
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780134580999
Author: Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
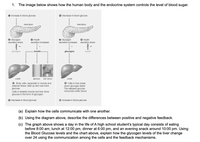
Transcribed Image Text:1. The image below shows how the human body and the endocrine system controls the level of blood sugar.
O Increase in blood glucose
O Decrease in blood glucose
PANCREAS
PANCREAS
O Glucagon
secretion slows
O Glucagon
secretion increases
O Insulin
secretion slows
Insulin
secretion increases
glucagon
insulin
glucagon
insulin
LIVER
MUSCLE
FAT CELLS
LIVER
O Body cells, especially in muscle and
adipose tissue, take up and use more
glucose.
O Cells in liver break
down glycogen faster.
The released glucose
monomers enter blood.
Cells in skeletal muscle and liver store
glucose in the form of glycogen.
O Decrease in blood glucose
O Increase in blood glucose
(a) Explain how the cells communicate with one another.
(b) Using the diagram above, describe the differences between positive and negative feedback.
(c) The graph above shows a day in the life of A high school student's typical day consists of eating
before 8:00 am, lunch at 12:00 pm, dinner at 6:00 pm, and an evening snack around 10:00 pm. Using
the Blood Glucose levels and the chart above, explain how the glycogen levels of the liver change
over 24 using the communication among the cells and the feedback mechanisms.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Andrew presented to his doctor at the age of 13 with weight loss, decreased energy levels, frequent urination, fatigue, nausea, and unquenchable thirst. Andrew's doctor tested his blood glucose level and found it was very high at 250 mg/dL. The normal blood sugar range is between 70 - 130 mg/dL. Andrew's doctor immediately started him on insulin at 11:00 am. Andrew's Blood Sugar Levels 300 250 200 150 100 50 8:00 AM 9:00 AM 10:00 AM 11:00 AM 12:00 PM 1:00 PM 2:00 PM 3:00 PM 4:00 PM 5.00 PM 6:00 PM 7:00 PM Time Based on the information, what is the best explanation for how the negative feedback mechanism works to control the amount of sugar in Andrew's blood? Glucose from the food stimulates the pancreas to produce more insulin to regulate blood sugar. The pancreas produces insulin after a meal to decrease the amount of glucose in the blood to maintain homeostasis. The pancreas does not control homeostatic blood glucose levels by secreting insulin. O Insulin production increases hunger…arrow_forwardTriglycerides are metabolized in what cell types? O Muscle Cell Fat Cells Brain Cells Liver Cells O Skin Cellsarrow_forwardWhich of the following statements is true regarding the blood glucose level of non-insulin-dependent diabetics compared with that of normal individuals? O Blood glucose levels of diabetics tend to be very stable, but at a higher level. O Blood glucose levels of diabetics tend to be variable and higher. O Blood glucose levels decrease more rapidly following a meal, often dropping lower than is toleráble. O Blood glucose levels average the same level in diabetics but reach higher peaks for short periods. O None of the above is true.arrow_forward
- Which of the following cell(s)/tissue(s) require insulin to absorb glucose? leukocytes skeletal muscle neural tissue cardiac musclearrow_forwardESGU is Exercise stimulated glucose uptake Exercise stimulated glucose usage Due to alternate insulin receptors specifically active during exercise O An enhanced response to insulin observed in musclesarrow_forwardWhat are the main causes and treatments for hyperinsulinemia? O Causes; sustained high levels of insulin due to overeating, treatment; diet and exercise O hyperinsulinemia is a hoax. Fake news. O Causes; too much sugar, treatment; insulin injections O None of these is correct O Causes; too little sugar in the diet, treatments; frontal lobotomyarrow_forward
- What causes type 2 diabetes? O body does not possess insulin receptors O body produces too much insulin at all times receptors are resistant to insulin body does not produce insulin Oarrow_forwardAnswer Human Nutrition If you consume more protein than you need, the excess amino acids are stored as fat. What is one thing you CAN do to change your body so that your protein stores are greater? Hormones + exercise: Be able to explain the connection between epinephrine and fat. Where is epinephrine secreted? How does epinephrine help a person who has been exercising for longer than 20 minutes continue exercising? Hormones + exercise: Is insulin needed for exercise activity? Does your body make more or less insulin while you exercise? Be able to summarize effects of hormones + exercise: As blood glucose levels drop during exercise, there is less glucose in the blood available to enter cells and provide energy. The body needs to bring glucose into the blood, so glucose can travel to and enter the cell. What signals the liver and fat cells to release stored energy as glucose? What is the form of that stored energy in the liver? in fat cells? Be able to list the factors that…arrow_forwardMany processes in fat metabolism are regulated by hormones. Which of the following are activated by glucagon? i. Lipolysis in adipocytes ii. Fatty acid synthesis iii. Triacylglycerol synthesis iv. Cholesterol synthesis O ii and iii O i only O i only O ii, iii, and iv O iv onlyarrow_forward
- Rapid weight loss during the first days of a new diet occurs primarily from loss of O body fat O lean body mass O body water toxins that are flushed outarrow_forwardSelect all that are hydrolyzable lipids. Check all that apply. Vitamin K Triacylglycerol Omega-3 acid E Cephalin Coconut oil Progesterone None of the abovearrow_forwardYour body releases Anti Diuretic Hormone (ADH) from the pituitary gland when When you're hungry (you need to increase blood glucose) When you're stuffed (you need to store excess blood glucose) O You need to retain water (you're thirsty) You need to excrete water (there's too much in your body)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education

Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780134580999
Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:PEARSON

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781259398629
Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa Stouter
Publisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,

Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780815344322
Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter Walter
Publisher:W. W. Norton & Company

Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781260159363
Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, Cynthia
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.

Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9781260231700
Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael Windelspecht
Publisher:McGraw Hill Education