
Concept explainers
MTI makes three types of lawn tractors: M3100, M4100, and M6100. In the past, it allocated
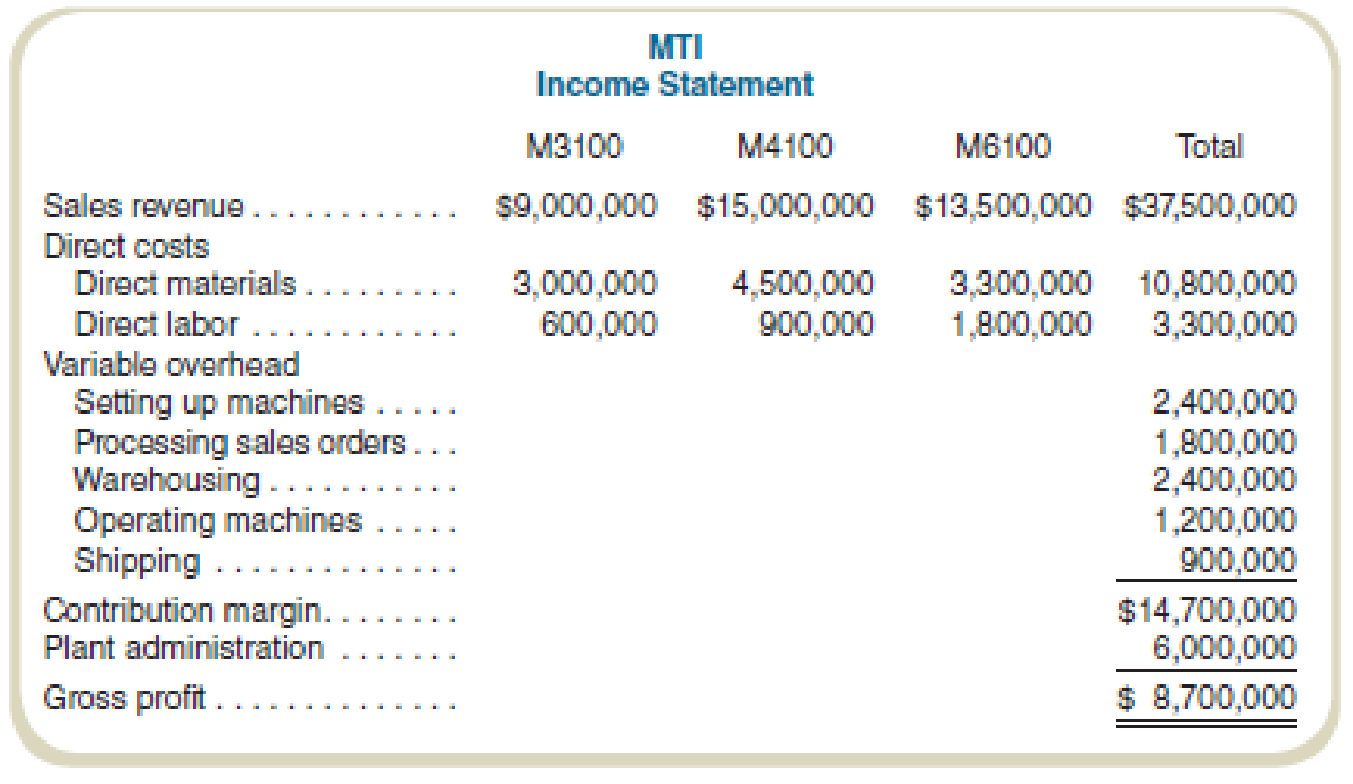
MTI’s controller has heard about activity-based costing and puts together an employee team to recommend cost allocation bases. The employee team recommends the following:

The employee team recommends that plant administration costs not be allocated to products.
Required
- a. Using machine-hours to allocate overhead, complete the income statement for MTI. Do not allocate plant administrative costs to products.
- b. Complete the income statement using the activity-based costing method suggested by the employee team.
- c. Write a brief report indicating how activity-based costing might result in better decisions by MTI.
- d. After hearing the recommendations, the president expresses concern about failing to allocate plant administrative costs. If plant administrative costs were to be allocated to products, how would you allocate them?
a.
Complete the income statement in accordance with the information given in the question.
Explanation of Solution
Activity-based costing:
Activity-based costing refers to the method of costing where the overhead cost is assigned to various products. This costing method identifies the relationship between the manufacturing overhead costs and the activities. This relationship is then used to allocate indirect costs to the products.
Complete the income statement:
| Particulars | M3100 | M4100 | M6100 | Total |
| Sales revenue | $9,000,000 | $15,000,000 | $13,500,000 | $37,500,000 |
| Add: Direct costs: | ||||
| Direct material | $3,000,000 | $4,500,000 | $3,300,000 | $10,800,000 |
| Direct labor | $600,000 | $900,000 | $1,800,000 | $3,300,000 |
|
Variable overhead | $2,088,000 | $3,132,000 | $3,480,000 | $8,700,000 |
| Contribution margin | $3,312,000 | $6,468,000 | $4,920,000 | $14,700,000 |
| Less: Plant admin | $6,000,000 | |||
| Gross profit | $8,700,000 |
Table: (1)
Working note 1:
Compute the machine hour rate:
b.
Complete the income statement in accordance with the information given in the question.
Explanation of Solution
Activity-based costing:
Activity-based costing refers to the method of costing where the overhead cost is assigned to various products. This costing method identifies the relationship between the manufacturing overhead costs and the activities. This relationship is then used to allocate indirect costs to the products.
Compute the cost driver rates:
| Particulars | Cost | Activity volume | Unit rate | |
| Setting up machines | $2,400,000 | 50 Production runs | $48,000 | |
| Processing sales orders | $1,800,000 | 800 Sales orders | $2,250 | |
| Warehousing | $2,400,000 | 400 Units | $6,000 | |
| Operating machines | $1,200,000 | 25,000 Machine-hours | $48 | |
| Shipping | $900,000 | 37,500 Units shipped | $24 |
Table: (2)
Complete the income statement using the activity-based costing system:
| Particulars | M3100 | M4100 | M6100 | Total |
| Sales revenue | $9,000,000 | $15,000,000 | $13,500,000 | $37,500,000 |
| Direct costs: | ||||
| Direct material | $3,000,000 | $4,500,000 | $3,300,000 | $10,800,000 |
| Direct labor | $600,000 | $900,000 | $1,800,000 | $3,300,000 |
| Variable overhead: | ||||
|
Setting up machines | $480,000 | $960,000 | $960,000 | $2,400,000 |
|
Processing orders | $405,000 | $900,000 | $495,000 | $1,800,000 |
|
Warehousing | $600,000 | $1,200,000 | $600,000 | $2,400,000 |
|
Operating machines | $288,000 | $432,000 | $480,000 | $1,200,000 |
|
Shipping | $240,000 | $420,000 | $240,000 | $900,000 |
| Contribution margin | $3,387,000 | $5,688,000 | $5,625,000 | $14,700,000 |
| Less: Plant admin | $6,000,000 | |||
| Gross profit | $8,700,000 |
Table: (3)
c.
Write a brief report according to the information given in the question.
Explanation of Solution
Activity-based costing:
Activity-based costing refers to the method of costing where the overhead cost is assigned to various products. This costing method identifies the relationship between the manufacturing overhead costs and the activities. This relationship is then used to allocate indirect costs to the products.
The relevance of the activity-based costing system according to the information given in the question:
The computed income statement by the machine-hour method and activity-based costing method are equal. Thus, the choice of method will not have any impact on the choice of the method used for the determination of profit and cost.
But, choosing the activity-based method of computation provides a better assessment of the costing structure. The allocation of cost on the basis of cost drivers helps management taking informed decision.
d.
Determine the cost allocation according to the information given in the question.
Explanation of Solution
Activity-based costing:
Activity-based costing refers to the method of costing where the overhead cost is assigned to various products. This costing method identifies the relationship between the manufacturing overhead costs and the activities. This relationship is then used to allocate indirect costs to the products.
The relevance of plant administration cost with respect to the information given in the question:
The allocation of the cost should be in a manner that can establish a relationship between benefits and the plant administration cost. The more information related to the plant administration cost would help establish the correlation better for the identification of the parts of the plant administration cost.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
Fundamentals Of Cost Accounting (6th Edition)
 Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning Excel Applications for Accounting PrinciplesAccountingISBN:9781111581565Author:Gaylord N. SmithPublisher:Cengage Learning
Excel Applications for Accounting PrinciplesAccountingISBN:9781111581565Author:Gaylord N. SmithPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,Principles of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,Principles of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning





