
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Topic Video
Question
22. A coconut falls out of a tree 10 m above the ground and hits a bystander 2.00 m tall on the top of the head. It
bounces back up 1 m before falling to the ground. If the mass of the coconut is 1.5 kg, calculate the potential energy
of the coconut relative to the ground at each of the following sites:
(a) while it is still in the tree, (b) when it hits the bystander on the head,
(c) when it bounces up to its maximum height, (d) when it lands on the ground,
(e) when it rolls into a groundhog hole, and falls 2 m to the bottom of the hole.
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1
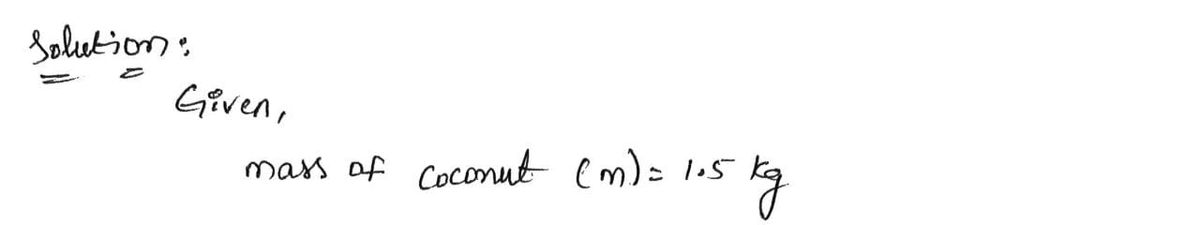
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- In the figure puck 1 of mass m₁ = 0.50 kg is sent sliding across a frictionless lab bench, to undergo a one-dimensional elastic collision with stationary puck 2. Puck 2 then slides off the bench and lands a distance d from the base of the bench. Puck 1 rebounds from the collision and slides off the opposite edge of the bench, landing a distance 5d from the base of the bench. What is the mass of puck 2? (Hint: Be careful with signs.) -5 d- Number i |d- Unitsarrow_forwardAt a post office, a package of mass 1.3 kg is pushed down a slanted chute with an initial speed of 1.8 m/s. The upper end of the chute if 4.0 m above the floor. When it reaches the floor, the package has a speed of 0.9 m/s. Determine the energy lost through air resistance and friction with the chute.arrow_forwardA 76.0-kg hiker is descending a mountain that has a peak altitude of 2350 m above sea level. The hiker has a device that measures her potential energy, and when she is at the peak of the mountain she decides to "zero" it (that is, she set's the zero point of potential energy to be the mountaintop). What does her potential energy device read sometime later on her descent when she is 1960 m above sea level?arrow_forward
- A cat's crinkle ball toy of mass 15 g is thrown straight up with an initial speed of 3 m/s. Assume in this problem that air drag is negligible. (a) What is the kinetic energy of the ball as it leaves the hand? (b) How much work is done by the gravitational force during the ball's rise to its peak? (c) What is the change in the gravitational potential energy of the ball during the rise to its peak?arrow_forward1. An object whose mass is 330.693 lb experiences changes in its kinetic and potential energies owing to the action of a resultant force R. The work done on the object by the resultant force is 163 Btu. There are no other interactions between the object and its surroundings. If the object's elevation increases by 90 ft and its final velocity is 150 ft/s, what is its initial velocity, in ft/s? Let g = 32.2 ft/s?.arrow_forwardA ball with a mass of 500 g is thrown directly upward by a boy standing over a 5 m hole in the ground. The ball leaves the boys hand at a height of 1 m above the ground and with a speed of 10 m/s. What is the total mechanical energy of the ball when it hits the bottom of the hole? Take ground level to be the zero of gravitational potential energy. Assume air resistance is negligible.arrow_forward
- A 350 g black was pressed against the spring of force constant of 1500 N/m until the block compresses the spring 8.0 cm. The spring rests at the bottom of a ramp inclined at θ=60.0° to the horizontal. By using energy considerations, determine how far up the incline the block moves from its initial position before it stops if: a) the ramp exerts no friction force on the block. b) if the coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.400.arrow_forward4arrow_forward"20 kg bear slides, from rest, 8 m down a Lodgepole Pine tree, moving with a speed of 5.6 m/s just before hitting the ground. What change occurs in the gravitational potential energy of the bear Earth system during the slide?"arrow_forward
- 1. A force of F = 5.6 Ni + 9.7 Nj + 7.9 Nk is applied to a particle in space to move it at a distance r = 2.6mi - 5.8mj - 9.7mk . Determine the work done by force.arrow_forward11:19 الامتحان النهائي العودة الوقت المتبقي :01. . . In the figure if h=10cm and the mass of the ball is 100g Find the potential energy of the ball at point a (relative (to the tabletop (g=10m/s²) ramp projectile Pats Table Top :Select one а. 1J b. 0.1J 10J d. 100J e. 0.01J أخل اختياري Plumb Line O o O O o IIarrow_forward2. A single conservative force acts on a 5.00 kg particle. The equation Fx describes the force, where x is in meters. As the particle moves along the x - axis from x = 1.00 m to x = 5.00m, calculate (a) the work done by this force (b) the change in the potential energy of the system (c) the kinetic energy of the article at x = 5.00 m if its speed is 3.00 m/s at x = 1.00 m. = (2.00x + 4.00) Narrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON