
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The preparation method for the given compound has to be given by taking ethyne as starting material.
Concept Introduction:
Acid Catalysed addition of water: When water is added to alkyne in the presence of an acid, the product formed will be an enol. Enol contains a double bond and an
If a carbonyl group is bonded to two alkyl groups, it is called as a ketone. The enol formed in the acid catalysed addition of water will be easily converted into a ketone.
Conversion of terminal
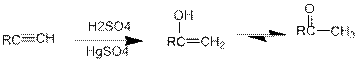
(b)
Interpretation:
The preparation method for the given compound has to be given by taking ethyne as starting material.
Concept Introduction:
Deprotonation: The reaction in which proton is removed from the compound using reagents is known as deprotonation.
Different reagents are used for the deprotonation and one of the common reagent is sodium amide.
Lindlar catalyst: The catalyst is used for the hydrogenation of alkynes in a syn manner. This means both hydrogen are added on the same side across the triple bond and the product obtained will be a cis product.
Sodium in liquid ammonia: The catalyst is used for the formation of trans
(c)
Interpretation:
The preparation method for the given compound has to be given by taking ethyne as starting material.
Concept Introduction:
Deprotonation: The reaction in which proton is removed from the compound using reagents is known as deprotonation.
Different reagents are used for the deprotonation and one of the common reagent is sodium amide.
Lindlar catalyst: The catalyst is used for the hydrogenation of alkynes in a syn manner. This means both hydrogen are added on the same side across the triple bond and the product obtained will be a cis product.
Sodium in liquid ammonia: The catalyst is used for the formation of trans alkenes from alkynes. Because of its more reactivity towards triple bonds, the reaction will stop at the formation of alkenes.
Acid Catalysed addition of water: When water is added to alkyne in the presence of an acid, the product formed will be an enol. Enol contains a double bond and an
If a carbonyl group is bonded to two alkyl groups, it is called as a ketone. The enol formed in the acid catalysed addition of water will be easily converted into a ketone.
Conversion of terminal alkynes into enol: If we want to convert terminal alkyne into an enol, the presence of mercuric ion as a catalyst should be needed and the catalyst will increase the rate of the reaction.
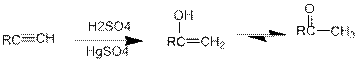
(d)
Interpretation:
The preparation method for the given compound has to be given by taking ethyne as starting material.
Concept Introduction:
Deprotonation: The reaction in which proton is removed from the compound using reagents is known as deprotonation.
Different reagents are used for the deprotonation and one of the common reagent is sodium amide.
Lindlar catalyst: The catalyst is used for the hydrogenation of alkynes in a syn manner. This means both hydrogen are added on the same side across the triple bond and the product obtained will be a cis product.
Sodium in liquid ammonia: The catalyst is used for the formation of trans alkenes from alkynes. Because of its more reactivity towards triple bonds, the reaction will stop at the formation of alkenes.
(e)
Interpretation:
The preparation method for the given compound has to be given by taking ethyne as starting material.
Concept Introduction:
Deprotonation: The reaction in which proton is removed from the compound using reagents is known as deprotonation.
Different reagents are used for the deprotonation and one of the common reagent is sodium amide.
Lindlar catalyst: The catalyst is used for the hydrogenation of alkynes in a syn manner. This means both hydrogen are added on the same side across the triple bond and the product obtained will be a cis product.
Sodium in liquid ammonia: The catalyst is used for the formation of trans alkenes from alkynes. Because of its more reactivity towards triple bonds, the reaction will stop at the formation of alkenes.
(f)
Interpretation:
The preparation method for the given compound has to be given by taking ethyne as starting material.
Concept Introduction:
Deprotonation: The reaction in which proton is removed from the compound using reagents is known as deprotonation.
Different reagents are used for the deprotonation and one of the common reagent is sodium amide.
Lindlar catalyst: The catalyst is used for the hydrogenation of alkynes in a syn manner. This means both hydrogen are added on the same side across the triple bond and the product obtained will be a cis product.
Sodium in liquid ammonia: The catalyst is used for the formation of trans alkenes from alkynes. Because of its more reactivity towards triple bonds, the reaction will stop at the formation of alkenes.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 7 Solutions
Organic Chemistry; Organic Chemistry Study Guide A Format: Kit/package/shrinkwrap
- What ketones are prepared by the following reactions?arrow_forwardShow how the following compound can be prepared from benzene:arrow_forwardAcetals are formed from the reaction of two alcohols with a carbonyl under acidic conditions. Acetal formation is faster with 1,2-ethanediol than with two methanol molecules. Choose the factor that explains the difference in reaction rates. A) The reaction with 1,2-ethanediol has a lower AH (enthalpy) of reaction. B) The reaction with 1,2-ethanediol has a higher AH (enthalpy) of reaction. C) The reaction with 1,2-ethanediol has a more favorable entropy of reaction.arrow_forward
- Starting from cyclohexanone, show how to make the two given products, include conditions to use in the reactions. CH3 CH3arrow_forwardHow could the following compound be prepared using an alkene as one of the starting materials?arrow_forwardDraw the major product(s) for reaction of methyl pentanoate with: NaOH, H2O, heat; then H3o*arrow_forward
- H₂SO4, H₂O Choose the enol(s) that can be formed from the following oxymercration reaction. OH ОН OH HgSO4 ОНarrow_forwardWhat is the reduction product of the following compound with H2/Pd? A 2-propyl-1-cyclohexanol B 2-propenyl-1-cyclohexanol C2-propylcyclohexanone D 1-propyl-2-cyclohexanol What is the oxidation product of this compound? H' A ethanoic acid acetic acid propanoic acid D propanone What is the oxidation product of this compound? A 3,4-dimethylpentanoic acid B 2,3-dimethylpentanoic acid C2,3-dimethylpentanone 3,4-dimethylpentanonearrow_forwardDraw in the reagents for the following reactions and products. Ox dantarrow_forward
 Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning




