
Concept explainers
(a)
The dimensional parameter generated by the given quantities.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
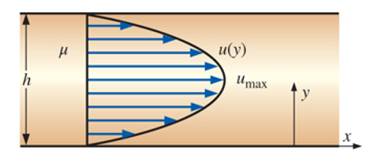
In the given question,
We use the method of variable to find the dimensionless quantity from the given data.
Total number of parameters given,
| n = 5 |
We define the function as,
Primary dimensions of all the given parameters,
The number of primary dimensions is (L, M, t).
Since the value of n is 5.
So,
J = 3,
And,
k = (N − J)
k = (5 − 3) = 2.
So, the number of pi-terms is two.
For further calculation we need to choose any three repeating quantities,
I choose
Thus, by using repeating variables, first independent pi- term is formed.
So, the substituting the values of variables to get a dimensionless relationship.
Thus, the required relationship is,
On simplifying,
(b)
The change in
Answer to Problem 96P
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
From subpart a,
On simplifying,
When h is doubled,
(c)
The change in
Answer to Problem 96P
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
From subpart a,
On simplifying,
When
(d)
The number of experiments required to describe complete relationship.
Answer to Problem 96P
The number of experiments required is 2.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
From previous problem,
There exist two pi-terms in the given question,
So, we need to perform two experiment for generation complete relationship between the given parameters.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 7 Solutions
Fluid Mechanics Fundamentals And Applications
- A proposed harmonic function F(x, y, z) is given byF = 2x2 + y3 - 4xz +f(y)(a) If possible, fi nd a function f (y) for which the laplacianof F is zero. If you do indeed solve part (a), can your fi nalfunction F serve as (b) a velocity potential or (c) a streamfunction?arrow_forwardfind mach and reynolds number and write out N-S eqnsarrow_forwardDefine the following dimensionless group number in fluid mechanics, a)Interpretation of force ratio, and what types of application. b)Reynolds number (Re) c)Euler number (Eu) d) Mach number (Ma) e) Weber number (We)arrow_forward
- In deriving the vorticity equation, we have used the identity divergence x (divergence P) = 0 Show that this identity is valid for any scalar lamda by checking it in Cartesian and cylindrical coordinates.arrow_forwardConsider fully developed two-dimensional Poiseuille flow—flow between two infinite parallel plates separated by distance h, with both the top plate and bottom plate stationary, and a forced pressure gradient dP/dx driving the flow as illustrated in Fig. (dP/dx is constant and negative.) The flow is steady, incompressible, and two-dimensional in the xy-plane. The velocity components are given by u = 1/2? dP/dx (y2 − hy) ? = 0where ?isthefluid’sviscosity.Isthisflowrotationalorirrotational? If it is rotational, calculate the vorticity component in the z-direction. Do fluid particles in this flow rotate clockwise or counterclockwise?arrow_forwarda) Contsioer THE velbeine Fieb: V- xy i+ xyj (ij UNIT VECTORS AbNG X-, AND Y DIRECTTONS) IF THE FIUID DENSITY is CONOTANT, is CONSERVATION OF MASS SATİSFİED! CONSIDER THE FolbwiNG STREAM FUNCTION is THE Flow FielD IRROTATIONAL ? WHAT is THE VelocitY POTENTIAl ? C) CONSIDER THE STREAM FUNCTION DESCRIBING A Flow Field iN THE UPPER plaNE xy yoo. FOR THERE is A plATE @ y=0. ) i) is No-slip SATİS FIED @ PIATE (y=o) DRAW THE STREAMLINES FIND THE PRESSURE AS A FUNCTION OF THE PRESSURE O ORIGIN Po. (ASSOME NO GRAVitr).arrow_forward
- The Reynolds transport theorem (RTT) is discussed in Chap. 4 of your textbook. For the general case of a moving and/or deforming control volume, we write the RTT as follows: d pb dV + pbV-ñ dA dt dt dB sys where Vr is the relative velocity, i.e., the velocity of the fluid relative to the control surface. Write the primary dimensions of each additive term in the equation and verify that the equation is dimensionally homogeneous. Show all your work. (Hint: Since B can be any property of the flow-scalar, vector, or even tensor—it can have a variety of dimensions. So, just let the dimensions of B be those of B itself, {B}. Also, b is defined as B per unit mass.)arrow_forwardConsider the pipe annulus sketched in fig. Assume that the pressure is constant everywhere (there is no forced pressure gradient driving the flow). However, let the inner cylinder be moving at steady velocity V to the right. The outer cylinder is stationary. (This is a kind of axisymmetric Couette flow.) Generate an expression for the x-component of velocity u as a function of r and the other parameters in the problem.arrow_forwardFind the vorticity of the fluid motion for the given velocity com- ponents. KINEMATICS OF FLUIDS (a) u A(x + y), v = - A(x + y) (b) u = 2Axz, (c) u Ay²+ By + C, v = A(c² + x² - z²) 1)=0arrow_forward
- solve the question given in the image provided quickly.arrow_forwardThe velocity field for a line vortex in the r?-plane is given byur = 0 u? = K / rwhere K is the line vortex strength. For the case with K = 1.5 m/s2, plot a contour plot of velocity magnitude (speed). Specifically, draw curves of constant speed V = 0.5, 1.0, 1.5, 2.0, and 2.5 m/s. Be sure to label these speeds on your plot.arrow_forwardAn incompressible velocity field is given by u=a(x°y²-y), v unknown, w=bxyz where a and b are constants. (a)What is the form of the velocity component for that the flow conserves mass? (b) Write Navier- Stokes's equation in 2-dimensional space with x-y coordinate system.arrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





