
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Transcribed Image Text:olackboard.com/ultra/courses/_165411_1/cl/outline
P pearson/MyLab M...
W WordCounter
Quizlet y LaundryView
Question Completion Status:
Price
63
Supply
(private cost)
42
36
Social value (private value
and extemal benefit)
24
15
Demand
(private value)
240
420
Quantity
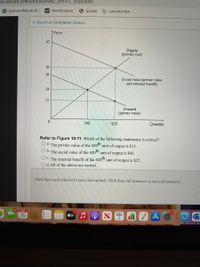
Refer to Figure 10-11. Which of the following statements is correct?
O a. The private value of the 420"" unit of output is $15.
O b. The social value of the 420 unit of output is $42.
O C. The external benefit of the 420 unit of output is $27.
O d. All of the above are correct.
Click Save and Submit to save and submit. Click Save All Answers to save all answers.
16
ty
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- (Figure: The Socially Optimal Quantity of Emissions from Coal Production) Use Figure The Socialy Optimal Quarety of Emissions from Coal Production in the figure, firms are the only beneficiaries of polution, and costs are borne solely by others in the society. Without government intervention Marginal social cost, marginal social benefit MSC of pollution MSB of pollution Quantity of pollution emissions (tons) O The outcome cannot be determined without more information Orms will continue to polute until the marginal benefit to them is $200 O firms will continue to pollute until the marginal benate to them is zero. O the quantity of pollution will be optimal.arrow_forwarduncements us es $10 Materials $7 -Hill $5 49 sources 20 30 D Q If this market has a tax of $5 per unit imposed on it, what is the Deadweight Loss? O $7 O $25 O $30 O $100 IT * zoomarrow_forward- My O 4 Schol 15909/quizzes/855329/take 1. Concepts & Price (5) OX₁ OS OX OD % Refer to Graph 3 below. Which curve represents the marginal private benefit? Graph 3 Help O Pa 5 A XX- 930 .C 40 6 C P 4 & 7 8 lyp MOX 4+ 8 Maket for the product of wwater polluting firm Quantity Chat 144 9 O htt Carrow_forward
- Figure 1. The graph depicts the market for plastic containers. Price 16- 14- 12- 10 8- 6 200 500 650 Social Cost Private Cost Demand Quantity Refer to Figure 1. In order to reach the social optimum, the government could O offer a subsidy of $8 per unit on the production of plastic containers. O impose a tax of $8 per unit on the production of plastic containers. O offer a subsidy of $4 per unit on the production of plastic containers. O impose a tax of $4 per unit on the production of plastic containers.arrow_forward45 40 35 30 25 20 P ($) Social cost Supply 15 10 Demand 5 0 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 wanted to tax or subsidize this good to achieve the Refer to the figure above. If the government socially-optimal level of output, it would Select one: O a introduce a subsidy of $10 per unit. O b. impose a tax of $10 per unit. Oo impose a tax of $15 per unit. Od introduce a subsidy of $15 per unit. 8arrow_forward2. Consider the following free market. $300 $200 $100 500 1200 Quantity i. Calculate consumer and producer surplus in this market. ii. If the marginal external cost of production is $10, the socially optimal quantity is 400 and the socially optimal price is $205. Show the new consumer and producer surplus and calculate them. Also show the deadweight loss on the graph and calculate it.arrow_forward
- Figure 5-1 Price (dollars per vaccination) $60 50 40 400 600 Supply D, Refer to Figure 5-1. The market equilibrium quantity is O 200 O 400 O 600 O > 600 D₂ Quantity (thousands of vaccinations) Figure 5-1 represents the market for vaccinations. Vaccinations are considered a benefit to society, and the figure shows both the marginal private benefit and the marginal social benefit from vaccinations. thousand vaccinations.arrow_forward11.00 10.00 9.00 8.00 7.00 6.00 5.00 4.00 3.00 2.00 1.00 Supply Marginal Social. Benefit Demand 300 600 900 1200 1500 1800 2100 2400 In the market depicted above, how large is the deadweight loss from the externality? O a. 1000 O b. 600 O c. 900 O d. 800arrow_forwardUse the figure below to answer the following questions. Price (dollars per uni 25 20 15 10 S 0 50 100 150 200 250 Quantity (unit) Refer to Figure 5.3.1. If the quantity produced is 100, Figure 5.3.1 Select one: O A. marginal social cost exceeds marginal social benefit. OB. deadweight loss is zero. OC. marginal social benefit is minimized. OD. marginal social benefit exceeds marginal social cost. OE. production is efficient.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education