
Principles of Economics 2e
2nd Edition
ISBN: 9781947172364
Author: Steven A. Greenlaw; David Shapiro
Publisher: OpenStax
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 8, Problem 3SCQ
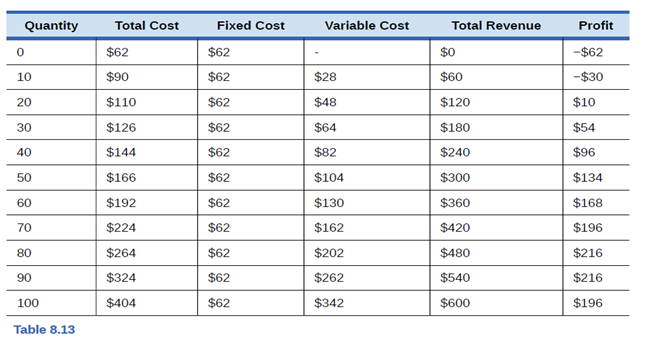
Look at Table 8.13. What would happen to the film’s profits if the market price increases to
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
13. You just got a patent for the first commercial self-driving car. The following table shows
the elasticity of the demand and the marginal cost of production of your cars in several
production centers across the globe. Assuming that this are constant, can you approximate
what would be the optimal price for your cars?
City Marginal Cost Elasticity
Price
Wolfburg, Germany
Barcelona, Spain
Tokyo, Japan
Ulsan, South Korea
East London, South Africa
Mexico City, Mexico
$20, 000
$18, 000
$22, 000
$16, 000
$10, 000
$12, 000
-1.5 $60, 000.00
$24, 000.00
$33, 000.00
$32, 000.00
$11, 428.60
$14, 400.00
-4.0
-3.0
-2.0
-8.0
-6.0
If Kiesel experienced an increase in orders from its websiteover a period of two weeks, should it expand its productioncapacity to make sure it can handle increased demand inthe future? Why or why not?
Comment on the following statement: “In the short run, Mr. Mohammed, a seller in the Fruit& Vegetable Market in Al-Aweer, faces a demand curve that is simply a horizontalline at themarket equilibrium price. In other words, competitive sellers, in this market, face perfectlyelastic demand in the short run.”
Chapter 8 Solutions
Principles of Economics 2e
Ch. 8 - Firms ill a perfectly competitive market are said...Ch. 8 - Would independent trucking fit the characteristics...Ch. 8 - Look at Table 8.13. What would happen to the films...Ch. 8 - Suppose that the market price increases to 6, as...Ch. 8 - Explain in words why a profit-maximizing film will...Ch. 8 - A firms marginal cost curve above the average...Ch. 8 - If new technology in a perfectly competitive...Ch. 8 - A market in perfect competition is in long-run...Ch. 8 - Productive efficiency and allocative efficiency...Ch. 8 - Explain how the profit-maximizing rule of setting...
Ch. 8 - A single firm in a perfectly competitive market is...Ch. 8 - What are the four basic assumptions of perfect...Ch. 8 - What is a price taker firm?Ch. 8 - How does a perfectly competitive firm decide what...Ch. 8 - What prevents a perfectly competitive firm from...Ch. 8 - How does a perfectly competitive film calculate...Ch. 8 - Briefly explain the reason for the shape of a...Ch. 8 - What two rules does a perfectly competitive firm...Ch. 8 - How does the average cost curve help to show...Ch. 8 - What two lines on a cost curve diagram intersect...Ch. 8 - Should a firm shut down immediately if it is...Ch. 8 - How does the average variable cost curve help a...Ch. 8 - What two lines on a cost curve diagram intersect...Ch. 8 - Why does entry occur?Ch. 8 - Why does exit occur?Ch. 8 - Do entry and exit occur in the short run, the long...Ch. 8 - What price will a perfectly competitive firm end...Ch. 8 - Will a perfectly competitive market display...Ch. 8 - Will a perfectly competitive market display...Ch. 8 - Finding a life partner is a complicated process...Ch. 8 - Can you name five examples of perfectly...Ch. 8 - Your company operates in a perfectly competitive...Ch. 8 - Since a perfectly competitive firm can sell as...Ch. 8 - Many films in the United States file for...Ch. 8 - Why will profits for films in a perfectly...Ch. 8 - Why will losses for firms in a perfectly...Ch. 8 - Assuming that the market for cigarettes is in...Ch. 8 - In the argument for why perfect competition is...Ch. 8 - The AAA Aquarium Co. sells aquariums for 20 each....Ch. 8 - Perfectly competitive firm Doggies Paradise Inc....Ch. 8 - A computer company produces affordable,...
Additional Business Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
What is the relationship between management by exception and variance analysis?
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis (16th Edition)
What is the best way to control labor costs? What tools are discussed in the chapter that may be used to help c...
Construction Accounting And Financial Management (4th Edition)
Sterlings records show the work in process Inventory had a beginning balance of $4000 and an ending balance of ...
Principles of Accounting Volume 2
Discussion Questions 1. What characteristics of the product or manufacturing process would lead a company to us...
Managerial Accounting (5th Edition)
E6-14 Using accounting vocabulary
Learning Objective 1, 2
Match the accounting terms with the corresponding d...
Horngren's Accounting (12th Edition)
E2-13 Identifying increases and decreases in accounts and normal balances
Learning Objective 2
Insert the mis...
Horngren's Accounting (11th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Only typed answer and please answer correctlyarrow_forwardThe following graph plots daily cost curves for a firm operating in the competitive market for fitness trackers. Hint: Once you have positioned the rectangle on the graph, select a point to observe its coordinates. PRICE(Dollars pertracker) 100 90 70 60 50 40 20 10 0 0 MO ATC AVC 50 60 70 80 10 20 30 40 QUANTITY (Thousands of trackers per day) 90 100 Profit or Loss In the short run, given a market price equal to $45 per tracker, the firm should produce a daily quantity of trackers. On the preceding graph, use the blue rectangle (circle symbols) to fill in the area that represents profit or loss of the firm given the market price of $45 and the quantity of production from your previous answer. Note: In the following question, enter a positive number regardless of whether the firm earns a profit or incurs a loss. The rectangular area represents a short-run thousand per day for the firm.arrow_forwardHow to Estimate demand, costs, and profits?arrow_forward
- Imagine you are the owner of the Omaha Surfboard Company. You have a branch in Omaha and in Long Beach CA. After some market research you find the following surfboard demand for each market, Omaha Demand: Qo = 1000 – 10P Long Beach Demand: QL = 1000 – 5P Combined/Total Demand: Q = 2000 – 15P Your marginal cost is constant at $40. a. Find your price and quantity if you treated the market as a single entity with a single price. What is your profit? (Hint: find Marginal Revenue and set equal to MC) b. If you treat each market separately, what is P and Quantity in each market, and final profit?arrow_forwardM1arrow_forwardDraw the demand and supply curves and equilibrium points in the decrease in cost of tealeaves, for milk tea.arrow_forward
- Why does a Starbucks coffeehouse face a downward–sloping demand curve while a dairy farmer has a horizontal demand curve? What other suppliers might face a downward–sloping demand curve?arrow_forwardThe following graph illustrates the weekly demand curve for motorized scooters in Scottsdale. Use the green rectangle (triangle symbols) to compute total revenue at various prices along the demand curve. Note: You will not be graded on any changes made to this graph. PRICE (Dollars per scooter) TOTAL REVENUE (Dollars) 8700 8100 7500 6900 6300 5700 5100 4500 3900 325 3300 300 275 250 225 200 175 150 125 100 75 On the following graph, use the green point (triangle symbol) to plot the weekly total revenue when the market price is $50, $75, $100, $125, $150, $175, and $200 per scooter. (?) 50 25 0 0 10 20 *4 0 25 50 Xo Demand 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 110 120 130 QUANTITY (Scooters) Total Revenue 75 100 125 150 175 200 225 250 275 300 325 PRICE (Dollars per scooter) (?) Total Revenue According to the midpoint method, the price elasticity of demand between points A and B is approximatelyarrow_forwardConsider a town in which only two residents, Jacques and Kyoko, own wells that produce water safe for drinking. Jacques and Kyoko can pump and sell as much water as they want at no cost. For them, total revenue equals profit. The following table shows the town's demand schedule for water. fill in every blank!! NOTE: options for first drop down question is (decreases or increases) options for second drop down question is (tying, a tit for tat strategy, a dominant strategy, a prisioners dilemma)arrow_forward
- Paulina sells beef in a competitive market where the price is $8 per pound. Her total revenue and total costs are given in the table below. Quantity of Total revenue Total cost beef (lb.) 0 1 2 3 4 ($) 0 8 16 24 32 ($) 4 8 13 19 27 Profit ($) 0 8 pounds Marginal revenue ($) c. What is the profit-maximizing (or loss-minimizing) quantity? Marginal Marginal cost ($) profit ($) a. Complete the table. Instructions: Enter your answers as a whole number. If you are entering any negative numbers be sure to include a negative sign (-) in front of those numbers. b. At what quantity does marginal revenue equal marginal cost? pounds Aarrow_forwardSuppose that a local government is considering placing a tax on the rental of rooms on Airbnb. Before the tax, the total revenue earned by hosts using Airbnb was $10,000,000 per year. a) If the government imposes a 10% tax on these rooms, will they earn more or less than $1,000,000 in tax revenue if the market is assumed to be perfectly competitive? b) Will local residents who rent their homes (as tenants) benefit from this policy? (Use a diagram to explain) c) Does your answer to a) or b) change if there are a fixed (and small) number of rooms available to rent in the area?arrow_forwardQuestion 18 Alex Potter owns the only well in a town that produces clean drinking water. He faces the following demand P=200-2Q, and marginal cost MC=50+2Q, marginal revenue MR= 200-4Q curves. In order to maximize profits, Alex should charge a price of $150 at the profit maximizing quantity with a marginal revenue equal to $150. $100 at the profit maximizing quantity with a marginal revenue equal to $150. $100 at the profit maximizing quantity with a marginal revenue equal to $100. $150 at the profit maximizing quantity with a marginal revenue equal to $100. O Oarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Microeconomics: Private and Public Choice (MindTa...EconomicsISBN:9781305506893Author:James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. MacphersonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Microeconomics: Private and Public Choice (MindTa...EconomicsISBN:9781305506893Author:James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. MacphersonPublisher:Cengage Learning Economics: Private and Public Choice (MindTap Cou...EconomicsISBN:9781305506725Author:James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. MacphersonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Economics: Private and Public Choice (MindTap Cou...EconomicsISBN:9781305506725Author:James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. MacphersonPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: Applications, Strategies an...EconomicsISBN:9781305506381Author:James R. McGuigan, R. Charles Moyer, Frederick H.deB. HarrisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: Applications, Strategies an...EconomicsISBN:9781305506381Author:James R. McGuigan, R. Charles Moyer, Frederick H.deB. HarrisPublisher:Cengage Learning Exploring EconomicsEconomicsISBN:9781544336329Author:Robert L. SextonPublisher:SAGE Publications, Inc
Exploring EconomicsEconomicsISBN:9781544336329Author:Robert L. SextonPublisher:SAGE Publications, Inc Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781337617383Author:Roger A. ArnoldPublisher:Cengage Learning
Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781337617383Author:Roger A. ArnoldPublisher:Cengage Learning

Microeconomics: Private and Public Choice (MindTa...
Economics
ISBN:9781305506893
Author:James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. Macpherson
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Economics: Private and Public Choice (MindTap Cou...
Economics
ISBN:9781305506725
Author:James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. Macpherson
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: Applications, Strategies an...
Economics
ISBN:9781305506381
Author:James R. McGuigan, R. Charles Moyer, Frederick H.deB. Harris
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Exploring Economics
Economics
ISBN:9781544336329
Author:Robert L. Sexton
Publisher:SAGE Publications, Inc

Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781337617383
Author:Roger A. Arnold
Publisher:Cengage Learning
