
(a)
Interpretation: The transition state of the given reaction is to be interpreted for the given conversion:
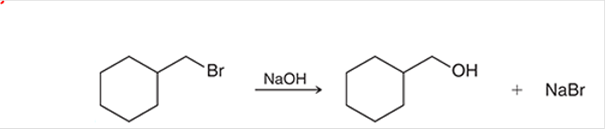
Concept introduction:
(b)
Interpretation: The transition state of the given reaction is to be interpreted for the given conversion:
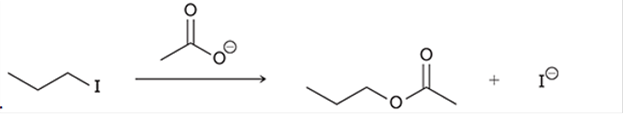
Concept introduction:
Haloalkanes can show the nucleophilic substitution reactions. There are two possible mechanisms
(c)
Interpretation: The transition state of the given reaction is to be interpreted for the given conversion:
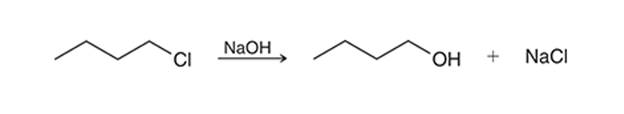
Concept introduction:
Haloalkanes can show the nucleophilic substitution reactions. There are two possible mechanisms
(d)
Interpretation: The transition state of the given reaction is to be interpreted for the given conversion:
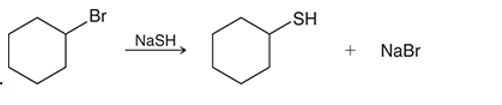
Concept introduction:
Haloalkanes can show the nucleophilic substitution reactions. There are two possible mechanisms
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 7 Solutions
ORG.CHEM.WILEYPLUSNEXTGEN.W/LLTEXT+STDY.
- Describe the mechanism of the following reaction. 1) H2N NH2 (excess) SH SH `CO2H AcO 2) КОН 3) H +arrow_forwardOf the following, which represents the intermediate that is most likely formed in the first step of the mechanism? Br ОН Br ОН ОН ОН OH2arrow_forwardHow many transition states are involved in the following reaction?arrow_forward
- Identify the correct transition state for an E2 reaction.arrow_forwardWhat are the reactions and mechanisms for the followingarrow_forwardPlease draw the mechanism for the following reaction. Which compound given below most closely matches the intermediate formed in the first step of the mechanism. Reaction 1 HBr DCM A В C H D H E F G H, H. но. H :0:arrow_forward
- (3R, 4R)-3-Bromo-4-phenylhexane reacts with t-butoxide ion, but the major product has potential stereoisomers. The question is which stereoisomer predominates as the major product? Using scratch paper, draw the starting material and reagent, and then use what you know about reaction mechanisms to determine the correct mechanism for this reaction. Then, identify the product and the correct stereoisomer of the final product (R, S, E, or Z). Fill in the blanks below with the necessary information. a. What mechanism is controlling this reaction (SN1, SN2, E1, or E2)? b. Which stereoisomer product predominates (R, S, E, or Z)? c. What is the full name of the major product?arrow_forwardOn the lowest energy pathway to form the product of the following reaction, which species is a plausible transition state? (Dotted lines represent bonds in the process of forming or breaking.) x● HBr H---Br Br-H H----Br ठ Br-H productarrow_forwardDraw a representation of the transition state for the following endergonic mechanistic step. H,C-CH=CH, H-OH, H3C–CH-CH3 H,0arrow_forward
- For the following reaction there are three (3) possible products. Two of the products are expected to be minor and one product is expected to be a major product. Br H₂O Name and draw out the step-by-step mechanisms by which each of the products is formed. Briefly explain why one of the three products is expected to be a major product.arrow_forward11. Predict the structure of the transition state for the following SN2 reaction: Br + NaOHarrow_forwardPredict the elimination products for the reaction. Identify the major and minor stereoisomers and draw them as indicated. H₂O Major and Minor isomers -Br H H3C Draw the major isomer. Draw the minor isomer. Select Draw Rings More Select Draw Rings Erase с H CH3 Erase Q2 Q More с H O Q2 Qarrow_forward
 Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax
Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax
