
Concept explainers
A fertilizer manufacturer has to fulfill supply contracts to its two main customers (650 tons to Customer A and 800 tons to Customer B). It can meet this demand by shipping existing inventory from any of its three warehouses. Warehouse 1 (W1) has 400 tons of inventory on hand, Warehouse 2 (W2) has 500 tons, and Warehouse 3 (W3) has 600 tons. The company would like to arrange the shipping for the lowest cost possible, where the per-ton transit costs are as follows:

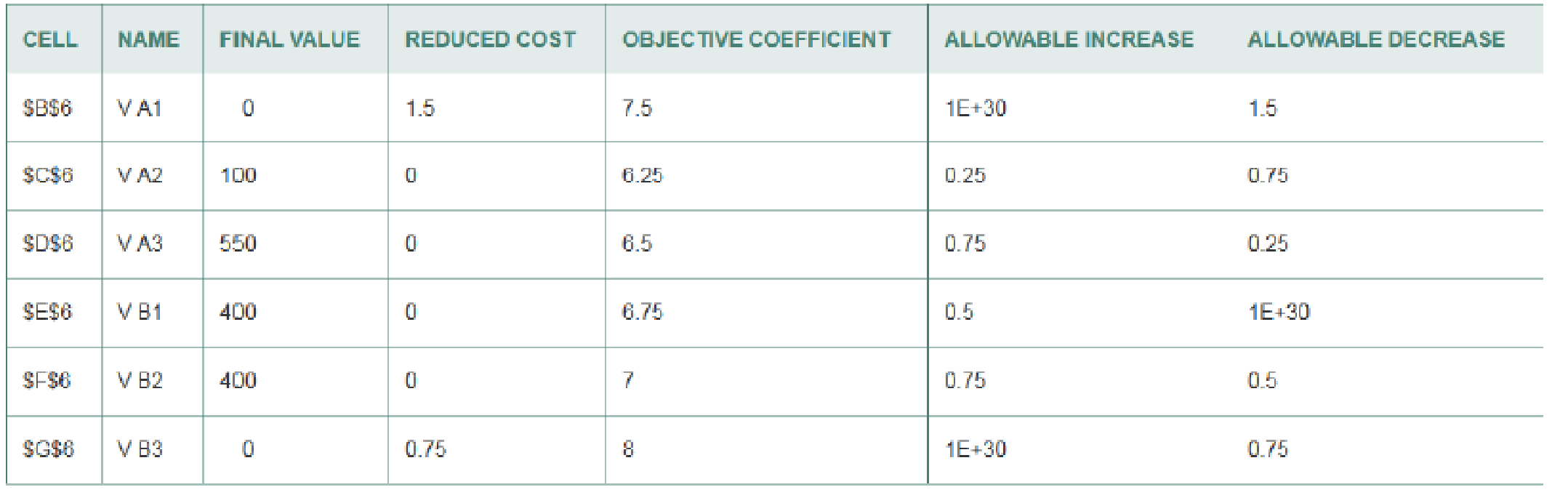
- a. Explain what each of the six decision variables (V) is: (Hint: Look at the Solver report below.)
V A1: _________
V A2: _________
V A3: _________
V B1: _________
V B2: _________
V B3: _________
- b. Write out the objective function in terms of the variables (V A1, V A2, etc,) and the objective coefficients.
- c. Aside from nonnegativity of the variables, what are the five constraints? Write a short description for each constraint, and write out the formula (and circle the type of equality/inequality).

After you formulate and enter the linear program for Problem B.27 in Excel, the Solver gives you the following sensitivity report:
Adjustable Cells
Constraints
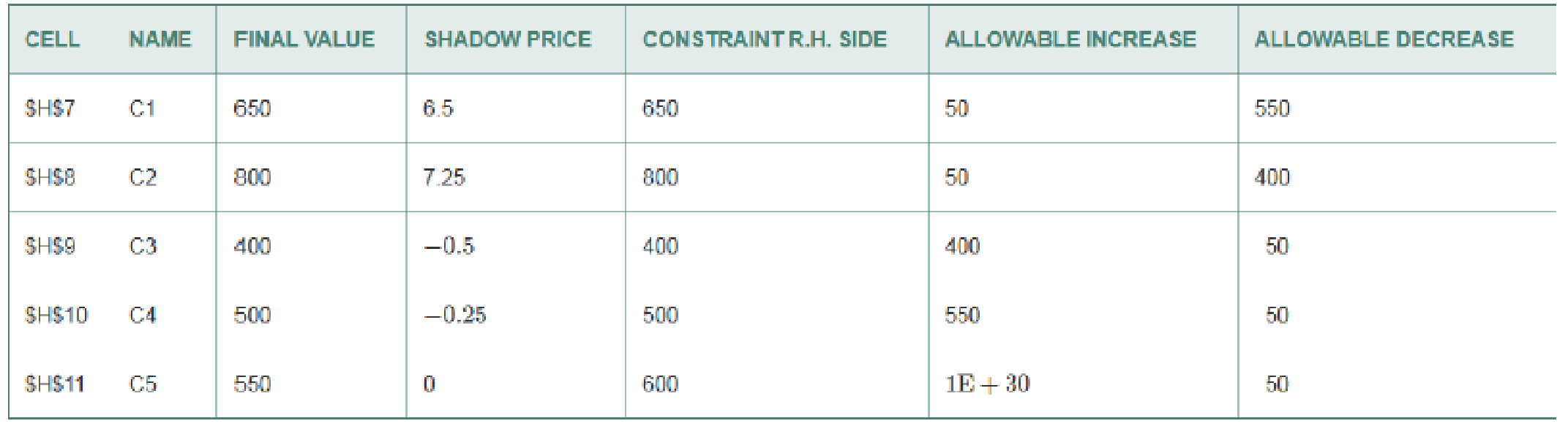
- d. d) How many of the constraints are binding?
- e. e) What is the range of optimality on variable V A3?
- f. f) If we could ship 10 tons less to Customer A, how much money might we be able to save? If we could choose to short either Customer A or Customer B by 10 tons, which would we prefer to short? Why?
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter B Solutions
Operations Management: Sustainability and Supply Chain Management (12th Edition)
- Scenario 3 Ben Gibson, the purchasing manager at Coastal Products, was reviewing purchasing expenditures for packaging materials with Jeff Joyner. Ben was particularly disturbed about the amount spent on corrugated boxes purchased from Southeastern Corrugated. Ben said, I dont like the salesman from that company. He comes around here acting like he owns the place. He loves to tell us about his fancy car, house, and vacations. It seems to me he must be making too much money off of us! Jeff responded that he heard Southeastern Corrugated was going to ask for a price increase to cover the rising costs of raw material paper stock. Jeff further stated that Southeastern would probably ask for more than what was justified simply from rising paper stock costs. After the meeting, Ben decided he had heard enough. After all, he prided himself on being a results-oriented manager. There was no way he was going to allow that salesman to keep taking advantage of Coastal Products. Ben called Jeff and told him it was time to rebid the corrugated contract before Southeastern came in with a price increase request. Who did Jeff know that might be interested in the business? Jeff replied he had several companies in mind to include in the bidding process. These companies would surely come in at a lower price, partly because they used lower-grade boxes that would probably work well enough in Coastal Products process. Jeff also explained that these suppliers were not serious contenders for the business. Their purpose was to create competition with the bids. Ben told Jeff to make sure that Southeastern was well aware that these new suppliers were bidding on the contract. He also said to make sure the suppliers knew that price was going to be the determining factor in this quote, because he considered corrugated boxes to be a standard industry item. Is Ben Gibson acting legally? Is he acting ethically? Why or why not?arrow_forwardScenario 3 Ben Gibson, the purchasing manager at Coastal Products, was reviewing purchasing expenditures for packaging materials with Jeff Joyner. Ben was particularly disturbed about the amount spent on corrugated boxes purchased from Southeastern Corrugated. Ben said, I dont like the salesman from that company. He comes around here acting like he owns the place. He loves to tell us about his fancy car, house, and vacations. It seems to me he must be making too much money off of us! Jeff responded that he heard Southeastern Corrugated was going to ask for a price increase to cover the rising costs of raw material paper stock. Jeff further stated that Southeastern would probably ask for more than what was justified simply from rising paper stock costs. After the meeting, Ben decided he had heard enough. After all, he prided himself on being a results-oriented manager. There was no way he was going to allow that salesman to keep taking advantage of Coastal Products. Ben called Jeff and told him it was time to rebid the corrugated contract before Southeastern came in with a price increase request. Who did Jeff know that might be interested in the business? Jeff replied he had several companies in mind to include in the bidding process. These companies would surely come in at a lower price, partly because they used lower-grade boxes that would probably work well enough in Coastal Products process. Jeff also explained that these suppliers were not serious contenders for the business. Their purpose was to create competition with the bids. Ben told Jeff to make sure that Southeastern was well aware that these new suppliers were bidding on the contract. He also said to make sure the suppliers knew that price was going to be the determining factor in this quote, because he considered corrugated boxes to be a standard industry item. As the Marketing Manager for Southeastern Corrugated, what would you do upon receiving the request for quotation from Coastal Products?arrow_forwardThe Tinkan Company produces one-pound cans for the Canadian salmon industry. Each year the salmon spawn during a 24-hour period and must be canned immediately. Tinkan has the following agreement with the salmon industry. The company can deliver as many cans as it chooses. Then the salmon are caught. For each can by which Tinkan falls short of the salmon industrys needs, the company pays the industry a 2 penalty. Cans cost Tinkan 1 to produce and are sold by Tinkan for 2 per can. If any cans are left over, they are returned to Tinkan and the company reimburses the industry 2 for each extra can. These extra cans are put in storage for next year. Each year a can is held in storage, a carrying cost equal to 20% of the cans production cost is incurred. It is well known that the number of salmon harvested during a year is strongly related to the number of salmon harvested the previous year. In fact, using past data, Tinkan estimates that the harvest size in year t, Ht (measured in the number of cans required), is related to the harvest size in the previous year, Ht1, by the equation Ht = Ht1et where et is normally distributed with mean 1.02 and standard deviation 0.10. Tinkan plans to use the following production strategy. For some value of x, it produces enough cans at the beginning of year t to bring its inventory up to x+Ht, where Ht is the predicted harvest size in year t. Then it delivers these cans to the salmon industry. For example, if it uses x = 100,000, the predicted harvest size is 500,000 cans, and 80,000 cans are already in inventory, then Tinkan produces and delivers 520,000 cans. Given that the harvest size for the previous year was 550,000 cans, use simulation to help Tinkan develop a production strategy that maximizes its expected profit over the next 20 years. Assume that the company begins year 1 with an initial inventory of 300,000 cans.arrow_forward
- The Tubular Ride Boogie Board Company has manufacturing plants in Tucson, Arizona and Toronto, Ontario. You have been given the job of coordinating distribution of the latest model, the Gladiator, to outlets in Honolulu and Venice Beach. The Tucson plant, when operating at full capacity, can manufacture 620 Gladiator boards per week, while the Toronto plant, beset by labor disputes, can produce only 410 boards per week. The outlet in Honolulu orders 500 Gladiator boards per week, while Venice Beach orders 530 boards per week. Transportation costs are as follows. Tucson to Honolulu: $10 per board; Tucson to Venice Beach: $5 per board. Toronto to Honolulu: $20 per board; Toronto to Venice Beach: $10 per board. (a) Assuming that you wish to fill all orders and ensure full capacity production at both plants, is it possible to meet a total transportation budget of $9,900? O Yes O No If so, how many Gladiator boards are shipped from each manufacturing plant to each distribution outlet? (If…arrow_forwardDivision A has costs of $30 per unit, and transfers goods to Division B which has additional costs of $20 per unit. Division B sells externally at $70 per unit. Division A can sell part-finished units externally for $40 per unit. There is unlimited demand externally from A, and A has limited production capacity. What are the minimum and maximum transfer prices in order to achieve goal congruent decisions?arrow_forward) O'Donnell & Joyce purchases components from three suppliers. Components purchased from Supplier A are priced at €7 each and used at the rate of 18,000 units per month. Components purchased from Supplier B are priced at €5 each and are used at the rate of 4,500 units per month. Components purchased from Supplier C are priced at €9 each and used at the rate of 1000 units per month. Currently, O'Donnell & Joyce purchases a separate truckload from each supplier. As part of its JIT drive, O'Donnell & Joyce has decided to aggregate purchases from the three suppliers. The trucking company charges a fixed cost of €550 for the truck with an additional charge of €120 for each stop. Thus, if O'Donnell & Joyce asks for a pickup from only one supplier, it charges €670; from two suppliers, it charges €790; and from three suppliers, it charges €910. What replenishment strategy would you suggest for O'Donnell & Joyce to minimize annual costs? Assume an annual holding cost of 25…arrow_forward
- please answer in 30 mins. do no attempt if not sure.arrow_forwardRuby-Star Incorporated is considering two different vendors for one of its top-selling products which has an average weekly demand of 30 units and is valued at $100 per unit. Inbound shipments from vendor 1 will average 300 units with an average lead time (including ordering delays and transit time) of 4 weeks. Inbound shipments from vendor 2 will average 490 units with an average lead time of 1 week. Ruby-Star operates 52 weeks per year; it carries a 4-week supply of inventory as safety stock and no anticipation inventory. a. The average aggregate inventory value of the product if Ruby-Star used vendor 1 exclusively is $39,000. (Enter your response as a whole number.) b. The average aggregate inventory value of the product if Ruby-Star used vendor 2 exclusively is $ (Enter your response as a whole number.)arrow_forwardRuby-Star Incorporated is considering two different vendors for one of its top-selling products which has an average weekly demand of 60 units and is valued at $60 per unit. Inbound shipments from vendor 1 will average 370 units with an average lead time (including ordering delays and transit time) of 5 weeks. Inbound shipments from vendor 2 will average 520 units with an average lead time of 1 week. Ruby-Star operates 52 weeks per year; it carries a 5-week supply of inventory as safety stock and no anticipation inventory. a. What would be the average aggregate inventory value of this product if Ruby-Star used vendor 1 exclusively?b. What would be the average aggregate inventory value of this product if Ruby-Star used vendor 2 exclusively?c. How would your analysis change if average weekly demand increased to 100 units per week?arrow_forward
- Please solve completearrow_forwardAfter applying the NWC Rule for the initial tableau of the given transportation model, evaluate the vacant cells. What is the cell which has the most negative evaluation value and what is the cell evaluation value? DESTINATION SOURCE DEMAND X Y N OX-R; 1 OY-S; -1 OX-S; -1 OY-S; -2 P 75 8 12 EI 11 Q 80 5 8 11 R 120 7 10 10 S 50 11 13 14 SUPPLY 100 125 100 325arrow_forwardBoston Company use a special part in manufacturing of its finished products. The unit cost thisspecial part is $ 35, and details of its manufacturing cost is as follows. The $35 unit productcost of this part is based on average 25,000 number of parts produced each year.An outside supplier has offered to supply the 25,000 parts at a cost of $30 per part. The specialequipment used to manufacture the above part. This equipment can only be used formanufacturing of this part and if not used it has no resale value.The total amount of general factory overhead, which is allocated based on direct labor-hours,would be unaffected by this decision because it is fixed cost..Suggest the management whether to stop producing internally and buy them from theoutside supplier?Description CAD Direct Materials 10Direct Labor 6Variable overheads…arrow_forward
 Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage,
Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage, Purchasing and Supply Chain ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781285869681Author:Robert M. Monczka, Robert B. Handfield, Larry C. Giunipero, James L. PattersonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Purchasing and Supply Chain ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781285869681Author:Robert M. Monczka, Robert B. Handfield, Larry C. Giunipero, James L. PattersonPublisher:Cengage Learning

