
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
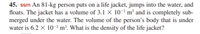
Transcribed Image Text:45. ssm An 81-kg person puts on a life jacket, jumps into the water, and
floats. The jacket has a volume of 3.1 × 10-² m² and is completely sub-
merged under the water. The volume of the person's body that is under
water is 6.2 x 10-²m³. What is the density of the life jacket?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- 10. A balloon is filled with helium (density = 0.180 kg/m³) to a volume that has a radius of 1.50 m and is then connected to a string as shown in the figure. If the mass of the skin of the balloon is 1.95 kg, determine the tension in the string when the balloon is at equilibrium. The density of air is 1.30 kg/m³. jph199 jph19** 19 jph199 jph199 jph199 jph199 140 661441 661445 661441 06146614df 661 ph199 stydf6 jph199 jph199 jph199 jph199 29 jph199 jph199 jph199 jph199 jpharrow_forward#13arrow_forward63. ssm An airplane wing is designed so that the speed of the air acrossthe top of the wing is 251 m/s when the speed of the air below the wingis 225 m/s. The density of the air is 1.29 kg/m3. What is the lifting force on a wing of area 24.0 m2 ?arrow_forward
- III the bd blood pressure in the brain? (Such action would probably be lethal.) U-I h2 P2 h-- h, P1 P2arrow_forwardC plsarrow_forwardA naval mine is a sphere (V=4/3 Ttr^3 ) of radius 0.5 m that would normally float in water (p_water=1000 kg/m^3 ). The mine (p_mine=700 kg/m^3 ) is held under the surface by a cable that attaches it to the sea floor. a. Find the volume of the naval mine. b. Find the mass of the naval mine. c. Find the tension in the cable that holds the mine under the surface using Newton's Second Law.arrow_forwardUU 2. Water is poured into a U-tube as shown in the A1 Ag Oil A1 A2 figure. The left arm of the tube has cross-sectional area A1 of 10.0 cm2, and the right arm has a cross- sectional area A2 of 5.00 cm2. 150 grams of oil are then poured into the right arm as shown. The two H. liquids do not mix. [Poit = 750 [Answer in kg m 3 significant figures] Water a) Determine the length of the oil column in the right arm of the U-tube. b) Determine the height (H) of the water column in the left arm above the water surface in the right arm?arrow_forwardA lost shipping container is found resting on the ocean floor and completely submerged. The container is 5.9 m long, 2.8 m wide, and 2.3 m high. Salvage experts attach a spherical balloon to the top of the container and inflate it with air pumped down from the surface. When the balloon's radius is 1.7 m, the shipping container just begins to rise towards the surface. What is the mass of the container? Ignore the mass of the balloon and the air within it. Do not neglect the buoyant force exerted on the shipping container by the water. The density of seawater is 1025 kg/m3.arrow_forwardAn airplane flies on a level path. There is a pressure difference of 520 Pa between the lower and upper surfaces of the wings. The area of each wing surface is about 190 m2. The air moves below the wings at a speed of 80.4 m/s. A- Estimate the weight of the plane. N B- Estimate the air speed above the wings. m/sarrow_forwardBowling balls are roughly the same size but come in a variety of weights. Given that the official radius a bowling ball should have is roughly 0.110 m, calculate the weight of the heaviest bowling ball that will float in a fluid of density 1.000 x 10° kg/m³. weight: Narrow_forward**73. ssm A solid brass sphere is subjected to a pressure of 1.0 × 10° Pa due to the earth's atmosphere. On Venus the pressure due to the atmo- sphere is 9.0 X 10° Pa. By what fraction Ar/r, (including the algebraic sign) does the radius of the sphere change when it is exposed to the Venu- sian atmosphere? Assume that the change in radius is very small relative to the initial radius.arrow_forwardThree liquids that will not mix are poured into a cylindrical container. The volumes and densities of the liquids are 0.670 L, 2.77 g/cm³; 0.356 L, 1.20 g/cm³; and 0.524 L, 0.653 g/cm³. What is the force on the bottom of the container due to these liquids? One liter = 1 L = 1000 cm³. (Ignore the contribution due to the atmosphere.) Number i Unitsarrow_forwardarrow_back_iosSEE MORE QUESTIONSarrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON