
For Problems 7-21, please provide the following information.
(a) What is the level of significance? Stale the null and alternate hypotheses, (b) Check Requirements What sampling distribution will you use? Do you think the sample size is sufficiently large? Explain Compute the value of the sample test statistic and corresponding z value. (c) Find the P-value of the test statistic Sketch the sampling distribution and show the area corresponding to the P-value.
(d) Based on sour answers in parts (a) to (c), will you reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis? Are the data statistic ally significant at level α?
(c) Interpret your conclusion in the context of the application.
Focus Problem: Benford's Law Please read the Focus Problem at the beginning of this chapter. Recall that Benford's Lam claims that numbers chosen from very large data files lend to have " 1“ as the first nonzero digit disproportionately often. In fact, research has shown that if you randomly draw a number from a very large data file, the
Now suppose you are an auditor for a very large corporation. The revenue report involves millions of numbers in a large computer file. Let us say you took a random sample of n = 215numerical entries from the file, and r = 46 of the entries had a first nonzero digit of 1. Let p represent the population proportion of all numbers in the corporate file that have a first nonzero digit of 1.
Test the claim that p is less than 0.301 Use α=0.01.
If p is in fact less than 0.301, would it make you suspect that there are not enough numbers in the data file with leading Is? Could this indicate that the books have been “cooked" by “pumping up" or inflating the numbers? Comment from the view point of a stockholder. Comment from the perspective of the Federal Bureau of Investigation as ii looks for money laundering in the form of false profits.
iii. Comment on the following statement “If we reject the null hypothesis at level of significance α. we have not proved H0 to be false. We can say that the probability is α that we made a mistake in rejecting H0.” Based on the outcome of the test, would you recommend further investigation before accusing the company of fraud ?
(i)
(a)
The level of significance, null and alternative hypothesis.
Answer to Problem 7P
Solution: The level of significance is α=0.01. The null hypothesis is H0:p=0.301 and alternative hypothesis HA:p<0.301.
Explanation of Solution
The level of significance is defined as the probability of rejecting the null hypothesis when it is true, it is denoted by α=0.01.
Null hypothesis H0:p=0.301
Alternative hypothesis HA:p<0.301
(b)
To find: The sampling distribution that should be used and compute the z value of the sample test statistic.
Answer to Problem 7P
Solution: The sampling distribution ˉx is normal. The sample test statistic, z is -2.78.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
The ˆp distribution is approximately normal, with mean p and standard deviation √pqn.
p=0.301, q=1−p=0.699ˆp=rnˆp=46215=0.214
The standardized sample test statistic for ˆp is
z=(ˆp−p)√pqnz=(0.214−0.301)√0.301(1−0.301)215z=−2.783z≈−2.78
(c)
To find: The P-value of the test statistic and sketch the sampling distribution showing the area corresponding to the P-value.
Answer to Problem 7P
Solution: The P-value of the test statistic is 0.0027.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
We have z = -2.78
P−value = P(z<−2.78)
Using Table 3 from the Appendix to find the specified area:
P−value = 0.0027
Thus P- value is 0.0027.
Graph:
To draw the required graphs using the Minitab, follow the below instructions:
Step 1: Go to the Minitab software.
Step 2: Go to Graph > Probability distribution plot > View probability.
Step 3: Select ‘Normal’ and enter Mean 0 and Standard deviation 1.
Step 4: Click on the Shaded area > X value.
Step 5: Enter X-value as -2.78 and select ‘Left tail’.
Step 6: Click on OK.
The obtained distribution graph is:
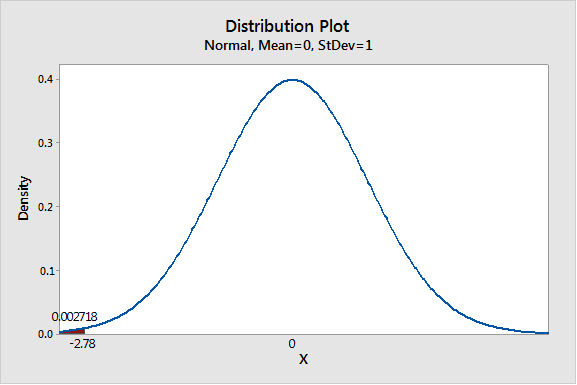
P−value ≈ 0.0027
(d)
Whether we reject or fail to reject the null hypothesisand whether the data is statistically significant for a level of significance of 0.01.
Answer to Problem 7P
Solution: The P-value <α, hence we have to reject the H0. The data is statistically significant for a level of significance of 0.01.
Explanation of Solution
The P-value of 0.0027 is less than the level of significance (α) of 0.01. Therefore we have enough evidence to reject the null hypothesis H0, hence the data is statistically significant for a level of significance of 0.01.
(e)
The interpretation for the conclusion.
Answer to Problem 7P
Solution: There is enough evidence to conclude that population proportion of numbers with leading “1” in the revenue file is less than the probability 0.301 predicted by Benford’s law.
Explanation of Solution
The P-value of 0.0027 is less than the level of significance (α) of 0.01. Therefore we have enough evidence to reject the null hypothesis H0. There is enough evidence to conclude that population proportion of numbers with leading “1” in the revenue file is less than the probability 0.301 predicted by Benford’s law.
(ii)
To explain: Whether it is suspect that there are not enough numbers in the data file with leading 1's.
Answer to Problem 7P
Solution: Yes. The revenue data file seems to include more numbers with higher first nonzero digits than Benford's law predicts.
Explanation of Solution
There are not enough numbers in the data file with leading 1's than Benford's law predicts. So, we cannot say that it is an indication of the books have been “cooked” by “pumping up” or inflating the numbers. From the viewpoint of a stockholder and the Federal Bureau of Investigation as it looks for money laundering, it may be true or false profit because there are not enough numbers in the data file with leading 1’s.
(iii)
To explain: Whether it recommends further investigation before accusing the company of fraud.
Answer to Problem 7P
Solution: Our data lead us to reject the null hypothesis, more investigation is merited.
Explanation of Solution
Since, we reject the null hypothesis H0 at level of significance 0.01 but we have not proved H0 to be false. Because our data lead us to reject the null hypothesis and we conclude that there are not enough numbers in the data file with leading 1's. Hence, we recommend further investigation before accusing the company of fraud because more investigation will give better results.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
Understanding Basic Statistics
- Question 6: Negate the following compound statements, using De Morgan's laws. A) If Alberta was under water entirely then there should be no fossil of mammals.arrow_forwardNegate the following compound statement using De Morgans's laws.arrow_forwardCharacterize (with proof) all connected graphs that contain no even cycles in terms oftheir blocks.arrow_forward
- Let G be a connected graph that does not have P4 or C3 as an induced subgraph (i.e.,G is P4, C3 free). Prove that G is a complete bipartite grapharrow_forwardProve sufficiency of the condition for a graph to be bipartite that is, prove that if G hasno odd cycles then G is bipartite as follows:Assume that the statement is false and that G is an edge minimal counterexample. That is, Gsatisfies the conditions and is not bipartite but G − e is bipartite for any edge e. (Note thatthis is essentially induction, just using different terminology.) What does minimality say aboutconnectivity of G? Can G − e be disconnected? Explain why if there is an edge between twovertices in the same part of a bipartition of G − e then there is an odd cyclearrow_forwardLet G be a connected graph that does not have P4 or C4 as an induced subgraph (i.e.,G is P4, C4 free). Prove that G has a vertex adjacent to all othersarrow_forward
- We consider a one-period market with the following properties: the current stock priceis S0 = 4. At time T = 1 year, the stock has either moved up to S1 = 8 (with probability0.7) or down towards S1 = 2 (with probability 0.3). We consider a call option on thisstock with maturity T = 1 and strike price K = 5. The interest rate on the money marketis 25% yearly.(a) Find the replicating portfolio (φ, ψ) corresponding to this call option.(b) Find the risk-neutral (no-arbitrage) price of this call option.(c) We now consider a put option with maturity T = 1 and strike price K = 3 onthe same market. Find the risk-neutral price of this put option. Reminder: A putoption gives you the right to sell the stock for the strike price K.1(d) An investor with initial capital X0 = 0 wants to invest on this market. He buysα shares of the stock (or sells them if α is negative) and buys β call options (orsells them is β is negative). He invests the cash balance on the money market (orborrows if the amount is…arrow_forwardDetermine if the two statements are equivalent using a truth tablearrow_forwardQuestion 4: Determine if pair of statements A and B are equivalent or not, using truth table. A. (~qp)^~q в. р л~9arrow_forward
- Determine if the two statements are equalivalent using a truth tablearrow_forwardQuestion 3: p and q represent the following simple statements. p: Calgary is the capital of Alberta. A) Determine the value of each simple statement p and q. B) Then, without truth table, determine the va q: Alberta is a province of Canada. for each following compound statement below. pvq р^~q ~рл~q ~q→ p ~P~q Pq b~ (d~ ← b~) d~ (b~ v d) 0 4arrow_forward2. Let X be a random variable. (a) Show that, if E X2 = 1 and E X4arrow_forward
 College Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305652231Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff HughesPublisher:Cengage Learning
College Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305652231Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff HughesPublisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill

