
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Note:
Provide a clear, step-by-step handwritten solution (no explanations included!) created entirely without AI assistance. The work must be of expert-level quality, as I will review and rate it based on its accuracy and overall presentation. Ensure you thoroughly double-check everything for precision before submitting.
Question:
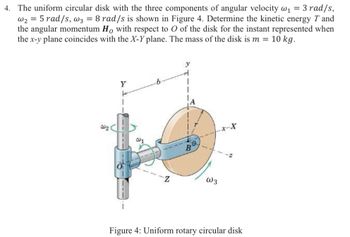
Transcribed Image Text:4. The uniform circular disk with the three components of angular velocity w₁ = 3 rad/s,
w25 rad/s, w3 = 8 rad/s is shown in Figure 4. Determine the kinetic energy T and
the angular momentum Ho with respect to O of the disk for the instant represented when
the x-y plane coincides with the X-Y plane. The mass of the disk is m = 10 kg.
Y
W2
W1
Z
y
x-X
B
W3
Figure 4: Uniform rotary circular disk
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- )= The disk with radius r is rolling (without slipping) with angular velocity @ through the bottom of the circular path of radius R. If @= 2 rad/sec, R = 0.5 m, r = 0.2 m, and the mass of the disk is 3 kg, calculate the magnitude of the normal force exerted by the path on the disk at that instant. Present your answer in Newtons using 3 significant figures. wwwwwarrow_forwardThe 10-kg bar is released from rest in the horizontal position 1 and falls to positions 2. The unstretched lengthy of the spring is 0.6 m and the spring constant is k=20 N/m .what will be the bar 's angular velocity when it is in position 2.arrow_forwardCan anyone help me with this questionarrow_forward
- 2 Problem The mechanized arm shown below is simulatenously rotating upward and extending as it holds a circular widget of mass 2 kg in its claw. At the instant shown, 0 = 45 deg., 0 = 30 deg/s. * = 120 deg/s², and L = 0.4m, L = 0.5 m/s, and Ï = -0.3 m/s². The constant length d = 1 m. Determine the components of the gripper's force exerted on the widget. Express the total force in components of the polar frame. Compare your answer with the total force on the widget if the mechanized arm suddenly stops and remains at rest. 0 L ----- Barrow_forwardTwo different amusement park rides are shown in the figure at the right. Each of the platforms is supported on frictionless pins by a pair of arms. All of the arms supporting the platforms rotate at the same angular velocity w. Compare the kinetic energies of the two identical platforms P and Q. Which is correct? Platform P has greater kinetic energy. Platform Q has greater kinetic energy. The kinetic energy of the platforms will be the same. Each will have zero kinetic energy. Not enough information is given.arrow_forwardFor the circular thin plate with a square hole as shown in the image below, its radius R = 0.49 m and the side of the square /= 0.22 m, and the material has a mass per unit area of 14 kg/m². If at the instant shown, it is subjected to a force P= 43 N, and has a counterclockwise angular velocity of W = 2.3 rad/s, determine the angular acceleration (in rad/s²) of this plate. Please pay attention: the numbers may change since they are randomized. Your answer must include 2 places after the decimal point. Take g = 9.81 m/s². R @ Your Answer: Answer 5 3 Parrow_forward
- For the circular thin plate with a square hole as shown in the image below, its radius R = 0.42 m and the side of the square /= 0.15 m, and the material has a mass per unit area of 15 kg/m2. If at the instant shown, it is subjected to a force P= 47 N, and has a counterclockwise angular velocity of w = 2.1 rad/s, determine the angular acceleration (in rad/s?) of this plate. Please pay attention: the numbers may change since they are randomized. Your answer must include 2 places after the decimal point. Take g = 9.81 m/s². R 4 3 Your Answer: Answerarrow_forwardBlocks A and B shown in the figure have masses of 5 kg and 10 kg respectively.If the pulley is treated as a 3 kg solid disk with a 15 cm radius, determine the acceleration of the block A. Disregard the rope mass and any slip on the pulley.Consider that the moment of inertia of the pulley is given by Ip = (1/2)mr² in which m is the mass of the pulley and r is of radius the pulley.arrow_forwardThe rod OA rotates clockwise at a constant angular velocity of 0 = (3) rad -. Two pin-connected slider block, located at B, move freely on OA. The curved rod is described by the equationr = (250 · (8 - cos 0)) m. Hint: 1. Remember clockwise rotation is negative velocity. A d3 d1 d2 Values for the figure are given in the following table. Note the figure may not be to scale. Variable Value 01 130 degrees di 0.45 m d2 dz 0.2 m 0.325 m Using cylindrical components, a. Determine the cylinders's radial and transverse components of velocity at the instant shown, vr and b. Determine the cylinders's radial and transverse components of acceleration at the instant shown, a, and ag. c. Determine the cylinder's magnitude of the velocity at the instant shown, v d. Determine the cylinder's magnitude of the acceleration at the instant shown, aarrow_forward
- For the circular thin plate with a square hole as shown in the image below, its radius R = 0.32 m and the side of the square /= 0.22 m, and the material has a mass per unit area of 14 kg/m2. If at the instant shown, it is subjected to a force P= 44 N, and has a counterclockwise angular velocity of W = 3.8 rad/s, determine the angular acceleration (in rad/s?) of this plate. Please pay attention: the numbers may change since they are randomized. Your answer must include 2 places after the decimal point. Take g = 9.81 m/s?. R Parrow_forwardA gear of mass m = 10 kg and radius R=0.25 m may rotate about its center of mass C, which is fixed. A rack of mass m = 10 kg is subjected to a constant force Fo = 20 N, as shown. The rack and gear are geared together (gear teeth not shown), so that the force Fo drives the rack to the right and rotates the gear. Find the angular ácceleration a of the gear and find the force f exerted by the rack on the gear. The gear is to be modeled as a uniform circular disc. Fixed Fo3 20 N Rackarrow_forwardPart A The smooth surface of the vertical cam is defined in part by the curve r = (0.2 cos 0+0.3) m. The forked rod is rotating with an angular acceleration of 0 = 2 rad/s as shown in (Figure 1), and when 0 = 45°, the angular velocity is 6 = 6 rad/s. Determine the force the cam and the rod exert on the 1.8-kg roller at this instant. The attached spring has a stiffnesss k = 100 N/m and an unstretched length of 0.1 m. Express your answers in newtons using three significant figures separated by a comma. ? Neam, Frud = N Submit Request Answer Figure 1 of 1 Provide Feedback Next >arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY