
An aqueous slurry at 30°C containing 20.0 wt% solids is fed to an evaporator in which enough w ater is vaporized at 1 atm to produce a product slurry containing 35.0 wt% solids. Heat is supplied to the evaporator by feeding saturated steam at 2.6 bar absolute into a coil immersed in the liquid. The steam condenses in the coil, and the slurry boils at the normal boiling point of pure water. The heat capacity of the solids may be taken to be half that of liquid water.
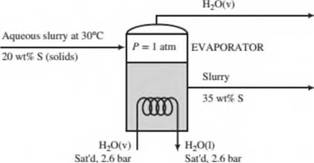
- Calculate the required steam feed rate (kg/h) for a slurry feed rate of 1.00 × 103 kg/h.
- Vapor recompression is often used in the operation of an evaporator. Suppose that the vapor (steam) generated in the evaporator described above is compressed to 2.6 bar and simultaneously heated to the saturation temperature at 2.6 bar, so that no condensation occurs. The compressed steam and additional saturated steam at 2.6 bar arc then fed to the evaporator coil, in which isobaric condensation occurs. How much additional steam is required?
- What more would you need to know to determine whether or not vapor recompression is economically advantageous in this process?
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Learn your wayIncludes step-by-step video

Chapter 8 Solutions
ELEM.PRINCIPLES OF CHEMICAL PROCESSES
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Introduction To Programming Using Visual Basic (11th Edition)
Starting Out with Java: From Control Structures through Data Structures (4th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
INTERNATIONAL EDITION---Engineering Mechanics: Statics, 14th edition (SI unit)
Modern Database Management
Management Information Systems: Managing The Digital Firm (16th Edition)
Starting Out with Programming Logic and Design (5th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
- Please, provide me the solution with details and plot.arrow_forwardQ2/ An adsorption study is set up in laboratory by adding a known amount of activated carbon to six which contain 200 mL of an industrial waste. An additional flask containing 200 mL of waste but no c is run as a blank. Plot the Langmuir isotherm and determine the values of the constants. Flask No. Mass of C (mg) Volume in Final COD Flask (mL) (mg C/L) 1 804 200 4.7 2 668 200 7.0 3 512 200 9.31 4 393 200 16.6 C 5 313 200 32.5 6 238 200 62.8 7 0 200 250arrow_forwardمشر on ۲/۱ Two rods (fins) having same dimensions, one made of brass(k=85 m K) and the other of copper (k = 375 W/m K), having one of their ends inserted into a furnace. At a section 10.5 cm a way from the furnace, the temperature brass rod 120°C. Find the distance at which the same temperature would be reached in the copper rod ? both ends are exposed to the same environment. 22.05 ofthearrow_forward
- 4.59 Using the unilateral z-transform, solve the following difference equations with the given initial conditions. (a) y[n]-3y[n-1] = x[n], with x[n] = 4u[n], y[− 1] = 1 (b) y[n]-5y[n-1]+6y[n-2]= x[n], with x[n] = u[n], y[-1] = 3, y[-2]= 2 Ans. (a) y[n] = -2+9(3)", n ≥ -1 (b) y[n]=+8(2)" - (3)", n ≥ -2arrow_forward(30) 6. In a process design, the following process streams must be cooled or heated: Stream No mCp Temperature In Temperature Out °C °C kW/°C 1 5 350 270 2 9 270 120 3 3 100 320 4 5 120 288 Use the MUMNE algorithm for heat exchanger networks with a minimum approach temperature of 20°C. (5) a. Determine the temperature interval diagram. (3) (2) (10) (10) b. Determine the cascade diagram, the pinch temperatures, and the minimum hot and cold utilities. c. Determine the minimum number of heat exchangers above and below the pinch. d. Determine a valid heat exchange network above the pinch. e. Determine a valid heat exchange network below the pinch.arrow_forwardUse this equation to solve it.arrow_forward
- Q1: Consider the following transfer function G(s) 5e-s 15s +1 1. What is the study state gain 2. What is the time constant 3. What is the value of the output at the end if the input is a unit step 4. What is the output value if the input is an impulse function with amplitude equals to 3, at t=7 5. When the output will be 3.5 if the input is a unit steparrow_forwardgive me solution math not explinarrow_forwardgive me solution math not explinarrow_forward
 Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781259696527Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark SwihartPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781259696527Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark SwihartPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9780133887518Author:H. Scott FoglerPublisher:Prentice Hall
Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9780133887518Author:H. Scott FoglerPublisher:Prentice Hall
 Industrial Plastics: Theory and ApplicationsChemical EngineeringISBN:9781285061238Author:Lokensgard, ErikPublisher:Delmar Cengage Learning
Industrial Plastics: Theory and ApplicationsChemical EngineeringISBN:9781285061238Author:Lokensgard, ErikPublisher:Delmar Cengage Learning Unit Operations of Chemical EngineeringChemical EngineeringISBN:9780072848236Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter HarriottPublisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The
Unit Operations of Chemical EngineeringChemical EngineeringISBN:9780072848236Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter HarriottPublisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The





