
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780134580999
Author: Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
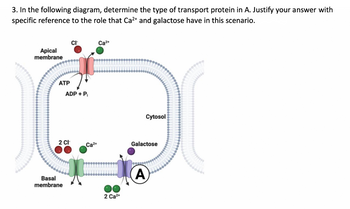
Transcribed Image Text:3. In the following diagram, determine the type of transport protein in A. Justify your answer with
specific reference to the role that Ca²+ and galactose have in this scenario.
Apical
membrane
ATP
2 CI
Basal
membrane
CI™
ADP + Pi
Ca²+
Ca²+
2 Ca²+
Cytosol
Galactose
A
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 21. Setup A contains a sucrose concentration of 30% , while setup B’s sucrose concentration is 15% Both were placed in a breaker of pure water. Which had the greater difference in concentration of water across the membrane?arrow_forwardWhich of these compounds will cross the cell membrane without the aid of a membrane transport protein, and why? H3 NH NH 2. By what transport process will the above compound be transported? What are the factors which drive movement across the membrane in this process? Does this process require input of energy?arrow_forwardMatch the following statement related to membrane transport processes to the appropriate term or terms: passive transport, facilitated transport, active transport. A transporter (or carrier) protein is necessary. (Select all that apply.) passive transport facilitated transport active transport O Oarrow_forward
- The formation of a membrane vesicle is a complex choreographed process, however very little energy is required for this event to occur. What is the only step of vesicle formation that requires the input of energy? Explain why the rest of the processes energetically favorable?arrow_forward7. Specificity of membrane transporters. A protein that transports amino acids across the cell membrane was found to bind only a few amino acids efficiently. To find the specificity, many different amino acids and substrate analogs were used as competitive inhibitors in transport studies at pH 5.9 with L-histidine (Km = 10 μM). The Ki values calculated from Lineweaver-Burk plots are shown in the table below. Comparing the structures of L-histidine and the competitive inhibitors (for which most of them, you should know their structures!), what can you conclude about the characteristics of molecules that this transport protein binds at its active site? K; (10-€ M) Amino acid or analog L-Lys L-Arg Gly L-Asp D-His Histamine Dehydrourocanate D-Arg 2 3 285 450 340 390 285 355 HN- + HN + Structure -ΝΗ -NH3 histamine ΝΗ -COO™ dehydrourocanatearrow_forward8. The cartoon at the right depicts a hypothetical cell that has a Lit-K* ATPase (shown as the filled circle with arrows). The cell also contains Lit and K* channels. The membrane is three times more permeable to K* than it is to Li*. The following are the steady state concentrations of Li* and K*: [Li*]out = 100 mM [Li*]in = 5 mM [K*]out = 4 mM Lit ADP + P, ATP [K*lin = 80 mM = 10°C Temp = Assuming that the Vm is produced only by the diffusion of Li* and K*, calculate the Vm.arrow_forward
- Label the diagram below as either passive transport (diffusion or facilitated diffusion) or active transport. Provide examples of solutes that are transported in these various ways across the cell membranearrow_forward1. Which of these compounds will cross the cell membrane without the aid of a membrane transport protein, and why? H3 NH NH 2. By what transport process will the above compound be transported? What are the factors which drive movement across the membrane in this process? Does this process require input of energy?arrow_forwardA cell with a K+1 concentration of 0.3 eq/L is placed into a solution with a K+1 concentration of 0.2 eq/L. It is assumed that the K+1 can pass through the cell membrane (the K+1 transport protein is open). Answer the following true or false questions. 1. K+1 will diffuse through the membrane down its concentration gradient due to Kinetic Theory 2. Movement of a solute through the membrane is called dialysis 3. K+1 will move out of the cellarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education

Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780134580999
Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:PEARSON

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781259398629
Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa Stouter
Publisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,

Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780815344322
Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter Walter
Publisher:W. W. Norton & Company

Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781260159363
Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, Cynthia
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.

Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9781260231700
Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael Windelspecht
Publisher:McGraw Hill Education