
Timothy Donaghy has developed a unique formula for growing hair. His proprietary lotion, used regularly for 45 days, will grow hair in bald spots (with varying degrees of success). Timothy calls his lotion Hair-Again and is selling it via the telephone and Internet. His major form of marketing is through 15-minute infomercials and Internet advertising. Timothy sells each 16- ounce bottle of Hair-Again for $15 and pays a commission of 3 percent of sales to telephone operators who field the 1-800 phone calls from potential customers. Fixed marketing expenses for each quarter of the coming year include:
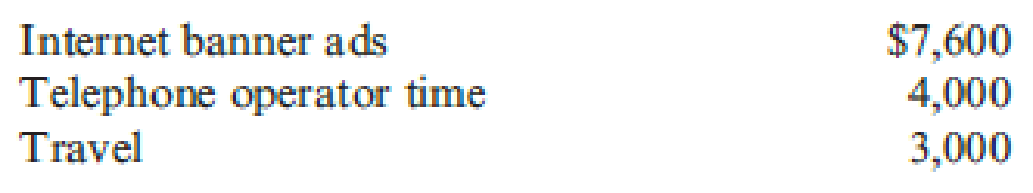
In addition, early next year Timothy intends to film and show infomercials on television. He expects the cost to be $10,000 in quarters 1 and 2, and that the cost will rise to $25,000 in each of quarters 3 and 4. Timothy expects the following unit sales of Hair-Again:

Required:
- 1. Construct a marketing expense budget for Hair-Again for the coming year. Show total amounts by quarter and in total for the year.
- 2. What if the cost of Internet ads rises to $15,000 in Quarters 2 through 4? How would that affect variable marketing expense? Fixed marketing expense? Total marketing expense?
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 8 Solutions
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Series)
- Questions Of General Account Microsoft Corp. will pay a dividend of $2.04 per share next year. Investors anticipate that the annual dividends will grow by 2% per year forever, and they require a 12% discount rate. Calculate the value of the stock.arrow_forwardWhat is Jorge's gain or loss realized on the machine on general accounting question?arrow_forwardDon't give wrong answer to this accounting questionarrow_forward
- How does business model evolution affect accounting adaption?arrow_forwardPlease give Answerarrow_forwardWhat role does assurance boundary definition play in attestation? a) Standard limits work always b) Boundaries never matter c) All areas need equal coverage d) Engagement scope limits determine verification responsibilitiesarrow_forward
 Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning
