Engineering Mechanics: Statics & Dynamics (14th Edition)
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780133915426
Author: Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 8.2, Problem 15P
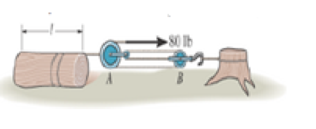
The log has a coefficient of state friction of, μs = 0.3 with the ground and a weight of 40 Ib/ft. If a man can pull on the rope with a maximum force of 80 Ib, determine the greatest length / of log he drag.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
For the position shown in the figure the spring is unstretched. The spring constant k, is designed such that after the system is released from rest, the speed of the mass is zero just as the 0.6 slug mass touches the floor. Find the spring constant, k and the maximum speed of block A and the location (distance above floor) where this occurs.
||!
Sign in
MMB241 - Tutorial L9.pd X PDF MMB241 - Tutorial L10.pX DE MMB241 - Tutorial L11.p x PDF Lecture W12 - Work and X
File C:/Users/KHULEKANI/Desktop/mmb241/MMB241%20-%20Tutorial%20L11.pdf
PDE Lecture W11 - Power and X
Draw
Alla | Ask Copilot
++
3
of 3
| D
6. If the 50-kg load A is hoisted by motor M so that the load has a constant velocity of 1.5
m/s, determine the power input to the motor, which operates at an efficiency € = 0.8.
1.5 m/s
2
7. The sports car has a mass of 2.3 Mg, and while it is traveling at 28 m/s the driver causes
it to accelerate at 5m/s². If the drag resistance on the car due to the wind is FD= 0.3v²N,
where v is the velocity in m/s, determine the power supplied to the engine at this instant.
The engine has a running efficiency of P = 0.68.
8. If the jet on the dragster supplies a constant thrust of T-20 kN, determine the power
generated by the jet as a function of time. Neglect drag and rolling resistance, and the loss
of fuel. The dragster has a mass of 1…
Q |
Sign in
PDE Lecture W09.pdf
PDF MMB241 - Tutorial L9.pdi X
PDF MMB241 - Tutorial L10.p X
PDF
MMB241 - Tutorial L11.p X
Lecture W12-Work and X
+
File C:/Users/KHULEKANI/Desktop/mmb241/Lecture%20W12%20-%20Work%20and%20Energy.pdf
||!
Draw
| IA | a | Ask Copilot
Class Work
+
33
of 34 D
Question 1
The engine of a 3500-N car is generating a constant power of 50 hp (horsepower)
while the car is traveling up the slope with a constant speed. If the engine is
operating with an efficiency of € 0.8, determine the speed of the car. Neglect
drag and rolling resistance. Use g 9.81 m/s² and 1 hp = 745.7 W.
10
го
Question 2
A man pushes on a 60-N crate with a force F. The force is always directed downward at an angle of 30°
from the horizontal, as shown in the figure. The magnitude of the force is gradually increased until the crate
begins to slide. Determine the crate's initial acceleration once it starts to move. Assume the coefficient of
static friction is μ = 0.6, the coefficient of kinetic…
Chapter 8 Solutions
Engineering Mechanics: Statics & Dynamics (14th Edition)
Ch. 8.2 - P81. Determine the friction force at the surface...Ch. 8.2 - P82. Determine M to cause impending motion of the...Ch. 8.2 - P83. Determine the force P to move block B.Ch. 8.2 - P84. Determine the force P needed to cause...Ch. 8.2 - F81. Determine the friction developed between the...Ch. 8.2 - F82. Determine the minimum force P to prevent the...Ch. 8.2 - Prob. 3FPCh. 8.2 - F84. If the coefficient of static friction at...Ch. 8.2 - F85. Determine the maximum force P that can be...Ch. 8.2 - F86. Determine the minimum coefficient of static...
Ch. 8.2 - F87. Blocks A, B, and C have weights of 50 N, 25...Ch. 8.2 - F88. If the coefficient of static friction at all...Ch. 8.2 - Prob. 9FPCh. 8.2 - Determine the maximum force P the connection can...Ch. 8.2 - The tractor exerts a towing force T=400 lb....Ch. 8.2 - The mine car and its contents have a total mass of...Ch. 8.2 - Prob. 4PCh. 8.2 - The automobile has a mass of 2 Mg and center of...Ch. 8.2 - The automobile has a mass of 2 Mg and canter of...Ch. 8.2 - The block brake consists of a pin-connected lever...Ch. 8.2 - The block brake consists of a pin-connected lever...Ch. 8.2 - Prob. 9PCh. 8.2 - Determine the angle at which the applied force P...Ch. 8.2 - Determine the maximum weight W the man can lift...Ch. 8.2 - Prob. 12PCh. 8.2 - Prob. 13PCh. 8.2 - The car has a mass of 1.6 Mg and center of mass at...Ch. 8.2 - The log has a coefficient of state friction of, s...Ch. 8.2 - Prob. 16PCh. 8.2 - The 180-Ib man climbs up the ladder and stops at...Ch. 8.2 - The spool of wire having a weight of 300 Ib rests...Ch. 8.2 - The spool of wire having a weight of 300 Ib rests...Ch. 8.2 - Prob. 20PCh. 8.2 - A man attempts to support a stack of books...Ch. 8.2 - The tongs are used to lift the 150-kg crate, whose...Ch. 8.2 - The beam is supported by a pin at A and a roller...Ch. 8.2 - The uniform thin pole has a weight of 30 Ib and a...Ch. 8.2 - The uniform pole has a weight of 30 Ib and a...Ch. 8.2 - The block brake is used to stop the wheel from...Ch. 8.2 - Solve Prob. 8-26 if the couple moment M0 is...Ch. 8.2 - A worker walks up the sloped roof that is defined...Ch. 8.2 - The friction pawl is pinned at A and rests against...Ch. 8.2 - Two blocks A and B have a weight of 10 Ib and 6...Ch. 8.2 - Two blocks A and B have a weight of 10 Ib and 6...Ch. 8.2 - Determine the smallest force P that must be...Ch. 8.2 - The man having a weight of 200 Ib pushes...Ch. 8.2 - The uniform hoop of weight W is subjected to the...Ch. 8.2 - Determine the maximum horizontal force P that can...Ch. 8.2 - Determine the minimum force P needed to push the...Ch. 8.2 - The coefficients of static and kinetic friction...Ch. 8.2 - The coefficient of static friction between the...Ch. 8.2 - Determine the smallest coefficient of static...Ch. 8.2 - If =30, determine the minimum coefficient of...Ch. 8.2 - Prob. 41PCh. 8.2 - Prob. 42PCh. 8.2 - Investigate whether the equilibrium can be...Ch. 8.2 - Prob. 44PCh. 8.2 - The beam AB has a negligible mass and thickness...Ch. 8.2 - Prob. 46PCh. 8.2 - Crates A and B weigh 200 Ib and 150 Ib,...Ch. 8.2 - Prob. 48PCh. 8.2 - The uniform crate has a mass of 150 kg. If the...Ch. 8.2 - Prob. 50PCh. 8.2 - Prob. 51PCh. 8.2 - Prob. 52PCh. 8.2 - Determine the smallest couple moment that can be...Ch. 8.2 - Prob. 54PCh. 8.2 - Prob. 55PCh. 8.2 - The disk has a weight W and lies on a plane that...Ch. 8.2 - The man has a weight of 200 lb, and the...Ch. 8.2 - Prob. 1CPCh. 8.2 - Prob. 4CPCh. 8.2 - Prob. 5CPCh. 8.4 - Determine the largest angle that will cause the...Ch. 8.4 - Prob. 59PCh. 8.4 - The wedge is used to level the member. Determine...Ch. 8.4 - The two blocks used in a measuring device have...Ch. 8.4 - If P=250 N, determine the required minimum...Ch. 8.4 - Determine the minimum applied force P required to...Ch. 8.4 - Prob. 64PCh. 8.4 - Prob. 65PCh. 8.4 - Prob. 66PCh. 8.4 - Prob. 67PCh. 8.4 - Prob. 68PCh. 8.4 - Prob. 69PCh. 8.4 - Prob. 70PCh. 8.4 - Prob. 71PCh. 8.4 - Prob. 72PCh. 8.4 - Prob. 73PCh. 8.4 - Prob. 74PCh. 8.4 - The shaft has a square-threaded screw with a lead...Ch. 8.4 - Prob. 76PCh. 8.4 - Prob. 77PCh. 8.4 - Prob. 78PCh. 8.4 - Prob. 79PCh. 8.4 - Prob. 80PCh. 8.4 - Prob. 81PCh. 8.4 - Determine the horizontal force P that must be...Ch. 8.5 - A cylinder having a mass of 250 kg is to be...Ch. 8.5 - Prob. 84PCh. 8.5 - A 180-lb farmer tries to restrain the cow from...Ch. 8.5 - The 100-lb boy at A is suspended from the cable...Ch. 8.5 - Prob. 87PCh. 8.5 - Prob. 88PCh. 8.5 - A cable is attached to the 20-kg plate B, passes...Ch. 8.5 - Prob. 90PCh. 8.5 - Prob. 91PCh. 8.5 - Determine the force P that must be applied to the...Ch. 8.5 - Prob. 93PCh. 8.5 - Prob. 94PCh. 8.5 - Prob. 95PCh. 8.5 - Determine the maximum and the minimum values of...Ch. 8.5 - Prob. 97PCh. 8.5 - Prob. 98PCh. 8.5 - Prob. 99PCh. 8.5 - Blocks A and B have a mass of 7 kg and 10 kg,...Ch. 8.5 - The uniform bar AB is supported by a rope that...Ch. 8.5 - Prob. 102PCh. 8.5 - Prob. 103PCh. 8.5 - Prob. 104PCh. 8.5 - A 10-kg cylinder D, which is attached to a small...Ch. 8.5 - Prob. 106PCh. 8.8 - The collar bearing uniformly supports an axial...Ch. 8.8 - The collar bearing uniformly supports an axial...Ch. 8.8 - The floor-polishing machine rotates at a constant...Ch. 8.8 - Prob. 110PCh. 8.8 - Prob. 111PCh. 8.8 - Prob. 113PCh. 8.8 - Prob. 114PCh. 8.8 - Prob. 115PCh. 8.8 - Prob. 116PCh. 8.8 - The collar fits loosely around a fixed shaft that...Ch. 8.8 - Prob. 118PCh. 8.8 - Prob. 119PCh. 8.8 - Prob. 120PCh. 8.8 - Solve Prob. 8-120 if the force P is applied...Ch. 8.8 - Prob. 122PCh. 8.8 - Prob. 123PCh. 8.8 - The uniform disk fits loosely over a fixed shaft...Ch. 8.8 - Prob. 125PCh. 8.8 - The bell crank fits loosely into a 0.5-in-diameter...Ch. 8.8 - The bell crank fits loosely into a 0.5-in-diameter...Ch. 8.8 - The vehicle has a weight of 2600 lb and center of...Ch. 8.8 - Prob. 129PCh. 8.8 - The handcart has wheels with a diameter of 6 in....Ch. 8.8 - Prob. 131PCh. 8.8 - Prob. 132PCh. 8.8 - R81. The uniform 20-lb ladder rests on the rough...Ch. 8.8 - R82. The uniform 60-kg crate C rests uniformly on...Ch. 8.8 - R83. A 35-kg disk rests on an inclined surface for...Ch. 8.8 - Prob. 4RPCh. 8.8 - Prob. 5RPCh. 8.8 - Prob. 6RPCh. 8.8 - Prob. 7RPCh. 8.8 - The hand cart has wheels with a diameter of 80 mm....
