
Database System Concepts
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780078022159
Author: Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. Sudarshan
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
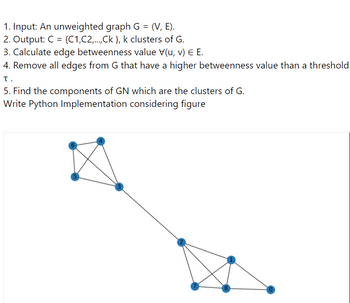
Transcribed Image Text:1. Input: An unweighted graph G = (V, E).
2. Output: C = {C1,C2,...,Ck }, k clusters of G.
3. Calculate edge betweenness value V(u, v) E E.
4. Remove all edges from G that have a higher betweenness value than a threshold
τ.
5. Find the components of GN which are the clusters of G.
Write Python Implementation considering figure
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, computer-science and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- unique please Your task for this assignment is to identify a spanning tree in one connected undirected weighted graph using C++. Implement a spanning tree algorithm using C++. A spanning tree is a subset of the edges of a connected undirected weighted graph that connects all the vertices together, without any cycles. The program is interactive. Graph edges with respective weights (i.e., v1 v2 w) are entered at the command line and results are displayed on the console. Each input transaction represents an undirected edge of a connected weighted graph. The edge consists of two unequal non-negative integers in the range 0 to 9 representing graph vertices that the edge connects. Each edge has an assigned weight. The edge weight is a positive integer in the range 1 to 99. The three integers on each input transaction are separated by space. An input transaction containing the string “end-of-file” signals the end of the graph edge input. After the edge information is read, the process…arrow_forwardJava programming.arrow_forwardProgram in C++arrow_forward
- RPN.java import java.util.Scanner; /** * Reverse Polish Notation calculator. It evaluates * a string with expressions in RPN format and prints * the results. Exampel of a stack use. */public class RPN{ /** * Given a string, return an integer version of * the string. Check if the string contains only * numbers, if so, then does the conversion. If * it does not, it reurns 0. * @param t string with numeric token * @return int version of the numeric token in t */ public int getValue(String t) { if (t.matches("[0-9]+")) { return Integer.parseInt(t); } else { return 0; } } /** * Evaluates a single token in an RPN expression. If it is * a number, it pushes the token to the stack. If it is an * operator, then it pulls 2 numbers from the stack, performs * the operation and pushes back into the stack the result. * @param token to be evaluated * @param stack holding values for…arrow_forwardYour task for this assignment is to identify a spanning tree in a connected undirected weighted graph using C++. 1. 2. 3. 4. Implement a spanning tree algorithm using C++. A spanning tree is an acyclic spanning subgraph of the of a connected undirected weighted graph. Your program will be interactive. Graph edges with respective weights (i.e., v1 v2 w) are entered at the command line and results are displayed on the console. Each input transaction represents an undirected edge of a connected weighted graph. The edge consists of two unequal uppercase letters representing graph vertices that the edge connects. Each edge has an assigned weight. The edge weight is a positive integer in the range 1 to 99. The three values on each input transaction are separated by a single space. An input transaction containing the string “end-of-file" signals the end of the graph edge input. After the edge information is read, the spanning tree evaluation process begins. Use an adjacency matrix for…arrow_forwardwrite a java code: Consider the following expression BNF: ::= * | / | :== + | - | ::= { }| :: 0|1|2|3|4|5|6|7|8|9 Using recursive descent, and only recursive descent, scan expressions that adhere to this BNF to build their expression tree; write an integer valued function that scans the tree to evaluate the expression represented by the tree. Input: A numeric expression adhering to this BNF. Output: Some representation of the expression tree. The result of evaluating the expression. write a java code for it.arrow_forward
- In Python the only import that may be used is Numpy Implement a function called page_rank which will take as input a numpy array M, which will represent the transition matrix of a directed graph, and a positive integer n. The output will be a numpy array which gives the page ranks of each vertex in the graph represented by M. You will iterate the update process n times.arrow_forwardPlease follow the instructions in the screenshots provided and use that to implement the code given below. Done in python 3.10 or later please. class WeightedAdjacencyMatrix : """A weighted graph represented as a matrix.""" __slots__ = ['_W'] def __init__(self, size, edges=[], weights=[]) : """Initializes a weighted adjacency matrix for a graph with size nodes. Graph is initialized with size nodes and a specified set of edges and edge weights. Keyword arguments: size -- Number of nodes of the graph. edges -- a list of ordered pairs (2-tuples) indicating the edges of the graph. The default value is an empty list which means no edges by default. weights -- a list of weights for the edges, which should be the same length as the edges list. The position of a value in the weights list corresponds to the edge in the same position of…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Database System ConceptsComputer ScienceISBN:9780078022159Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. SudarshanPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Database System ConceptsComputer ScienceISBN:9780078022159Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. SudarshanPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780134444321Author:Tony GaddisPublisher:PEARSON
Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780134444321Author:Tony GaddisPublisher:PEARSON Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780132737968Author:Thomas L. FloydPublisher:PEARSON
Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780132737968Author:Thomas L. FloydPublisher:PEARSON C How to Program (8th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780133976892Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey DeitelPublisher:PEARSON
C How to Program (8th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780133976892Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey DeitelPublisher:PEARSON Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337627900Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven MorrisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337627900Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven MorrisPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersComputer ScienceISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersComputer ScienceISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Database System Concepts
Computer Science
ISBN:9780078022159
Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. Sudarshan
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:9780134444321
Author:Tony Gaddis
Publisher:PEARSON

Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:9780132737968
Author:Thomas L. Floyd
Publisher:PEARSON

C How to Program (8th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:9780133976892
Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey Deitel
Publisher:PEARSON

Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...
Computer Science
ISBN:9781337627900
Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven Morris
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Computer Science
ISBN:9780073373843
Author:Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education