
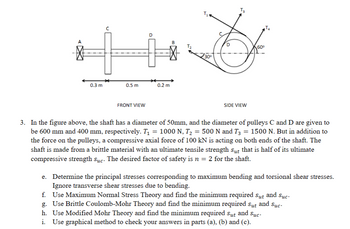
In the figure above, the shaft has a diameter of 50mm, and the diameter of pulleys C and D are given to
be 600 mm and 400 mm, respectively. ?1 = 1000 N, ?2 = 500 N and ?3 = 1500 N. But in addition to
the force on the pulleys, a compressive axial force of 100 kN is acting on both ends of the shaft. The
shaft is made from a brittle material with an ultimate tensile strength ??? that is half of its ultimate
compressive strength ???. The desired factor of safety is ? = 2 for the shaft.
e. Determine the principal stresses corresponding to maximum bending and torsional shear stresses.
Ignore transverse shear stresses due to bending.
f. Use Maximum Normal Stress Theory and find the minimum required ??? and ???.
g. Use Brittle Coulomb-Mohr Theory and find the minimum required ??? and ???.
h. Use Modified Mohr Theory and find the minimum required ??? and ???.
i. Use graphical method to check your answers in parts (a), (b) and (c).
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 2 images

 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





