
Concept explainers
Choosing an Activity-Based Costing System
Pickle Motorcycles, Inc. (PMI), manufactures three motorcycle models: a cruising bike (Route 66), a street bike (Main Street), and a starter model (Alley Cat). Because of the different materials used, production processes for each model differ significantly in terms of machine types and time requirements. Once parts are produced, however, assembly time per unit required for each type of bike is similar. For this reason, PMI allocates
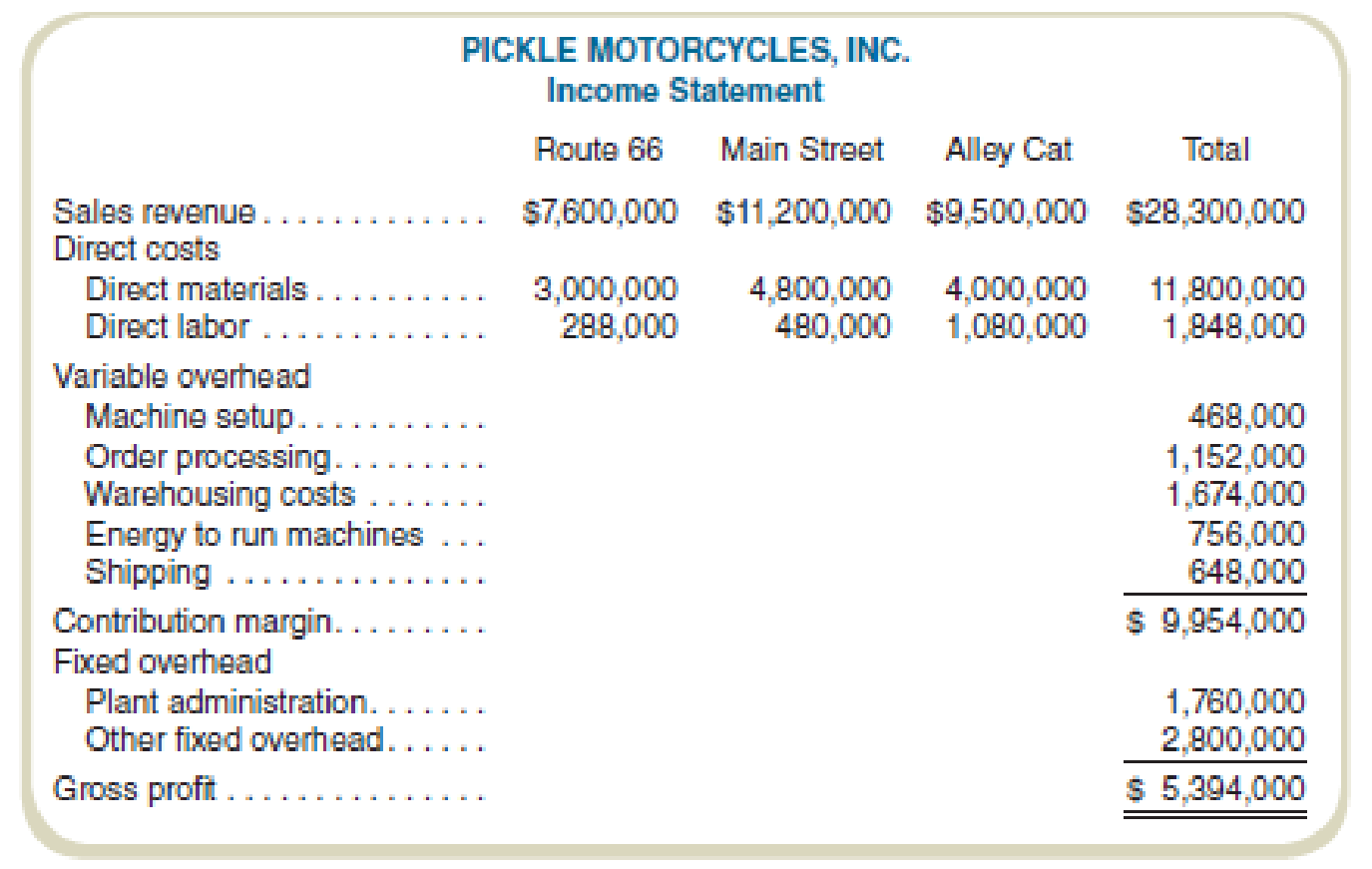
PMI’s chief financial officer (CFO) hired a consultant to recommend cost allocation bases. The consultant recommended the following:

The consultant found no basis for allocating the plant administration and other fixed overhead costs and recommended that these not be applied to products.
Required
- a. Using machine-hours to allocate production overhead, complete the income statement for Pickle Motorcycles. (See the “using energy” activity for machine-hours.) Do not attempt to allocate plant administration or other fixed overhead.
- b. Complete the income statement using the bases recommended by the consultant.
- c. How might activity-based costing result in better decisions by Pickle Motorcycles’s management?
- d. After hearing the consultant’s recommendations, the CFO decides to adopt activity-based costing but expresses concern about not allocating some of the overhead to the products (plant administration and other fixed overhead). In the CFO’s view, “Products have to bear a fair share of all overhead or we won’t be covering all of our costs.” How would you respond to this comment?
a.
Complete the income statement.
Explanation of Solution
Traditional labor-hour based costing method:
Traditional labor-hour based costing method assumes that the direct labor-hour is the base allocation of the process. The process of allocation of overhead computes the indirect overhead with respect to the labor-hours only.
Complete the income statement:
| Particulars | Route 66 | Main street | Alley cat | Total |
| Sales revenue | $7,600,000 | $11,200,000 | $9,500,000 | $28,300,000 |
| Direct costs: | ||||
| Direct materials | $3,000,000 | $4,800,000 | $4,000,000 | $11,800,000 |
| Direct labor | $288,000 | $480,000 | $1,080,000 | $1,848,000 |
|
Variable overhead | $939,600 | $1,503,360 | $2,255,040 | $4,698,000 |
| Contribution margin | $3,372,400 | $4,416,640 | $2,164,960 | $9,954,000 |
| Fixed overhead: | ||||
| Plant admin | $1,760,000 | |||
| Other | $2,800,000 | |||
| Gross profit | $5,394,000 |
Table: (1)
Compute the rate of variable overhead:
Thus, the rate of variable overhead is $93.96.
b.
Complete the income statement using the recommendations.
Explanation of Solution
Activity-based costing (ABC):
Activity-based costing is the method of costing where the overhead cost is assigned to various products. This method of costing establishes the relationship between the manufacturing overhead costs and the activities. The relationship is then implemented for the allocation of indirect costs to the products.
Complete the income statement using the recommendations:
| Particulars | Route 66 | Main street | Alley cat | Total |
| Sales revenue | $7,600,000 | $11,200,000 | $9,500,000 | $28,300,000 |
| Direct costs: | ||||
| Direct materials | $3,000,000 | $4,800,000 | $4,000,000 | $11,800,000 |
| Direct labor | $288,000 | $480,000 | $1,080,000 | $1,848,000 |
| Variable overhead | ||||
|
Machine setup | $102,960 | $159,120 | $205,920 | $468,000 |
|
Order processing | $288,000 | $432,000 | $432,000 | $1,152,000 |
|
Warehousing | $418,500 | $418,500 | $837,000 | $1,674,000 |
|
Energy | $151,200 | $241,920 | $362,880 | $756,000 |
|
Shipping | $43,200 | $172,800 | $432,000 | $648,000 |
|
Contribution margin | $3,308,140 | $4,495,660 | $2,150,200 | $9,954,000 |
| Fixed overhead | ||||
| Plant admin | $1,760,000 | |||
| Other | $2,800,000 | |||
| Gross profit | $5,394,000 |
Table: (2)
Compute the applicable rate:
| Particulars | Total cost | Total respective units | Applicable rate |
| Machine setup | $468,000 | 100 | $4,680 |
| Order processing | $1,152,000 | 1,600 | $720 |
| Warehousing | $1,674,000 | 800 | $2,093 |
| Energy | $756,000 | 50,000 | $15 |
| Shipping | $648,000 | 15,000 | $43 |
Table: (3)
c.
Determine how activity-based costing result is better.
Explanation of Solution
Activity-based costing (ABC):
Activity-based costing is the method of costing where the overhead cost is assigned to various products. This method of costing establishes the relationship between the manufacturing overhead costs and the activities. The relationship is then implemented for the allocation of indirect costs to the products.
Traditional labor-hour based costing method:
Traditional labor-hour based costing method assumes that the direct labor-hour is the base allocation of the process. The process of allocation of overhead computes the indirect overhead with respect to the labor-hours only.
The relevance of ABC method:
The ABC method gives a better and detailed cost structure of the process. A better cost report will provide a better assessment of the costing. The information that is churned out enables the management to take appropriate decisions.
d.
Provide the appropriate response to the statement in question.
Explanation of Solution
Activity-based costing (ABC):
Activity-based costing is the method of costing where the overhead cost is assigned to various products. This method of costing establishes the relationship between the manufacturing overhead costs and the activities. The relationship is then implemented for the allocation of indirect costs to the products.
The statement in question:
“Products have to bear a fair share of all overhead, or we won’t be covering all of our costs.”
The relevance of statement with respect to the ABC:
There are few costs that do not correlate with volume or any other base of activity. Allocation of such costs would make information distorted. Preferable means to record these costs would require determination of contribution margin from each product.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
Fundamentals of Cost Accounting
- Nonearrow_forwardBig Company has the following production data for January: units transferred out 30,000, and ending work in process 10,000 units that are 100% complete for materials and 45% complete for conversion costs. If unit materials cost is $3 and unit conversion cost is $5, determine the costs to be assigned to the units transferred out. a. $240,000 b. $80,000 c. $90,000 d. $150,000arrow_forwardGeneral accounting questionarrow_forward
 Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College Excel Applications for Accounting PrinciplesAccountingISBN:9781111581565Author:Gaylord N. SmithPublisher:Cengage Learning
Excel Applications for Accounting PrinciplesAccountingISBN:9781111581565Author:Gaylord N. SmithPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,





