
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
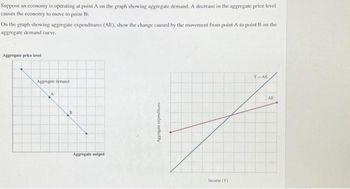
Transcribed Image Text:Suppose an economy is operating at point A on the graph showing aggregate demand. A decrease in the aggregate price level
causes the economy to move to point B
On the graph showing aggregate expenditures (AE), show the change caused by the movement from point A to point B on the
aggregate demand curve.
Aggregate price level
Aggregate demand
Aggregate output
Aggregate expenditures
Income (Y)
Y-AE
AE
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- An economy is characterized by the following desired consumption and investment functions: C = 543 + 0.72Y and I = 752. Part (a): Calculate the equilibrium level of GDP and the multiplier for this economy. Round your answer for the multiplier to 3 decimal places. Example: 0.001 Part (b): Suppose the level of desired investment changed to I = 731, with no change to desired consumption. What is the new equilibrium GDP level for the economy? Part (c): Using 1 to 2 sentences, describe how this change to desired investment affects the AE function graphically. Part (d): Suppose the desired investment levels returns to I = 752, but now consumers spend 86 cents of every dollar earned. What is the new equilibrium GDP level for the economy? Part (e): Using 1 to 2 sentences, describe how this change to consumption habits affects the AE function graphically.arrow_forwardIn 250 words or less, answer the following question. With reference to the multiplier process, discuss how a shock to an exogenous component of aggregate expenditure may lead to a larger than proportionate change in economic output in equilibrium.arrow_forwardThe aggregate demand function: yad =C+1+G₁ = 500+ 0.75Y is plotted on the graph to the right. The graph also shows the 45° line where aggregate output Y equals aggregate demand yad for all points. What happens to aggregate output if government spending rises by 100? The equilibrium level of output rises by $ billion. (Round your response to the nearest billion.) Consumption Expenditure, C ($ billions) 3000- 2800- 2600- 2400- 2200- 2000- 1800- 1600- 1400- 1200- 1000- 800- 600- 400- 200- 0- 0 yad =C+I+G₁ = 500 +0.75Y Y = yad 45° 400 800 1200 1600 2000 2400 2800 Disposable Income ($ billions)arrow_forward
- The total expenditure in Macroland begins with these initial levels (in trillions of dollars): autonomous consumption=1, Investment = 2; Net Exports = 0, T=2, and MPC = 0.75. Assume that equilibrium has been achieved. Suddenly there is an external shock and as a result investment goes down to 1. What is the change in GDP? Use the base model to answer this question. Equilibrium GDP goes down by 1 Equilibrium GDP goes up by 1 Equilibrium GDP goes up by 4 Equilibrium GDP goes down by 4arrow_forwardRight click on image and click on open image in new tab to see the full and clear image. Consider two closed economies that are identical except for their marginal propensity to consume (MPC). Each economy is currently in equilibrium with real GDP and total expenditure equal to $100 billion, as shown by the black points on the following two graphs. Neither economy has taxes that change with income. The grey lines show the 45-degree line on each graph. The first economy's MPC is 0.5. Therefore, its initial total expenditure line has a slope of 0.5 and passes through the point (100, 100). The second economy's MPC is 0.75. Therefore, its initial total expenditure line has a slope of 0.75 and passes through the point (100, 100). Now, suppose there is a decrease of $20 billion in investment in each economy. Place a green line (triangle symbol) on each of the previous graphs to indicate the new total expenditure line for each economy. Then place a black point (plus symbol) on each graph…arrow_forwardPlease answer everything in the photo including the graph.arrow_forward
- The levels of real disposable income and aggregate expenditures for an economy are given in the following table. -- Use the blue points (circle symbol) to plot the expenditures line for this economy on the following graph. Line segments will automatically connect the points. The black line represents the 45-degree line, where aggregate expenditures equal real GDP. Use the black point (plus symbol) to indicate equilibrium real GDP. - - In the previous graph, if the economy produces at an output level that is higher than equilibrium GDP, then the economy is in because aggregate expenditures are real GDP, and unplanned inventory investment is Read GDP (Y) Aggregate Expenditures (AE) (Trillions of dollars per year) (Trillions of dollars per year) 0 1 1 1.75 2 2.5 3 3.25 4 4 5 4.75 6 5.5 7 6.25 8 7 Use the blue points (circle symbol) to plot the expenditures line for this economy on the following graph. Line segments will automatically connect the points. The black line represents the…arrow_forwardWhich of the following is most likely to cause a decrease in the aggregate expenditure (AE) curve? Select an answer and submit. For keyboard navigation, use the up/down arrow keys to select an answer. A decrease in wealth a b A government stimulus check An increase in unemployment benefits d An increase in education spendingarrow_forwardSuppose there is some hypothetical economy in which households spend $0.50 of each additional dollar they earn and save the $0.50 they have left over. The following graph plots the economy's initial aggregate demand curve (AD₁). Suppose now that the government increases its purchases by $3.5 billion. Use the green line (triangle symbol) on the following graph to show the aggregate demand curve (AD2) after the multiplier effect takes place. Hint: Be sure the new aggregate demand curve (AD2) is parallel to AD₁. You can see the slope of AD₁ by selecting it on the following graph. PRICE LEVEL 116 114 112 110 108 106 104 102 100 100 AD1 102 106 108 110 OUTPUT (Billions of dollars) 104 112 114 1 116 AD2 AD 3 ?arrow_forward
- Consider the hypothetical country of Kejimkujik. Suppose that national income in Kejimkujik is $300 billion, households pay $100 billion in taxes, household consumption is equal to $160 billion, and the marginal propensity to consume (MPC) is 0.6. On the following graph, use the blue line (circle symbol) to plot the economy's consumption function. Consumption Function050100150200250300350400450500500450400350300250200150100500CONSUMPTION (Billions of dollars)DISPOSABLE INCOME (Billions of dollars) Suppose now that Kejimkujik’s national income increases to $330 billion. Assuming the amount paid in taxes is fixed at $100 billion and that MPC = 0.6, what is the new amount of household consumption? $148 billion $219.4 billion $220.6 billion $178 billionarrow_forward#1 Consider an economy defined by the following (in $billions and price level is fixed): C = 25+ 0.6YD T = 10+ 0.15Y 1 = 30 G = 40 X = 15 M = 0.01Y a) What is the marginal propensity to spend and what is the aggregate expenditure multiplier?arrow_forwardQuestion 3 of 16 Income and consumption changes for five people are shown in the table. Given this information, rank the marginal propensities to consume (MPC) for the five people from largest to smallest. Largest MPC Smallest MPC Answer Bank Bert Doug Eli Carter Al Name Income change Consumption change Al +$5,000+$5,000 +$3,000+$3,000 Bert +$2,500+$2,500 +$800+$800 Carter +$1,000+$1,000 +$800+$800 Doug −$2,500−$2,500 −$1,750−$1,750 Eli −$5,000−$5,000 −$2,000−$2,000arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education