
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
3. Suppose that air pollution is a problem.
a. Describe a "cap and trade" policy as a possible solution
b What, if any, externalities are addressed by this program. Include in your explanation whether these are positive or negative, and how the policy ameliorates them.
c.What might be some drawbacks to this policy?
Your answers to the above should be complete enough to answer the question. You can use verbal, graphical, mathematical explanations in your answer. Your answer to #3 a, should be at least 250 -500 words.
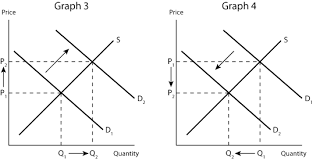
Transcribed Image Text:Price
Graph 3
Q₁ +Q₂
S
D₂
Quantity
Price
Graph 4
Q₂- .Q₁
M
D₁
Quantity
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- In a cap and trade system, when allowances are given away for free, regulated firms can enjoy rents compared to when allowances are auctioned. a. Explain why rent is generated. b. Does this mean that firms do not pay for their emissions, and therefore they do not have the incentive to reduce emissions? Explain. c. Same distributional effects can be achieved with an emissions tax where the tax applies only to emissions beyond a certain level. How would this system work in terms of giving incentives to the firms to reduce emissions? Discuss this with the help of a MB and MC of abatement diagram where the emissions tax is set at where MB = MC and the tax-exempt amount of emissions is between the maximum and the efficient level of abatement.arrow_forwardHow would I solve b c and darrow_forwarda. Which of the following situations exhibits a positive externality? __ Alan purchases a new watch as a gift for his father. __ Sean spends the afternoon cleaning his garage. __ Richard renovates a dilapidated historic home in the center of town. b. when there is a positive externality associated with the market __ too little is produced. __ too much is produced. __ the socially optimal amount is produced. c. Governments may stimulate the economy to move toward the socially optimal output by __ taxing the product __ subsidizing the product. __ implementing a price ceiling.arrow_forward
- 5.. "Since a public good is enjoyed by all members of society, willingness to pay for the good will not diminish as the amount produced increases." Evaluate and use an example to support your answer. This statement is (correct incorrect). Public goods face (increasing, constant, diminishing ) returns like any other good. Consider the number of highways in a town, for example. Citizens of a town are very willing to pay for the first highway, as it produces large gains to the town. Successive highways produce (more and more, less and less ) willingness to pay because the citizens face lower and lower gains from the increased number of highways. In a town of, say 20,000, 15 highways (would, would not) produce much more benefit than just 2 or 3 highways because of ( increasing, constant, diminishing ) returns.arrow_forwardExternalities - Definition and examples An externality arises when a firm or person engages in an activity that affects the wellbeing of a third party, yet neither pays nor receives any compensation for that effect. If the impact on the third party is adverse, it is called a ___________ externality. The following graph shows the demand and supply curves for a good with this type of externality. The dashed drop lines on the graph reflect the market equilibrium price and quantity for this good.arrow_forwarda. What sector produces most of Australia’s GHG emissions? Clearly state the relevant references.b. Why do firms pollute?arrow_forward
- 2. Refer to Graph 10-1. Assume the externality is not internalised. What is the loss to society from the last unit of the good produced by the market? A. P3-P2 B. P2-P1 C. P3-P1 D. ZeroGraph 10-1 Note:- Do not provide handwritten solution. Maintain accuracy and quality in your answer. Take care of plagiarism. Answer completely. You will get up vote for sure.arrow_forward1. Suppose 20 people each have the demand Q = 20 − P for streetlights and 5 people have the demand Q = 18 − 2P for streetlights. The cost of building each streetlight is $10.a. Write the social marginal benefit equation: MBS = _______ - _________ Q/2. Hint: Type integers.b. The socially optimal number of street lights is ________. Hint: Type the number in two decimal places. 2. The __________ theorem states: As long as negotiation costs are negligible and affected consumers can negotiate freely with each other, the court could allocate the entitlement to either party, and an efficient allocation would result. Hint: The answer is case sensitive. PLEASE FILL OUT THE SPACESarrow_forwarda) Explain how the positive externalities normally created by activities such assnow shovelling lead to an inefficiency from a social point of view.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education