed about a bolt circle are often called upon to resist an external bending moment as shown in the figure. The external moment is 19 kip-in and the bolt circle has a diameter of 15 in. The neutral axis for bending is a diameter of the bolt circle. What needs to be determined is the most severe external load seen by a bolt in the assembly. M Neutral axis R NOTE: This is a multi-part question. Once an answer is submitted, you will be unable to return to this part. View the effect of the bolts as placing a line load around the bolt circle whose intensity FÅ, in pounds per inch, varies linearly with the distance from the neutral axis according to the relation Fb Fb,max R sin 8. The load on any particular bolt can be viewed as the effect of the line load over the arc associated with the bolt. For example, there are 12 bolts shown in the figure. Thus, each bolt load is assumed to be distributed on a 30° arc of the bolt circle. Under these conditions, what is the largest bolt…arrow_forward
- The figure shows the combined design of an angular contact ball bearing on two fulcrums. The radial loads R1 and R2 and axial load Fa of bearings 1 and 2 are shown in the figure. The relationship between the derived axial force S and radial load R is: S = 0.25R. Calculate the actual axial force of bearing 1 and bearing 2? Fa= 360N R1=4000N R2=4250N Problem 5) Figurearrow_forwardRequired Information A rotating shaft of 25-mm diameter is simply supported by bearing reaction forces Rjand R2. The shaft Is loaded with a transverse load of 13 kN as shown in the figure. The shaft is made from AISI 1045 hot-rolled steel. The surface has been machined. NOTE: This is a multi-part question. Once an answer is submitted, you will be unable to return to this part. 200 mm 25 mm 13 kN 50 mm- Not to scale Determine the endurance limit, adjusted as necessary with Marin factors. The endurance limit is 210.7 MPa.arrow_forwardPravinbhaiarrow_forward
- A solid round bar with diameter of 2 in has a groove cut to a diameter of 1.8 in, with a radius of 0.1 in. The bar is not rotating. The bar is loaded with a repeated bending load that causes the bending moment at the groove to fluctuate between 0 and 25 000 lbf in. The bar is hot-rolled AISI 1095, but the groove has been machined. Determine the factor of safety for fatigue based on infinite life and the factor of safety for yielding. Plars & .arrow_forwardProblem 17 A joint shown has the basic layout shown in the diagram below. (All dimensions on the diagram are in inches.) A single pin of diameter 0.5 inches (A = 0.2 in2) holds together the yoke and bar as shown. The material has an ultimate strength in tension of 80 ksi, and an ultimate strength in shear of 45 ksi. The load P has a value of 10000 lb. By examining the shear stress in the pin, the normal stress in the yoke, and the normal stress in the bar, find the overall factor of safety for the joint. P=10,000 lb YOKE -0.5 PIN BAR P=10,000 lb 1.5- 20 1.5 0.5 0.5arrow_forward8-75 A vertical channel 152 X 76 (see Table A–7) has a cantilever beam bolted to it as shown. The channel is hot-rolled AISI 1006 steel. The bar is of hot-rolled AISI 1015 steel. The shoulder bolts are M10 × 1.5 ISO 5.8. Assume the bolt threads do not extend into the joint. For a design factor of 2.0, find the safe force F that can be applied to the cantilever. 8T-8 12 Problem 8-75 in millimeters. 50 -50→-50→261! 125 000arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY