
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
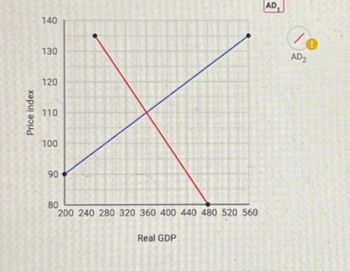
The graph below shows, the aggregate demand and supply for the economy of Etrusca.
a. Draw AD2 on the graph below assuming an increase of $60 in aggregate demand. Plot only the endpoints of the curve below
b. What is the new level of equilibrium GDP ?
c. What is the new equilibrium price level?
d. How much is the reduction in GDP due to the crowding out effect?
Transcribed Image Text:140
AD
/0
AD2
130
Price index
120
110
100
90
96
80
80
200 240 280 320 360 400 440 480 520 560
Real GDP
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- hi there is another picture as wellarrow_forwardCourse: Macroeconomic - IS-LM Model Prove mathematically the following: Given an increase in the proportional tax on income(t), what happens to the level of output and to the tax?" . Hint: for demostration, use the IS general function for a closed economy Y = C + I + G, where C = a + c*YD and YD = Y + TR - Y*t (where t = proportional income tax) and realize changes i.e., from "t1" to "t2"arrow_forwardMacroeconomics: Assuming marginal propensity to consume is 0.5. If there is a shock to the economy that increases investment spending by 200 billion dollars what will the total Change to GDP be? (Ignore taxes and imports)arrow_forward
- SRAS PL2 PL AD2 AD REAL GDP The Aggregate Demand Model shows an increase in Aggregate Demand or an increase in GDP. Which Fiscal Policy Action would cause this change O Raise Taxes & Cut Government Spending O Decrease Taxes & Government Spending O Increase Taxes & Government Spending O Cut Taxes and Increase Government Spending PRICE LEVELarrow_forwardthe question is true or false: "An increase in business investment spending has the same effect on the level of ad as an increase in the same amount of government spending" can you explain what the answer is? Would they equal each other out?arrow_forwardTOPIC: Crowding Out.arrow_forward
- US President Collin Hawkins is concerned about the economy. He orders the Treasury to issue direct stimulus payments to citizens in an effort to prevent a recession. On average citizens save 20% of their income. The total of this stimulus amount is $1.3 trillion USD. What is the multiplier? What is the total economic impact of this injection? $ "instead of using 'O's, simply note the number using "m", "b", or "t" for 'million, "billion, or 'trillion. For example if your answer is "$56,100,000,000", you should instead type "$56.1b"arrow_forwardSuppose an economy had aggregate demand components with the following relationships: Consumption spending, C=140+.60*(DY) Investment spending,I=25+.15*Y Government Spending, G= 0 Net Export Spending,X=0 Tax collections, Tx=0 a. What is the equilibrium income for this economy? b. If the government decided to increase G spending by 6, what would be the new equilibrium income for this economy? c. If instead the government decided to reduce Tx (taxes) by 10, what would be the new equilibrium income for the economy? d. If instead the government decided to increase G spending and Increase Tx (taxes) by 20, what would be the new equilibrium for this economy?arrow_forwardWhen households cut back on their spending, then in the short run we tend to see the price level ______ and equilibrium output __________. fall; fall rise; fall rise; rise fall; risearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education