
FUNDAMENTALS OF PHYSICS (LLF)+WILEYPLUS
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781119459132
Author: Halliday
Publisher: WILEY
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 6, Problem 62P
A 5.00 kg stone is rubbed across the horizontal ceiling of a cave passageway (Fig. 6-48). If the coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.65 and the force applied to the stone is angled at θ = 70.0°, what must the magnitude of the force be for the stone to move at constant velocity?
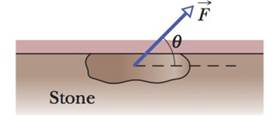
Figure 6-48 Problem 62.
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
A 6,5 kg stone is rubbed across the horizontal ceiling of a cave passageway If the coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.13 and the force applied to the stone is angled at θ= 70°, what must the magnitude of the force be for the stone to move at constant velocity?
A 5.00 kg stone is rubbed across the horizontal ceiling of a cave passageway . If the coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.65 and the force applied to the stone is angled at u 70.0°, what must the magnitude of the force be for the stone to move at constant velocity?
The maximum limiting friction between a shoe and the track has been calculated to be 500 N. If a motive force of 560 N is applied to the shoe when it is at rest on the track, the magnitude of the friction present will be
Chapter 6 Solutions
FUNDAMENTALS OF PHYSICS (LLF)+WILEYPLUS
Ch. 6 - In Fig. 6-12, if the box is stationary and the...Ch. 6 - Prob. 2QCh. 6 - In Fig. 6-13, horizontal force F1 of magnitude 10...Ch. 6 - In three experiments, three different horizontal...Ch. 6 - If you press an apple crate against a wall so hard...Ch. 6 - In Fig. 6-14, a block of mass m is held stationary...Ch. 6 - Reconsider Question 6 but with the force F now...Ch. 6 - In Fig. 6-15, a horizontal force of 100 N is to be...Ch. 6 - Prob. 9QCh. 6 - Prob. 10Q
Ch. 6 - A person riding a Ferris wheel moves through...Ch. 6 - During a routine flight in 1956, test pilot Tom...Ch. 6 - A box is on a ramp that is at angle to the...Ch. 6 - The floor of a railroad flatcar is loaded with...Ch. 6 - In a pickup game of dorm shuffleboard, students...Ch. 6 - SSM WWW A bedroom bureau with a mass of 45 kg,...Ch. 6 - A slide-loving pig slides down a certain 35 slide...Ch. 6 - GO A 2.5 kg block is initially at rest on a...Ch. 6 - A baseball player with mass m 79 kg, sliding into...Ch. 6 - SSM ILW A person pushes horizontally with a force...Ch. 6 - The mysterious sliding stones. Along the remote...Ch. 6 - GO A 3.5 kg block is pushed along a horizontal...Ch. 6 - Figure 6-20 shows an initially stationary block of...Ch. 6 - SSM A 68 kg crate is dragged across a floor by...Ch. 6 - In about 1915, Henry Sincosky of Philadelphia...Ch. 6 - A worker pushes horizontally on a 35 kg crate with...Ch. 6 - Figure 6-22 shows the cross section of a road cut...Ch. 6 - The coefficient of static friction between Teflon...Ch. 6 - A loaded penguin sled weighing 80 N rests on a...Ch. 6 - In Fig. 6-24, a force P acts on a block weighing...Ch. 6 - GO You testify as an expert witness in a case...Ch. 6 - A 12 N horizontal force F pushes a block weighing...Ch. 6 - GO In Fig. 6-27, a box of Cheerios mass mC = 1.0...Ch. 6 - An initially stationary box of sand is to be...Ch. 6 - GO In Fig. 6-23, a sled is held on an inclined...Ch. 6 - When the three blocks in Fig. 6-29 are released...Ch. 6 - A 4.10 kg block is pushed along a floor by a...Ch. 6 - SSM WWW Block B in Fig. 6-31 weighs 711 N. The...Ch. 6 - GO Figure 6-32 shows three crates being pushed...Ch. 6 - GO Body A in Fig. 6-33 weighs 102 N, and body B...Ch. 6 - In Fig. 6-33, two blocks are connected over a...Ch. 6 - GO In Fig. 6-34, blocks A and B have weights of 44...Ch. 6 - A toy chest and its contents have a combined...Ch. 6 - SSM Two blocks, of weights 3.6 N and 7.2 N, are...Ch. 6 - GO A block is pushed across a floor by a constant...Ch. 6 - SSM A 1000 kg boat is traveling at 90 km/h when...Ch. 6 - GO In Fig. 6-37, a slab of mass m1= 40 kg rests on...Ch. 6 - ILW The two blocks m = 16 kg and M = 88 kg in Fig....Ch. 6 - The terminal speed of a sky diver is 160 km/h in...Ch. 6 - Continuation of Problem 8. Now assume that Eq....Ch. 6 - Assume Eq. 6-14 gives the drag force on a pilot...Ch. 6 - Calculate the ratio of the drag force on a jet...Ch. 6 - In downhill speed skiing a skier is retarded by...Ch. 6 - A cat dozes on a stationary merry-go-round in an...Ch. 6 - Suppose the coefficient of static friction between...Ch. 6 - ILW What is the smallest radius of an unbanked...Ch. 6 - During an Olympic bobsled run, the Jamaican team...Ch. 6 - SSM ILW A student of weight 667 N rides a steadily...Ch. 6 - A police officer in hot pursuit drives her car...Ch. 6 - A circular-motion addict of mass 80 kg rides a...Ch. 6 - A roller-coaster car at an amusement park has a...Ch. 6 - GO In Fig. 6-39, a car is driven at constant speed...Ch. 6 - An 85.0 kg passenger is made to move along a...Ch. 6 - SSM WWW An airplane is flying in a horizontal...Ch. 6 - An amusement park ride consists of a car moving in...Ch. 6 - An old streetcar rounds a flat corner of radius...Ch. 6 - In designing circular rides for amusement parks,...Ch. 6 - A bolt is threaded onto one end of a thin...Ch. 6 - GO A banked circular highway curve is designed for...Ch. 6 - GO A puck of mass m = 1.50 kg slides in a circle...Ch. 6 - Brake or turn? Figure 6- 44 depicts an overhead...Ch. 6 - SSM ILW In Fig. 6-45, a 1.34 kg ball is connected...Ch. 6 - GO In Fig. 6-46, a box of ant aunts total mass m1...Ch. 6 - SSM A block of mass mt = 4.0 kg is put on top of a...Ch. 6 - A 5.00 kg stone is rubbed across the horizontal...Ch. 6 - In Fig. 6-49, a 49 kg rock climber is climbing a...Ch. 6 - A high-speed railway car goes around a flat,...Ch. 6 - Continuation of Problems 8 and 37. Another...Ch. 6 - GO In Fig. 6-50, block 1 of mass m1 = 2.0 kg and...Ch. 6 - In Fig. 6-51, a crate slides down an inclined...Ch. 6 - Engineering a highway curve. If a car goes through...Ch. 6 - A student, crazed by final exams, uses a force P...Ch. 6 - GO Figure 6-53 shows a conical pendulum, in which...Ch. 6 - An 8.00 kg block of steel is at rest on a...Ch. 6 - A box of canned goods slides down a ramp from...Ch. 6 - In Fig. 6-54, the coefficient of kinetic friction...Ch. 6 - A 110 g hockey puck sent sliding over ice is...Ch. 6 - A locomotive accelerates a 25-car train along a...Ch. 6 - A house is built on the top of a hill with a...Ch. 6 - What is the terminal speed of a 6.00 kg spherical...Ch. 6 - A student wants to determine the coefficients of...Ch. 6 - SSM Block A in Fig. 6-56 has mass mA = 4.0 kg, and...Ch. 6 - Calculate the magnitude of the drag force on a...Ch. 6 - SSM A bicyclist travels in a circle of radius 25.0...Ch. 6 - In Fig. 6-57, a stuntman drives a car without...Ch. 6 - You must push a crate across a floor to a docking...Ch. 6 - In Fig. 6-58, force F is applied to a crate of...Ch. 6 - In the early afternoon, a car is parked on a...Ch. 6 - A sling-thrower puts a stone 0.250 kg in the...Ch. 6 - SSM A car weighing 10.7 kN and traveling at 13.4...Ch. 6 - In Fig. 6-59, block 1 of mass m1 = 2.0 kg and...Ch. 6 - SSM A filing cabinet weighing 556 N rests on the...Ch. 6 - In Fig. 6-60, a block weighing 22 N is held at...Ch. 6 - Prob. 91PCh. 6 - A circular curve of highway is designed for...Ch. 6 - A 1.5 kg box is initially at rest on a horizontal...Ch. 6 - A child weighing 140 N sits at rest at the top of...Ch. 6 - In Fig. 6-61 a fastidious worker pushes directly...Ch. 6 - A child places a picnic basket on the outer rim of...Ch. 6 - SSM A warehouse worker exerts a constant...Ch. 6 - In Fig. 6-62, a 5.0 kg block is sent sliding up a...Ch. 6 - An 11 kg block of steel is at rest on a horizontal...Ch. 6 - A ski that is placed on snow will stick to the...Ch. 6 - Playing near a road construction site, a child...Ch. 6 - A 100 N force, directed at an angle above a...Ch. 6 - A certain string can withstand a maximum tension...Ch. 6 - A four-person bobsled total mass = 630 kg comes...Ch. 6 - As a 40 N block slides down a plane that is...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
Ice skaters, ballet dancers, and basketball players executing vertical leaps often give the illusion of hanging...
Essential University Physics (3rd Edition)
Rooms A and B are the same size, and are connected by an open door. Room A, however, is warmer (perhaps because...
An Introduction to Thermal Physics
Making a Living. Consider various methods by which life “makes a living” (the ways in which it acquires energy ...
Life in the Universe (4th Edition)
Why does a piece of room-temperature metal feel cooler to the touch than paper, wood, or cloth?
Conceptual Physics: The High School Physics Program
6. For a simple harmonic oscillator, when (if ever) are the displacement and velocity vectors in the same direc...
Physics: Principles with Applications
(a) Derive an expression for the potential energy of an object subject to a force Fx = ax bx3, where a = 5 N/m...
Essential University Physics: Volume 1 (3rd Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Answer A and B for question 2 2. An object was a mass of 10.0 kg is at rest at the top of a frictionless inclined plane of length 8.00 m and an angle of inclination 30.0° with the horizontal. The object is released from this position and it stops at a distance d from the bottom of the inclined plane along a horizontal surface, as shown in Fig. 8-6. The coefficient of kinetic friction for the horizontal surface of 0.400. (a) What is the speed of the object at the bottom of the inclined plane? (b) At what horizontal distance from the bottom of the inclined plane will this object stop?arrow_forward6) Z. A thin non-condu cting rod of ma ss m and length L = 60cm, slides frictionl essly at a constant speed V = 0.5 m/s along the rails placed on the surface and at the edges of an inclined plane with the effect of an external force. The rails at the edges of the inclined plane are connected with each other via the rail at the bottom edge of the plane, so the rod and rails forms a rectangular closed loop as seen in the figure. The plane of the rails makes an angle 0 = 55° with the horizontal plane (xz plane). Before sliding, the rod stays at the di stan ce S = 4m measured from the bottom edge of the inclined plane. The inclined plane and the rod are under the effect of a uniform magnetic field given by B = 0.40î + 3ĵ + 0.8k(T). After the rod starts to slide, what will be the magnetic flux passing through the surface formed by the rod, the rails at the edges, and the rail at the bottom edge of the inclined plane at t=4s? A) 1.50 Wb B) 7.53 Wb C) 0.083 Wb D) 0.147 Wb E) 1.67 Wbarrow_forward79. ssm A student is skateboarding down a ramp that is 6.0 m long and inclined at 18° with respect to the horizontal. The initial speed of the skateboarder at the top of the ramp is 2.6 m/s. Neglect friction and find the speed at the bottom of the ramp.arrow_forward
- 65 In Fig. 7-45, a cord runs around two massless, frictionless pul- leys. A canister with mass m = 20 kg hangs from one pulley, and you exert a force F on the free end of the cord. (a) What must be the magnitude of F if you are to lift the canister at a constant speed? (b) To lift the canister by 2.0 cm, how far must you pull the free end of the cord? During that lift, what is the work done on the canister by (c) your force (via the cord) and (d) the gravitational force? (Hint: When a cord loops around a pulley as shown, it pulls on the pulley with a net force that is twice the tension in the cord.) FV Fig. 7-45 Problem 65.arrow_forwardA man pushing a crate of mass m = 92.0 kg at a speed of v = 0.855 m/s encounters a rough horizontal surface of length ℓ = 0.65 m. If the coefficient of kinetic friction between the crate and rough surface is 0.357 and he exerts a constant horizontal force of 277 N on the crate, find the magnitude and direction of the net force on the crate while it is on the rough surface.arrow_forwardIn a circus performance, a monkey is strapped to a sled and both are given an initial speed of 3.0 m/s up a 21.0° inclined track. The combined mass of monkey and sled is 16 kg, and the coefficient of kinetic friction between sled and incline is 0.20. How far up the incline do the monkey and sled move?arrow_forward
- A warehouse worker is pushing a 90.0 kg crate with a horizontal force of 276N at a speed of v = 0.875m/s across the warehouse floor. He encounters a rough horizontal section of the floor that is 0.75 m long and where the coefficient of kinetic friction between the crate and floor is 0.353. (a) Determine the magnitude and direction of the net force acting on the crate while it is pushed over the rough section of the floor. magnitude Ndirection ---Select--- up down in the same direction as the motion of the crate in the opposite direction as the motion of the crate (b) Determine the net work done on the crate while it is pushed over the rough section of the floor. J (c) Find the speed of the crate when it reaches the end of the rough surface. m/sarrow_forward10) Starting from rest, a 97.0 kg firefighter slides down a fire pole. The average frictional force exerted on him by the pole has a magnitude of 800 N, and his speed at the bottom of the pole is 3.60 m/s. How far did he slide down the pole?arrow_forwardA block of mass M = 2 kg starts from rest from the top of an inclined plane of length L= 69 cm and angle of inclination 0 = 45 °. If pk = 0.3333 is the coefficient of kinetic friction between both surfaces, then the speed of the block at the end of the plane will be: a) v = 2.5249 m/s b) v = 3.5708 m/s c) v = 6.3753 m/s d) v= 12.7506 m/sarrow_forward
- 6-arrow_forwardA 86 kg diver steps off a 10 m high diving board and drops from rest straight down in to the water. If he comes to the rest 7.20 m beneath the surface of the water determine the average resistive force exerted by the water.arrow_forwardAn object with a mass of 10 kg is initially at rest at the top of a frictionless inclined plane that rises at 30° above the horizontal. At the top, the object is initially 8.0 m from the bottom of the incline, as shown in the figure. When the object is released from this position, it eventually stops at a distance d from the bottom of the inclined plane along a horizontal surface, as shown. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the horizontal surface and the object is 0.20, and air resistance is negligible. Find the distance d.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning
Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning

Classical Dynamics of Particles and Systems
Physics
ISBN:9780534408961
Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. Marion
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Conservative and Non Conservative Forces; Author: AK LECTURES;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=vFVCluvSrFc;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY