
Rearrange the Clausius-Clapeyron equation, equation 6.14 in terms of the pressure
Interpretation:
The vapor pressures of
Concept introduction:
The Clausius-Clapeyron equation can be obtained from the rearrangement and integration of Clapeyron equation. The Clausius-Clapeyron equation is generally used for gas-phase equilibria, to predict the equilibrium temperatures and pressures and also for the determination of enthalpy for phase transition.
Answer to Problem 6.70E
The plot between vapor pressure and temperature for
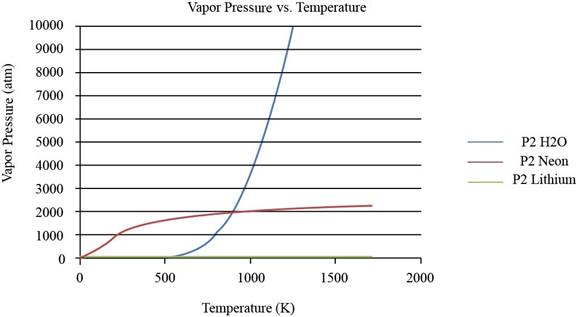
Figure 1
From the plot, the common observation is that for the given substances the increase in vapor pressure is slow until the normal boiling point.
Explanation of Solution
The Clausius-Clapeyron equation 6.14 is,
Rearrange the given equation for the partial pressure
Given boiling point of
Calculation of partial pressure
Calculation of partial pressure
Calculation of partial pressure
The plot between vapor pressure and temperature for
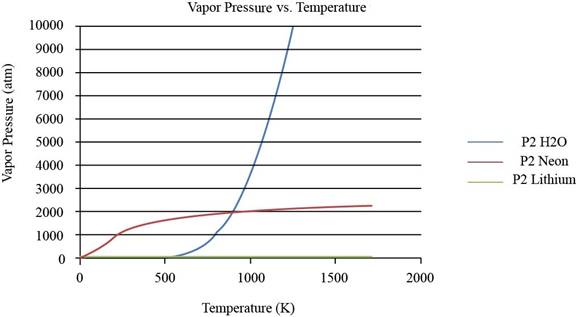
Figure 1
To observe the change in the plot of lithium, the values of vapor pressure is considered till
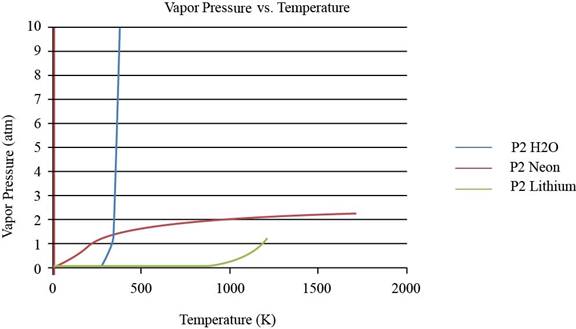
Figure 2
From the plot, the common observation is that for the given substances the increase in vapor pressure is slow until the normal boiling point. After the normal boiling point, the increase in vapor pressure is exponential. As the temperature increases from lower normal boiling point to higher values, the exponent value changes from negative to positive.
From the plot, the common observation is that for the given substances, the increase in vapor pressure is slow until the normal boiling point.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
Physical Chemistry
- Hi!! Please provide a solution that is handwritten. Ensure all figures, reaction mechanisms (with arrows and lone pairs please!!), and structures are clearly drawn to illustrate the synthesis of the product as per the standards of a third year organic chemistry course. ****the solution must include all steps, mechanisms, and intermediate structures as required. Please hand-draw the mechanisms and structures to support your explanation. Don’t give me AI-generated diagrams or text-based explanations, no wordy explanations on how to draw the structures I need help with the exact mechanism hand drawn by you!!! I am reposting this—ensure all parts of the question are straightforward and clear or please let another expert handle it thanks!!arrow_forwardIn three dimensions, explain the concept of the velocity distribution function of particles within the kinetic theory of gases.arrow_forwardIn the kinetic theory of gases, explain the concept of the velocity distribution function of particles in space.arrow_forward
- In the kinetic theory of gases, explain the concept of the velocity distribution function of particles.arrow_forwardHi!! Please provide a solution that is handwritten. this is an inorganic chemistry question please answer accordindly!! its just one question with parts JUST ONE QUESTION with its parts spread out till part (g), please answer EACH part till the end and dont just provide wordy explanations wherever asked for structures, please DRAW DRAW them on a paper and post clearly!! answer the full question with all calculations step by step EACH PART CLEARLY please thanks!! im reposting this please solve all parts and drawit not just word explanations!!arrow_forwardHi!! Please provide a solution that is handwritten. this is an inorganic chemistry question please answer accordindly!! its just one question with parts JUST ONE QUESTION, please answer EACH part PART A AND PART B!!!!! till the end and dont just provide wordy explanations wherever asked for structures, please DRAW DRAW them on a paper and post clearly!! answer the full question with all details EACH PART CLEARLY please thanks!! im reposting this please solve all parts and drawit not just word explanations!!arrow_forward
- Hi!! Please provide a solution that is handwritten. this is an inorganic chemistry question please answer accordindly!! its just one question with parts JUST ONE QUESTION, please answer EACH part till the end and dont just provide wordy explanations wherever asked for structures, please DRAW DRAW them on a paper and post clearly!! answer the full question with all details EACH PART CLEARLY please thanks!! im reposting this please solve all parts and drawit not just word explanations!!arrow_forward8b. Explain, using key intermediates, why the above two products are formed instead of the 1,2-and 1,4- products shown in the reaction below. CIarrow_forward(5pts) Provide the complete arrow pushing mechanism for the chemical transformation depicted below Use proper curved arrow notation that explicitly illustrates all bonds being broken, and all bonds formed in the transformation. Also, be sure to include all lone pairs and formal charges on all atoms involved in the flow of electrons. CH3O H I I CH3O-H H I ① Harrow_forward
 Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning


