
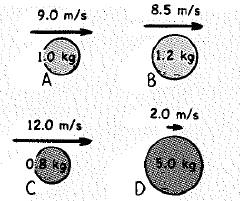
The balls have different masses and speeds.
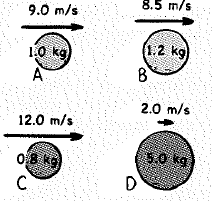
Rank the following from greatest to least.
a. momentum
b. the impulse needed to stop them
(a)
To rank: The momentum of the balls from greatest to least.
Answer to Problem 20A
B, D, C, A.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The mass and velocity of four different balls are as given in the figure 1.
Mass of the ball A is mA=1.0 kg
Velocity of the ball A is vA=9.0 m/s
Mass of the ball B is mB=1.2 kg
Velocity of the ball B is vB=8.5 m/s
Mass of the ball C is mC=0.8 kg
Velocity of the ball C is vC=12 m/s
Mass of the ball D is mD=5.0 kg
Velocity of the ball D is vD=2.0 m/s
Formula used:
The momentum (p) of an object of mass (m) moving with a velocity (v) is given by
p=mv (1)
Calculation:
Substituting the numerical values in equation (1) ,
The momentum of the ball A is,
pA=(1.0 kg)(9.0 m/s)=9.0 kg.m/s
The momentum of the ball B is,
pB=(1.2 kg)(8.5 m/s)=10.2 kg.m/s
The momentum of the ball C is,
pC=(0.8 kg)(12.0 m/s)=9.6 kg.m/s
The momentum of the ball D is,
pD=(5.0 kg)(2.0 m/s)=10.0 kg.m/s
Conclusion:
The rank of the balls having the momentum greatest to least is B, D, C, A.
(b)
To rank: The impulse needed to stop the balls from greatest to least.
Answer to Problem 20A
B, D, C, A.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
Mass of the ball A is mA=1.0 kg
Initial velocity of the ball A is vAi=9.0 m/s
Final velocity of the ball A is vAf=0.0 m/s
Mass of the ball B is mB=1.2 kg
Initial velocity of the ball B is vBi=8.5 m/s
Final velocity of the ball B is vBf=0.0 m/s
Mass of the ball C is mC=0.8 kg
Initial velocity of the ball C is vCi=12 m/s
Final velocity of the ball C is vCf=0.0 m/s
Mass of the ball D is mD=5.0 kg
Initial velocity of the ball D is vDi=2.0 m/s
Final velocity of the ball D is vDf=0.0 m/s
Formula used:
Initial momentum of the ball is
pi=mvi
Final momentum of the ball is
pf=mvf
From the impulse - momentum theorem, the impulse needed to stop the ball can be written as
FΔt=pf−pi
Substituting for pf and pi ,
FΔt=mvf−mvi
⇒FΔt=m(vf−vi) (2)
Calculation:
Substituting the numerical values in equation (2) ,
The impulse needed to stop the ball A is,
FΔt=(1.0 kg)( 0.0 m/s−9.0 m/s)=− 9.0 kg.m/s
The impulse needed to stop the ball B is,
FΔt=(1.2 kg)( 0.0 m/s−8.5 m/s)=− 10.2 kg.m/s
The impulse needed to stop the ball C is,
FΔt=(0.8 kg)( 0.0 m/s−12.0 m/s)=− 9.6 kg.m/s
The impulse needed to stop the ball D is,
FΔt=(5.0 kg)( 0.0 m/s−2.0 m/s)=− 10.0 kg.m/s
Conclusion:
The rank of the impulse needed to stop the balls from greatest to least is B, D, C, A.
Chapter 8 Solutions
Conceptual Physics: The High School Physics Program
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Laboratory Experiments in Microbiology (12th Edition) (What's New in Microbiology)
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (3rd Edition)
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
Anatomy & Physiology (6th Edition)
Human Anatomy & Physiology (2nd Edition)
- A-E pleasearrow_forwardA 11.8 L gas tank containing 3.90 moles of ideal He gas at 26.0°C is placed inside a completely evacuated insulated bell jar of volume 39.0 L .A small hole in the tank allows the He to leak out into the jar until the gas reaches a final equilibrium state with no more leakage. Part A What is the change in entropy of this system due to the leaking of the gas? ■ ΜΕ ΑΣΦ AS = ? J/K Submit Request Answer Part B Is the process reversible or irreversible?arrow_forwardA-E pleasearrow_forward
- Three moles of an ideal gas undergo a reversible isothermal compression at 20.0° C. During this compression, 1900 J of work is done on the gas. For related problem-solving tips and strategies, you may want to view a Video Tutor Solution of Entropy change in a free expansion. Part A What is the change of entropy of the gas? ΤΕ ΑΣΦ AS = Submit Request Answer J/Karrow_forward5.97 Block A, with weight 3w, slides down an inclined plane S of slope angle 36.9° at a constant speed while plank B, with weight w, rests on top of A. The plank is attached by a cord to the wall (Fig. P5.97). (a) Draw a diagram of all the forces acting on block A. (b) If the coefficient of kinetic friction is the same between A and B and between S and A, determine its value. Figure P5.97 B A S 36.9°arrow_forwardPlease take your time and solve each part correctly please. Thank you!!arrow_forward
- help me answer this with explanations! thanks so mucharrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvote Alreadyarrow_forwardWhat fuel economy should be expected from a gasoline powered car that encounters a total of 443N of resistive forces while driving down the road? (Those forces are from air drag, rolling resistance and bearing losses.) Assume a 30% thermodynamic efficiency.arrow_forward
- No chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward12. What is the angle between two unit vectors if their dot product is 0.5?arrow_forwardIf the car in the previous problem increases its power output by 10% (by pressing the gas pedal farther down), at what rate will the car accelerate? Hint: Consider the net force. In the previous problem the power was 31.8kWarrow_forward
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON





