
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
thumb_up100%
Please help me with Req 4. I believe something is missing or incorrect from it. Thanks! :) If you zoom in I believe you can see the info more clearly.
Transcribed Image Text:decimal places.)
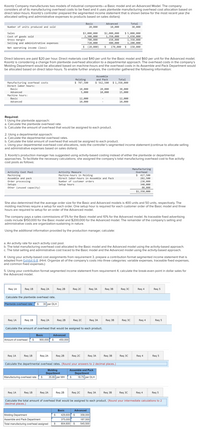
Koontz Company manufactures two models of industrial components-a Basic model and an Advanced Model. The company
considers all of its manufacturing overhead costs to be fixed and it uses plantwide manufacturing overhead cost allocation based on
direct labor-hours. Koontz's controller prepared the segmented income statement that is shown below for the most recent year (he
allocated selling and administrative expenses to products based on sales dollars):
Basic
20,00e
Advanced
Total
Number of units produced and sold
10,000
30.eee
$3.000, eee
2,300.000
700,000
720,000
$ 5,000, eee
3,650, e00
1,350.000
1,200, e0e
Sales
Cost of goods sold
Gross margin
Selling and administrative expenses
$2.000,e0e
1,350,000
650,000
480,000
$ (20,000) $ 170,000 $ 150,000
Net operating income (loss)
Direct laborers are paid $20 per hour. Direct materials cost $40 per unit for the Basic model and $60 per unit for the Advanced model.
Koontz is considering a change from plantwide overhead allocation to a departmental approach. The overhead costs in the company's
Molding Department would be allocated based on machine-hours and the overhead costs in its Assemble and Pack Department would
be allocated based on direct labor-hours. To enable further analysis, the controller gathered the following information:
Assenble
and Pack
Molding
$ 787,5ee
Total
Manufacturing overhead costs
Direct labor hours:
$ 562,500 $1350,000
Basic
10,000
5,000
20,e00
1e,e00
30,000
15,000
Advanced
Machine hours
Basic
Advanced
12,e00
10,000
12,000
10,000
Required:
1. Using the plantwide approach:
a. Calculate the plantwide overhead rate.
b. Calculate the amount of overhead that would be assigned to each product.
2. Using a departmental approach:
a. Calculate the departmental overhead rates.
b. Calculate the total amount of overhead that would be assigned to each product.
c. Using your departmental overhead cost allocations, redo the controller's segmented income statement (continue to allocate selling
and administrative expenses based on sales dollars).
3. Koontz's production manager has suggested using activity-based costing instead of either the plantwide or departmental
approaches. To facilitate the necessary calculations, she assigned the company's total manufacturing overhead cost to five activity
cost pools as follows:
Manufacturing
Overhead
$ 417.500
282, 5e0
Activity Cost Pool
Machining
Assemble and pack
Order processing
Setups
Other (unused capacity)
Activity Measure
Machine-hours in Molding
Direct labor-hours in Assemble and Pack
Number of customer orders
Setup hours
230,000
340.000
88, 000
$1,350,eee
She also determined that the average order size for the Basic and Advanced models is 400 units and 50 units, respectively. The
molding machines require a setup for each order. One setup hour is required for each customer order of the Basic model and three
hours are required to setup for an order of the Advanced model.
The company pays a sales commissions of 5% for the Basic model and 10% for the Advanced model. Its traceable fixed advertising
costs include $150,000 for the Basic model and $200,000 for the Advanced model. The remainder of the company's selling and
administrative costs are organization-sustaining in nature.
Using the additional information provided by the production manager, calculate:
a. An activity rate for each activity cost pool.
b. The total manufacturing overhead cost allocated to the Basic model and the Advanced model using the activity-based approach.
c. The total selling and administrative cost traced to the Basic model and the Advanced model using the activity-based approach.
4. Using your activity-based cost assignments from requirement 3, prepare a contribution format segmented income statement that is
adapted from Exhibit 6-8. (Hint: Organize all of the company's costs into three categories: variable expenses, traceable fixed expenses,
and common fixed expenses.)
5. Using your contribution format segmented income statement from requirement 4, calculate the break-even point in dollar sales for
the Advanced model.
Reg 1A
Reg 18
Reg 2A
Req 28
Reg 20
Reg 3A
Reg 38
Reg 3C
Reg 4
Reg 5
Calculate the plantwide overhead rate.
Plantwide overhead rate s 30 per DLH
Reg 1A
Reg 18
Reg 2A
Reg 28
Reg 20
Reg 3A
Reg 38
Reg 30
Reg 4
Reg 5
Calculate the amount of overhead that would be assigned to each product.
Basic
Advanced
Amount of overhead
s
900.000 s
450,000
Reg 1A
Reg 18
Reg 2A
Reg 28
Reg 20
Reg 3A
Reg 38
Reg 30
Reg 4
Reg 5
Calculate the departmental overhead rates. (Round your answers to 2 decimal places.)
Molding
Department
35.80 per MHS
Assemble and Pack
Department
Manufacturing overhead rates
18.75 per DLH
Reg 26
Reg 3A
Reg 1A
Reg 18
Reg 2A
Req 20
Reg 3B
Reg 30
Reg 4
Reg 5
Calculate the total amount of overhead that would be assigned to each product. (Round your intermediate calculations to 2
decimal places.).
Basic
Advanced
Molding Department
Assemble and Pack Department
Total manufacturing overhead assigned
429,600s
358,000
375,000
187,500
804,600 S
545.500
Transcribed Image Text:Reg 1A
Reg 18
Reg 2A
Reg 28
Reg 20
Reg 3A
Reg 38
Reg 30
Reg 4
Reg 5
Using your departmental overhead cost allocations, redo the controller's segmented income statement (continue to allocate
selling and administrative expenses based on sales dollars). (Round your intermediate calculations to 2 decimal places.)
Basic
Advanced
Sales
$ 3,000,000 s 2.000,000
2.204,600
Cost of goods sold
Gross margin
Seling and administrative expenses
1,445,500
554,500
480,000
S
795,400
720,000
Net operating income
75.400
74,500
Reg 1A
Reg 18
Req 2A
Reg 28
Reg 20
Reg 3A
Reg 38
Reg 30
Reg 4
Reg 5
Calculate an activity rate for each activity cost pool. (Round your answers to 2 decimal places.)
Activity Cost Pool
Activity Rate
Machining
18.98 per MH
Assemble and pack
9.42 per DLH
Order processing
Setups
920.00 per order
523.08 per hour
Req 1A
Reg 18
Reg 2A
Reg 28
Reg 20
Reg 3A
Reg 38
Reg 30
Req 4
Reg 5
Calculate the total manufacturing overhead cost allocated to the Basic model and the Advanced model using the activity-
based approach. (Round your Intermediate calculations to 2 decimal places.)
Basic
Advanced
Machining
$ 227.700rs
189.800
188,400
46.000
Assemble and pack
94.200
Order processing
Setups
184.000
26,154
488.314 S
313.848
Total overhead cost assigned $
781.848
Reg 1A
Reg 18
Reg 2A
Reg 2B
Reg 20
Reg 3A
Reg 38
Reg 30
Reg 4
Reg 5
Calculate the total selling and administrative cost traced to the Basic model and the Advanced model using the activity-based
approach.
Basic
Advanced
Total traceable selling and administrative cost
300.000s
400.000
Reg 1A
Reg 18
Reg 2A
Req 28
Reg 20
Reg 3A
Reg 38
Reg 30
Reg 4
Reg 5
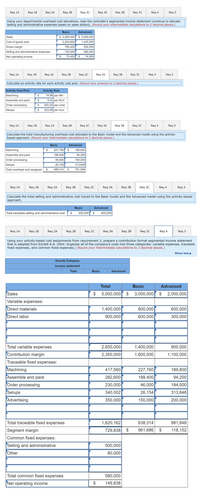
Using your activity-based cost assignments from requirement 3, prepare a contribution format segmented income statement
that is adapted from Exhibit 6-8. (Hint: Organize all of the company's costs into three categories: variable expenses, traceable
fixed expenses, and common fixed expenses.) (Round your intermediate calculations to 2 decimal places.)
Show less a
Koontz Company
Income statement
Total
Basic
Advanced
Total
Basic
Advanced
Sales
$ 5,000,000 s 3,000,000 s 2,000,000
Variable expenses:
Direct materials
1,400,000
800,000
600,000
Direct labor
900,000
600,000
300,000
2,650,000
2,350,000
Total variable expenses
1,400,000
900,000
Contribution margin
1,600,000
1,100,000
Traceable fixed expenses:
Machining
417,560
227,760
189,800
Assemble and pack
282,600
188,400
94,200
Order processing
230,000
46,000
184,000
Setups
Advertising
340,002
26,154
313,848
350,000
150,000
200,000
Total traceable fixed expenses
1,620,162
638,314
981,848
Segment margin
729,838 S
961,686 $
118,152
Common fixed expenses:
Selling and administrative
500,000
Other
80,000
Total common fixed expenses
580,000
Net operating income
149,838
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- How would I calculate this problem? I just guessed on which answer made sense to me. Please help. thank you in advance.arrow_forwardhi im looking at the solution above and have a quuestion-im a littlepuzzled on exactly how i should be plugging in the numbersfor example, the chart liists Time (ln2/(ln(1+r)) but how exactly should i type this in my calculatorto get =l3/J3? maybe im overthinking itarrow_forwardPlease do not rely too much on chatgpt, because its answer may be wrong. Please consider it carefully and give your own answer. You can borrow ideas from gpt, but please do not believe its answer.Very very grateful!Please do not rely too much on chatgpt, because its answer may be wrong. Please consider it carefully and give your own answer. You can borrow ideas from gpt, but please do not believe its answer.Very very grateful!arrow_forward
- During the research process, if you are unsure whether or not you've found all the relevant literature, what should you do? A. Google it to see if there is anything else you've missed. B. Call your manager to verify that you've found it all. C. Use the search engine included in the Codification. D. Complain that it's too much work and call it a day.arrow_forwardHi, Could you please show me how to solve this with formulas? not excel, I should have clarified. Thanksarrow_forwardwhat is the differnce between quickbooks online and QuickBooks desktop?arrow_forward
- Explain the Golsen Rule and, in your own words, provide an example of the application of the Golsen Rule. 4 MacBook Air Foarrow_forwardis there a way to do this question with formulas and a calculator instead of excel? if so please upload the solution this wayarrow_forwardFurther info is in the attached images For the Excel part of the question give the solutions in the form of the Excel equations. Please and thank you! :) Download the Applying Excel form and enter formulas in all cells that contain question marks. For example, in cell B34 enter the formula "= B9". After entering formulas in all of the cells that contained question marks, verify that the dollar amounts match the example in the text. Check your worksheet by changing the beginning work in process inventory to 100 units, the units started into production during the period to 2,500 units, and the units in ending work in process inventory to 200 units, keeping all of the other data the same as in the original example. If your worksheet is operating properly, the cost per equivalent unit for materials should now be $152.50 and the cost per equivalent unit for conversion should be $145.50. Thank you!arrow_forward
- Any help is appreciated, here is the question. https://drive.google.com/file/d/0B-AOAJtLKPhfOEJhR0RWRWtmT3BGVVljQUZaRko0Zkh2NDRr/view?usp=sharingarrow_forwardHow do you get a report into PDF format? Select an answer: You need to email the report and then convert it to PDF. Click on the Export button and Click on Export as PDF. You cannot export reports into PDF. You have to print the report and then scan it as a PDF.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education