
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The
Concept introduction:
The compounds which have the same molecular formula but have different arrangements of atoms are known as isomers. The phenomenon is called isomerism. The isomers are generally classified as structural isomers and stereoisomers. Stereoisomers are further divided into two categories diastereomers and enantiomers.
Answer to Problem 9.44AP
The isomers of
Explanation of Solution
The structures of
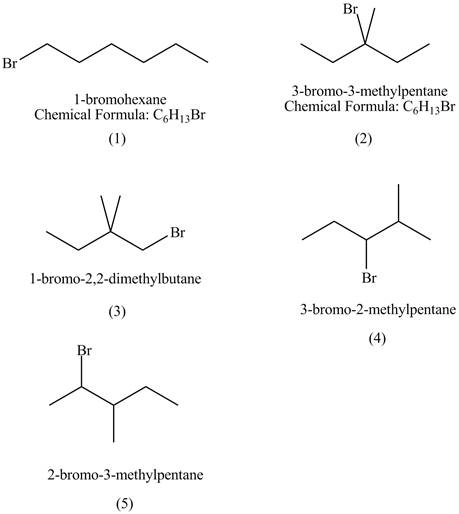
Figure 1
The compounds that have chiral centers can exist as enantiomers. The compound
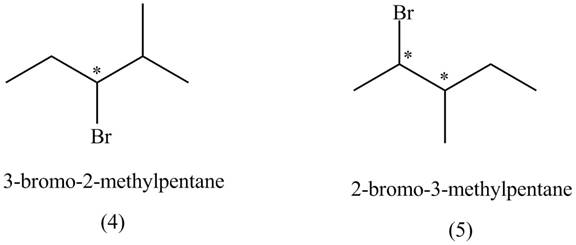
Figure 2
Therefore,
The compounds
(b)
Interpretation:
The alkyl halides among
Concept introduction:
The compounds which have the same molecular formula but have different arrangements of atoms are known as isomers. The phenomenon is called isomerism. The isomers are generally classified as structural isomers and stereoisomers. Stereoisomers are further divided into two categories diastereomers and enantiomers.
Answer to Problem 9.44AP
The isomer of
Explanation of Solution
The structures of
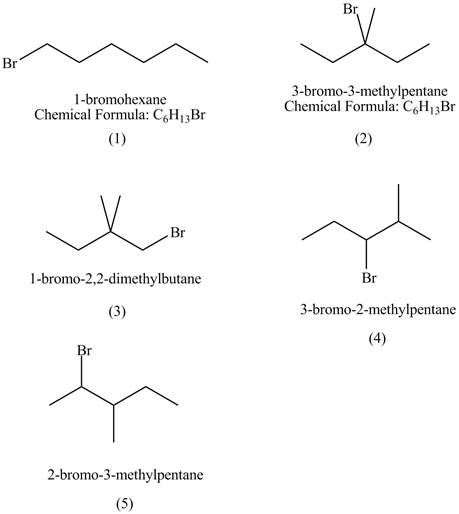
Figure 1
The compounds that have two chiral centers can exist as enantiomers. The compound
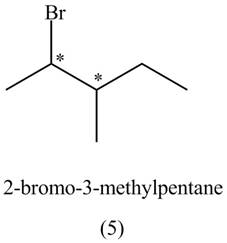
Figure 3
Therefore,
The compound
(c)
Interpretation:
The alkyl halides among
Concept introduction:
The replacement or substitution of one functional group with another different functional group in any chemical reaction is termed as a substitution reaction. In a nucleophilic substitution reaction, nucleophile takes the position of leaving the group by attacking on the electron-deficient carbon atom.
Answer to Problem 9.44AP
The fastest
Explanation of Solution
The structures of
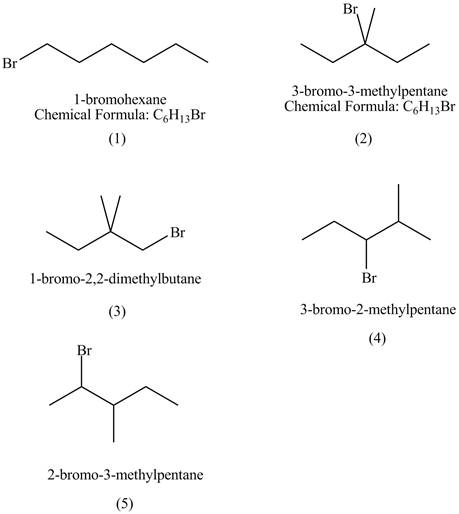
Figure 1
The rate of
The compound
The compound
(d)
Interpretation:
The alkyl halides among
Concept introduction:
The replacement or substitution of one
Answer to Problem 9.44AP
The isomer of
Explanation of Solution
The structures of

Figure 1
The compound
The compound,
(e)
Interpretation:
The alkyl halides among
Concept introduction:
The elimination reaction of alkyl halide involves removal of the halogen atom and hydrogen atom from the adjacent carbon atoms, which leads to the formation of the alkene. A bulky base increases the chance of elimination reaction of substitution reaction.
Answer to Problem 9.44AP
The compound
Explanation of Solution
The structures of
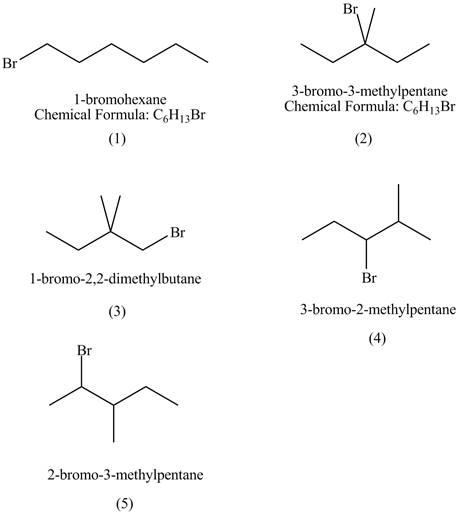
Figure 1
The compound
The
(f)
Interpretation:
The alkyl halides among
Concept introduction:
The replacement or substitution of one functional group with another different functional group in any chemical reaction is termed as a substitution reaction. In a nucleophilic substitution reaction, nucleophile takes the position of leaving the group by attacking on the electron-deficient carbon atom.
Answer to Problem 9.44AP
The alkyl halide among
Explanation of Solution
The structures of
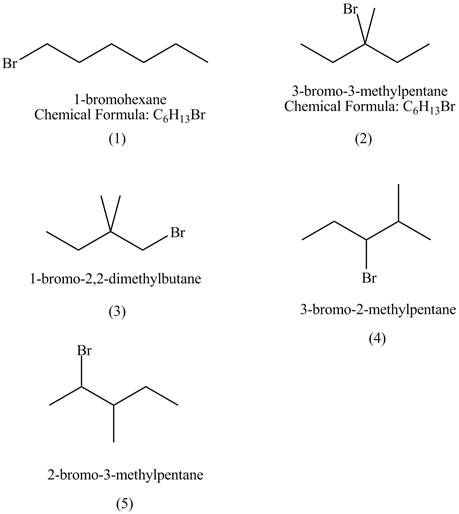
Figure 1
The rate of
The steric hindrance in case of
The isomer of
(g)
Interpretation:
The alkyl halides among
Concept introduction:
The replacement or substitution of one functional group with another different functional group in any chemical reaction is termed as a substitution reaction. In a nucleophilic substitution reaction, nucleophile takes the position of leaving the group by attacking on the electron-deficient carbon atom.
Answer to Problem 9.44AP
The alkyl halides among
Explanation of Solution
The structures of

Figure 1
The stability of tertiary carbocation is more than the stability of secondary carbocation. Therefore, in case of
The isomer of
(h)
Interpretation:
The alkyl halide among
Concept introduction:
The replacement or substitution of one functional group with another different functional group in any chemical reaction is termed as a substitution reaction. In a nucleophilic substitution reaction, nucleophile takes the position of leaving the group by attacking on the electron-deficient carbon atom.
Answer to Problem 9.44AP
The alkyl halide among
Explanation of Solution
The structures of

Figure 1
The rate of
Therefore,
The isomer of
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- 19.57 Using one of the reactions in this chapter, give the correct starting material (A-L) needed to produce each structure (a-f). Name the type of reaction used. (b) ہ مرد (d) HO (c) དང་ ་་ཡིན་ད་དང་ (f) HO Br B D of oli H J Br K C 人 ↑arrow_forwardInductive effect (+I and -I) in benzene derivatives.arrow_forward7. Helparrow_forward
 Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning