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- state is Derive an expression for the volume expansivity of a substance whose equation of RT P = v-b a v(v + b)TZ where a and b are empirical constants.arrow_forwardFor a gas whose equation of state is P(v-b)=RT, the specified heat difference Cp-Cv is equal to which of the following (show all work): (a) R (b) R-b (c) R+b (d) 0 (e) R(1+v/b)arrow_forwardof state is Derive an expression for the specific heat difference of a substance whose equation RT P = v-b a v(v + b)TZ where a and b are empirical constants.arrow_forward
- Temperature may alternatively be defined as T = ди v Prove that this definition reduces the net entropy change of two constant-volume systems filled with simple compressible substances to zero as the two systems approach thermal equilibrium.arrow_forwardUsing the Maxwell relations, determine a relation for equation of state is (P-a/v²) (v−b) = RT. Os for a gas whose av Tarrow_forward(◉ Homework#8arrow_forward
- Homework#8arrow_forwardBox A has a mass of 15 kilograms and is attached to the 20 kilogram Box B using the cord and pulley system shown. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the boxes and surface is 0.2 and the moment of inertia of the pulley is 0.5 kg * m^ 2. After 2 seconds, how far do the boxes move? A бро Barrow_forwardBox A has a mass of 15 kilograms and is attached to the 20 kilogram Box B using the cord and pulley system shown. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the boxes and surface is 0.2 and the moment of inertia of the pulley is 0.5 kg * m^2. Both boxes are 0.25 m long and 0.25 m high. The cord is attached to the bottom of Box A and the middle of box B. After 2 seconds, how far do the boxes move? A From бро Barrow_forward
- Homework#8arrow_forwardSign in PDF Lecture W09.pdf PDF MMB241 - Tutorial L9.pdf File C:/Users/KHULEKANI/Desktop/mmb241/MMB241%20-%20Tutorial%20L9.pdf II! Draw | I│Alla | Ask Copilot + of 4 D Topic: Kinetics of Particles: - Forces in dynamic system, Free body diagram, newton's laws of motion, and equations of motion. TQ1. The 10-kg block is subjected to the forces shown. In each case, determine its velocity when t=2s if v 0 when t=0 500 N F = (201) N 300 N (b) TQ2. The 10-kg block is subjected to the forces shown. In each case, determine its velocity at s-8 m if v = 3 m/s at s=0. Motion occurs to the right. 40 N F = (2.5 s) N 200 N 30 N (b) TQ3. Determine the initial acceleration of the 10-kg smooth collar. The spring has an unstretched length of 1 m. 1 σ Q ☆ Q 6 ا الى ☑arrow_forwardSign in PDF Lecture W09.pdf PDF MMB241 - Tutorial L9.pdf File C:/Users/KHULEKANI/Desktop/mmb241/MMB241%20-%20Tutorial%20L9.pdf II! Draw | I│Alla | Ask Copilot + 4 of 4 | D TQ9. If motor M exerts a force of F (10t 2 + 100) N determine the velocity of the 25-kg crate when t kinetic friction between the crate and the plane are μs The crate is initially at rest. on the cable, where t is in seconds, 4s. The coefficients of static and 0.3 and μk = 0.25, respectively. M 3 TQ10. The spring has a stiffness k = 200 N/m and is unstretched when the 25-kg block is at A. Determine the acceleration of the block when s = 0.4 m. The contact surface between the block and the plane is smooth. 0.3 m F= 100 N F= 100 N k = 200 N/m σ Q Q ☆ ا الى 6 ☑arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
Dynamics - Lesson 1: Introduction and Constant Acceleration Equations; Author: Jeff Hanson;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7aMiZ3b0Ieg;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY