
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
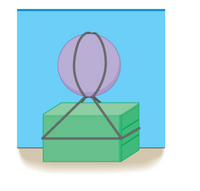
A lost shipping container is found resting on the ocean floor and completely submerged. The container is 5.9 m long, 2.8 m wide, and 2.3 m high. Salvage experts attach a spherical balloon to the top of the container and inflate it with air pumped down from the surface. When the balloon's radius is 1.7 m, the shipping container just begins to rise towards the surface. What is the mass of the container? Ignore the mass of the balloon and the air within it. Do not neglect the buoyant force exerted on the shipping container by the water. The density of seawater is 1025 kg/m3.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- OSU has been given a large model of the solar system which consists of hollow Styrofoam spheres of different sizes representing the Sun and planets. The planets are all connected to the center of the sun by means of steel rods of varying lengths and at varying angles relative to the x-axis as shown above. The steel rods are all 0.5 cm in diameter and are made of steel having a density of 7.88 g/cm3. We’d like to suspend the model from it’s center of mass, but it doesn’t look like the center of mass coincides with the position of the Sun. Find the center of mass of the model (direction and angle) relative to the Sun in the center of the model. The Styrofoam spheres are so much lighter in comparison to the rods, that their mass can be neglected. Hint: calculate the center of mass for the x and y dimensions separately, then combine them to get the final answerarrow_forwardA large spherical air balloon is filled with helium. If the balloon is to support (meaning produce a net acceleration of 0) a total load of 300 kg, including its own mass, calculate the minimum radius of the balloon. Assume values of the density of air and helium to be 1.29 kg/m and 0.18 kg/m respectively 4.8 m 3.6 m O 3.8 m O 3.1 m O 4.5 marrow_forwardSuppose that a solid cube of some material floats motionless on the surface of an oil puddle at a service station with 61.5% of its volume submerged. The density of the oil is 907 kg/m3. What is the density ? of the cube's material? 1000 kg/m3 558 kg/m3 796 kg/m3 145 kg/m3arrow_forward
- A fuel pump sends gasoline from a car's fuel tank to the engine at a rate of 7.06x10-2 kg/s. The density of the gasoline is 730 kg/m3, and the radius of the fuel line is 2.20x10-3 m. What is the speed at which gasoline moves through the fuel line?arrow_forwardPlease asaparrow_forwardThree liquids that will not mix are poured into a cylindrical container. The volumes and densities of the liquids are 0.45 L, 2.6 g/cm³; 0.20 L, 1.0 g/cm³; and 0.40 L, 0.65 g/cm³. What is the force on the bottom of the container due to these liquids? One liter = 1 L = 1000 cm³. (Ignore the contribution due to the atmosphere.) Narrow_forward
- A child has a spherical helium balloon tied to her wrist as she walks through the park at a constant speed of 0.46 m/s in the +ŷ-direction. The balloon has a diameter of 7 cm, and it is tied to a 1 m long string. Take the density of air to be 1.108 kg/m³, the density of helium to be 0.122 kg/m³, and the density of the latex of the balloon to be 0.013 kg/m². The viscous drag constant of the balloon is 0.00148 kg/s. What is the direction of the string from the girl's wrist to the balloon? û = xŷ + X 2arrow_forwardA probe on a dwarf planet collects 5 moles [mol] of dust material. The sample, which completely fills a cube with a side length of 4 centimeter [cm], weighs 0.19 newtons [N] on the dwarf planet. The density of the material is determined to be 3160 grams per liter [g/L].Determine the gravity of the dwarf planet in units of meters per seconds squared [m/s2].arrow_forwardProblem 1: The puffer fish (tetradontiade) can employ a defense mechanism whereby it fills its stomach with water until the fish is almost spherical in shape. The shape, in conjunction with its external spines, are a significant deterrent to predators. Suppose that a puffer fish takes in water until its mass has increased by f = 1.52 times its initial mass. In this state, and initially at rest, the puffer fish expels the water with a speed s in one direction, while the fish recoils in the opposite direction at a speed v. For this problem neglect the drag-force effects of the surrounding ocean water. Part (a) Write an expression for v/s in terms of f. Part (b) What is the numerical value of your answer to part (a)?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON