
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation: The order of stability is to be interpreted for the given
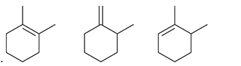
Concept introduction:
(b)
Interpretation: The order of stability is to be interpreted for the given alkenes:
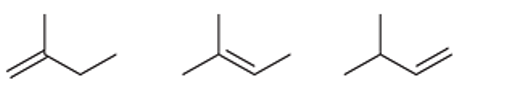
Concept introduction:
Unsaturated hydrocarbons with at least one double bond between the carbon atoms are known as alkenes. The presence of pi bonds in these molecules makes them more reactive compared to saturated hydrocarbons; alkanes. The stability of alkenes depends on their substitution.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 7 Solutions
ORG.CHEM.WILEYPLUSNEXTGEN.W/LLTEXT+STDY.
- Which one alkene will exhibit cis-trans isomerism? A B OC OA u B Darrow_forwardDehydrohalogenation of 1-chloro-1-methylcyclopropane affords two alkenes (A and B) as products. Explain why A is the major product despite the fact that it contains the less substituted double bond.arrow_forwardDraw the alkene that would react with the reagent given to account for the product formed. CH3 HCI CH3 CHCCH, ? + Či CH3 You do not have to consider stereochemistry. • You do not have to explicitly draw H atoms. • In cases where there is more than one answer, just draw one.arrow_forward
- Five isomeric alkanes (A–E) having the molecular formula C6H14 are each treated with Cl2 + hv to give alkyl halides having molecular formulaC6H13Cl. A yields five constitutional isomers. B yields four constitutionalisomers. C yields two constitutional isomers. D yields threeconstitutional isomers, two of which possess stereogenic centers. Eyields three constitutional isomers, only one of which possesses astereogenic center. Identify the structures of A–E.arrow_forwardDraw the alkene that would react with the reagent given to account for the product formed. ? + + H₂O **** H₂S04 • You do not have to consider stereochemistry. • You do not have to explicitly draw H atoms. • In cases where there is more than one answer, just draw one. CH3 CH3 CHCCH3 | | OH CH3 +1arrow_forwardDraw the alternative chair conformations for the product formed by the addition of bromine to 4-tert-butylcyclohexene. The Gibbs free energy differences between equatorial and axial substituents on a cyclohexane ring are 21 kJ (4.9 kcal)/mol for tert-butyl and 2.0–2.6 kJ (0.48–0.62 kcal)/mol for bromine. Estimate the relative percentages of the alternative chair conformations you drew in the first part of this problemarrow_forward
- State what alkene or alkyne (with only carbons and hydrogens) and what other reactants you should use to most effectively synthesize the following in the fewest number of steps and with the highest yield. H;C-CH,- C CH3arrow_forwardG.133.arrow_forwardDraw the alkene that would react with the reagent given to account for the product formed. ? + H₂O H₂SO4 CH3 CH3 CHCCH3 OH CH3 • You do not have to consider stereochemistry. • You do not have to explicitly draw H atoms. • In cases where there is more than one answer, just draw one. Sn [F ChemDoodlearrow_forward
- Draw the alkene that would react with the reagent given to account for the product formed. ? + HCI My 3 You do not have to consider stereochemistry. • You do not have to explicitly draw H atoms. • In cases where there is more than one answer, just draw one. CH3 CH₂ CHOCH3 TT CI CH3 L ▼ {n [F ? ChemDoodleⓇarrow_forwardWhat type of stereochemistry does catalytic hydrogenation afford? Anti-Addition Syn-Addition What is the product of a dissolving metal reduction of an alkyne? An alkyne An alkane OA trans-alkene A cis-alkene Reaction of an alkene with potassium permanganate affords: An anti-diol A syn-diolarrow_forwardDraw the alkene that would react with the reagent given to account for the product formed. ? + H₂O ● You do not have to consider stereochemistry. You do not have to explicitly draw H atoms. • In cases where there is more than one answer, just draw one. 8 H₂SO4 // CH3 CH3CHCCH3 OH CH3 ? [F Previous Email Instructarrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

