
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780134580999
Author: Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
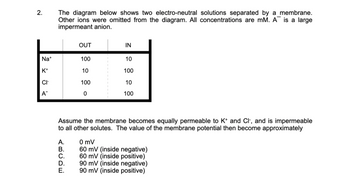
Transcribed Image Text:2.
Na+
K+
CI
A™
The diagram below shows two electro-neutral solutions separated by a membrane.
Other ions were omitted from the diagram. All concentrations are mM. A is a large
impermeant anion.
ABCDE
A.
B.
C.
D.
OUT
Assume the membrane becomes equally permeable to K+ and Cl-, and is impermeable
to all other solutes. The value of the membrane potential then become approximately
E.
100
10
100
0
IN
10
100
10
100
0 mV
60 mV (inside negative)
60 mV (inside positive)
90 mV (inside negative)
90 mV (inside positive)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- please explainarrow_forwardA Removing water is to osmosis A Adding water is to osmolarity B. Gated channels are to mediated transport B Lipid bilayers are to net flux. C.A 600 mOsm cell is to a 200 mOsm solution. (all nonpenetraing) C 53 molar (H₂0) cell is to a 54 molar (H2O) solution (all nonpenetraing) D Transporters are to simple diffusion. D Voltage-gated channels are to secondary active i transport A Removing water is to concentration A Adding solute is to dilution B. Heat energy is to diffusion B Transporters are to downhill gradients. CA 350 mOsm solution is to an 300 mOsm cell (all) nonpenetraing) C 550 mOsm.cell is to a 550 mOsm solution (all nonpenetraing) D: Channels are to facilitated diffusion D Aquaporins are to membrane potentials A: Adding solute is to molarity as: B: ATP is to active transport as: C: Hypertonicity is to cell size as: D: Pumps are to active transport as: Reserarrow_forward1. An artificial membrane with a pore size of 24 Angstrom (Å) separates two chambers (X and Y) in glassware containing equal amounts of fluid. a. 2.0 M NaCI is present in chamber X, whereas 5 percent KI is present in chamber Y. (Na diameter: 1.96 Å; Cl diameter: 3.7 Å; KI diameter: 2.8 Á) Y b. The albumin in chamber X is 3%, whereas the potato starch in chamber Y is 2%. (Albumin diameter: 38 Å; Starch: 3O0k -1 million Å)arrow_forward
- Compare and contrast the selectivity mechanisms of water channels and potassium channels. The use of diagrams is recommended.arrow_forward9. You are performing an experiment at with an artificial membrane (i.e not a living cell). You place a NaCl solution on each side of the membrane. You discover that if you place a 10-fold NaCl concentration gradient across this membrane (higher NaCl concentration outside than inside) you initially see a +20 mV membrane potential develop. If the Cl permeability is assigned a value of 1, what value would you assign to the Na" permeability? Assume 2.3RT/F = 60 mV.arrow_forward8. The cartoon at the right depicts a hypothetical cell that has a Lit-K* ATPase (shown as the filled circle with arrows). The cell also contains Lit and K* channels. The membrane is three times more permeable to K* than it is to Li*. The following are the steady state concentrations of Li* and K*: [Li*]out = 100 mM [Li*]in = 5 mM [K*]out = 4 mM Lit ADP + P, ATP [K*lin = 80 mM = 10°C Temp = Assuming that the Vm is produced only by the diffusion of Li* and K*, calculate the Vm.arrow_forward
- . Lysozyme is placed in a dialysis tube. The protein has a charge of +18 at pH 7.0. If the protein is dialyzed against 0.1L of 0.1M NaCl, predict the sign of the membrane potential using the Donnan Potential.arrow_forwardWhich of the following is a way for electrolytes in an aqueous solution to move from an area of high solute concentration to an area of low concentration? O a. Active transport O b. Osmosis O c. Simple diffusion Od. Facilitated diffusion O e. None of thesearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education

Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780134580999
Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:PEARSON

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781259398629
Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa Stouter
Publisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,

Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780815344322
Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter Walter
Publisher:W. W. Norton & Company

Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781260159363
Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, Cynthia
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.

Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9781260231700
Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael Windelspecht
Publisher:McGraw Hill Education