
Concept explainers
Determine the sizes of
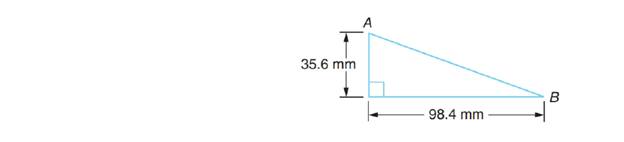
Find the sizes of
Answer to Problem 1A
The angle:-
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The triangle shown with the problem.
Calculations:
From the triangle shown-
Conclusion:
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 67 Solutions
Mathematics for Machine Technology
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Pathways To Math Literacy (looseleaf)
Precalculus: Mathematics for Calculus (Standalone Book)
Intermediate Algebra (13th Edition)
College Algebra (7th Edition)
Probability And Statistical Inference (10th Edition)
APPLIED STAT.IN BUS.+ECONOMICS
- Let x and y be functions of t. Find the general solution of the system of equations below by first converting the system into a second-order differential equation involving only y or only x. Find a particular solution for the initial conditions. Use a computer system or graphing calculator to construct a direction field and typical solution curves for the given system. x' = 2y, y' =8x; x(0) = 12, y(0) = -16arrow_forwardThe coefficient matrix A below is the sum of a nilpotent matrix and a multiple of the identity matrix. Use this fact to solve the given initial value problem. 1 3 7 6 x=0 1 3 x, x(0) = 7 0 0 1 8arrow_forwardFind the general solution of the given system. Use a computer system or graphing calculator to construct a direction field and typical solution curves for the system. 1 9 x' = 1-7arrow_forward
- Find a particular solution of the indicated linear system that satisfies the initial conditions x₁ (0) = 1, x2(0) = 5, and x3 (0) = 4. - 33 - 34 2 6 1 1 x' = 30 31 - 2 X, X = e -5×2 = e³t X3 -30-30 3 5 1 0arrow_forwardFind a general solution of the linear system below. = x" -5x+2y, y" =2x-8yarrow_forwardsolutions to 91x^2 + y^2 = 1arrow_forward
- The eigenvalues of the coefficient matrix can be found by inspection or factoring. Apply the eigenvalue method to find a general solution of the system. ×₁ = 3×₁ + 3x2 + 2x3, x2' = -2x₁ - 2x2 - 3x3, x3' = 2x₁ + 2x2 + 3x3arrow_forwardFirst verify that the given vectors are solutions of the given system. Then use the Wronskian to show that they are linearly independent. Finally, write the general solution of the system. - 37 - 40 0 - 5 5t x' = 32 350X; X1=e -32 -32 3 4 -4X2=e 1 1 3t X3 =e -1 1 0arrow_forwardFirst calculate the operational determinant of the given system in order to determine how many arbitrary constants should appear in a general solution. Then attempt to solve the system explicitly. (D²+1)x-2D2y=2e (D²-1)x+2D2y=0arrow_forward

 Mathematics For Machine TechnologyAdvanced MathISBN:9781337798310Author:Peterson, John.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Mathematics For Machine TechnologyAdvanced MathISBN:9781337798310Author:Peterson, John.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Algebra: Structure And Method, Book 1AlgebraISBN:9780395977224Author:Richard G. Brown, Mary P. Dolciani, Robert H. Sorgenfrey, William L. ColePublisher:McDougal Littell
Algebra: Structure And Method, Book 1AlgebraISBN:9780395977224Author:Richard G. Brown, Mary P. Dolciani, Robert H. Sorgenfrey, William L. ColePublisher:McDougal Littell Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781337278461Author:Ron LarsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781337278461Author:Ron LarsonPublisher:Cengage Learning





